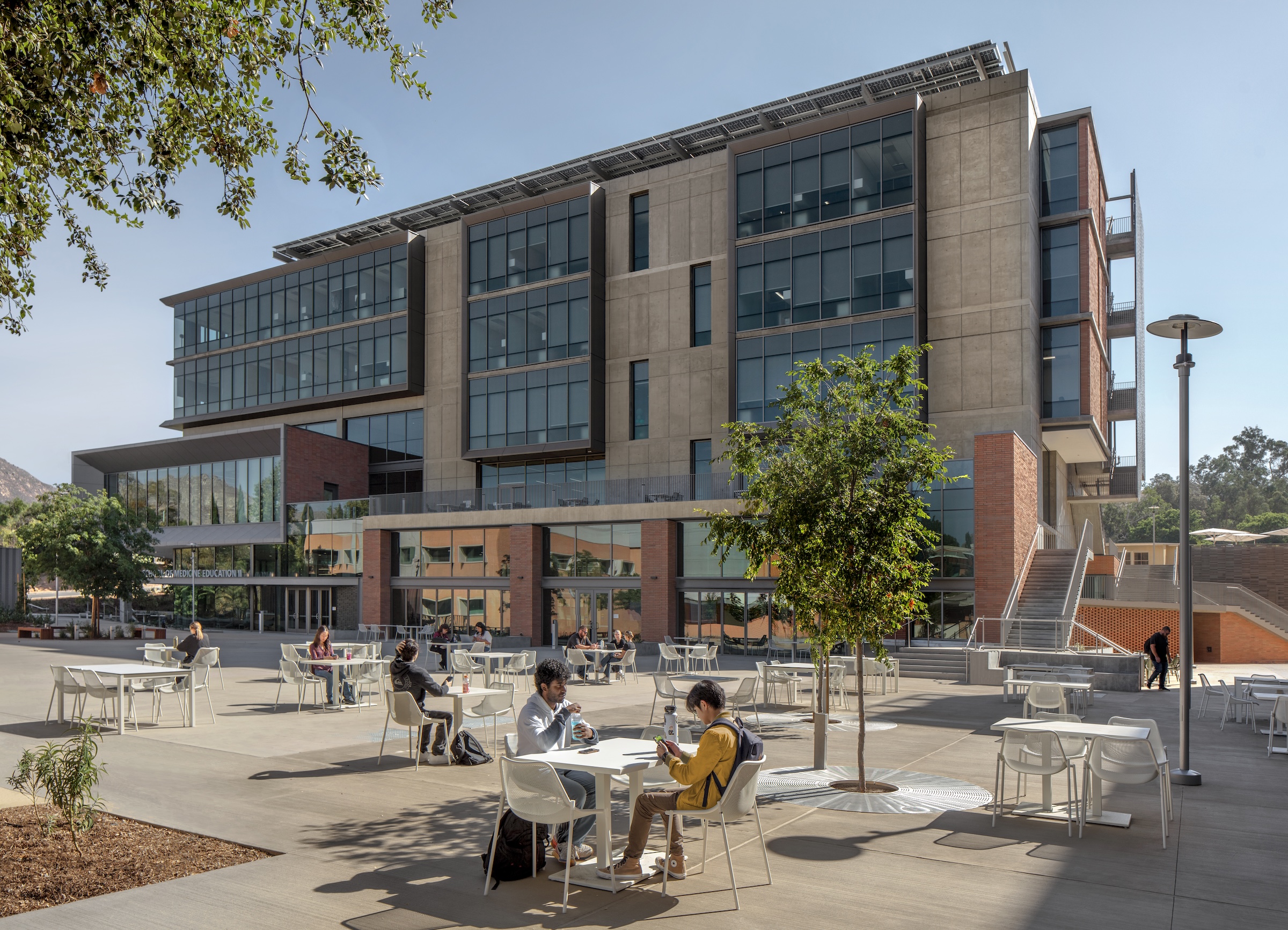
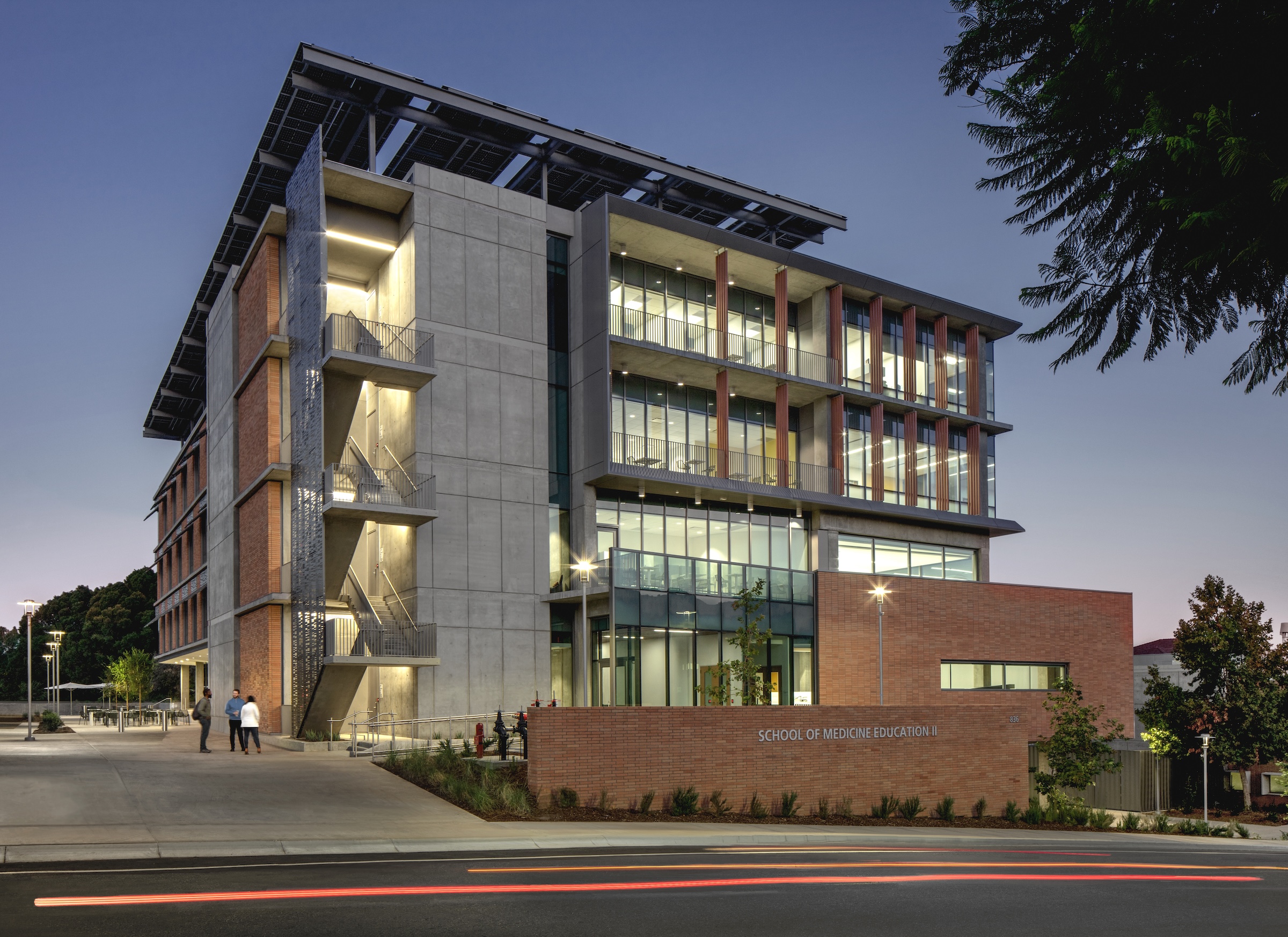
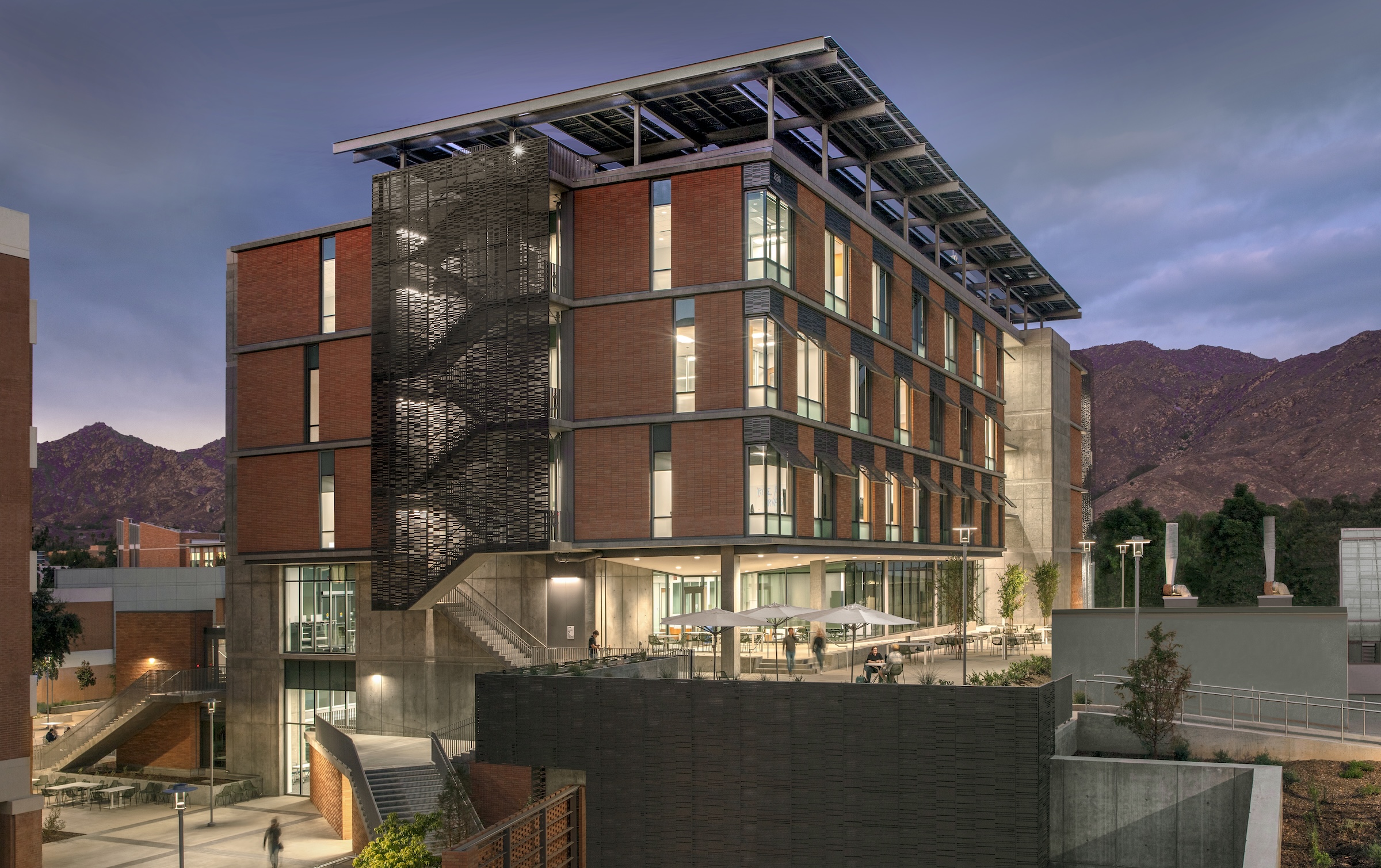
The University of California, Riverside, School of Medicine has opened the 94,576-sf, five-floor Education Building II (EDII). Created by the design-build team of CO Architects and Hensel Phelps, the medical school’s new home supports team-based student learning, offers social spaces, and provides departmental offices for faculty and staff.
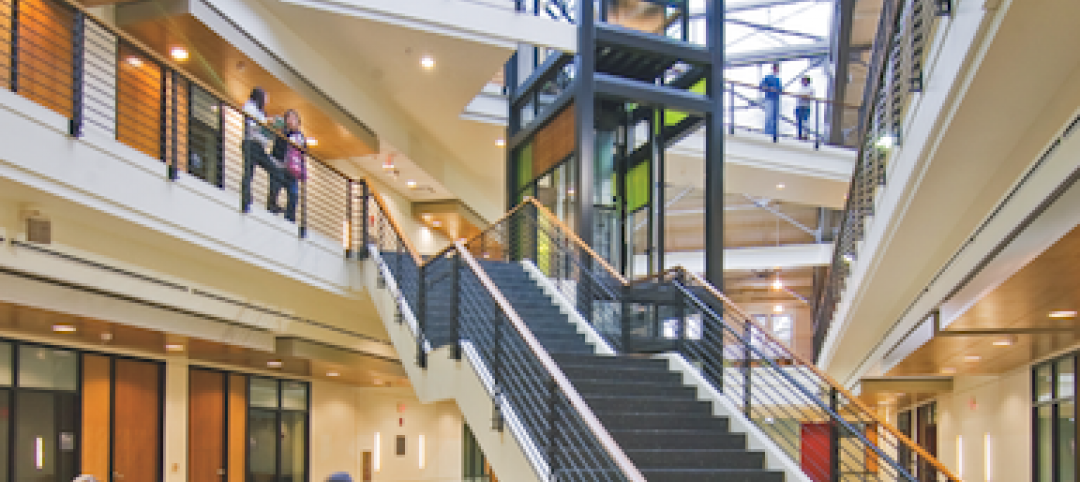
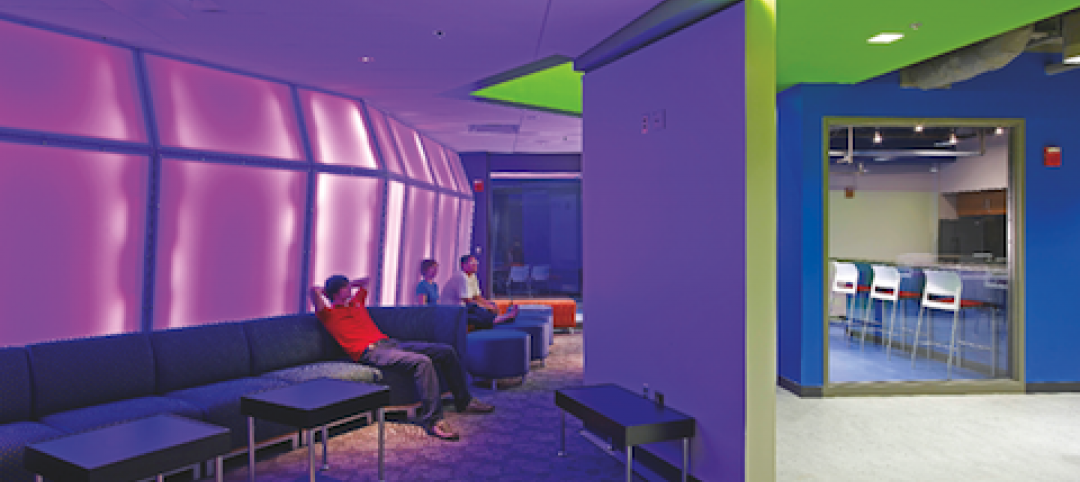
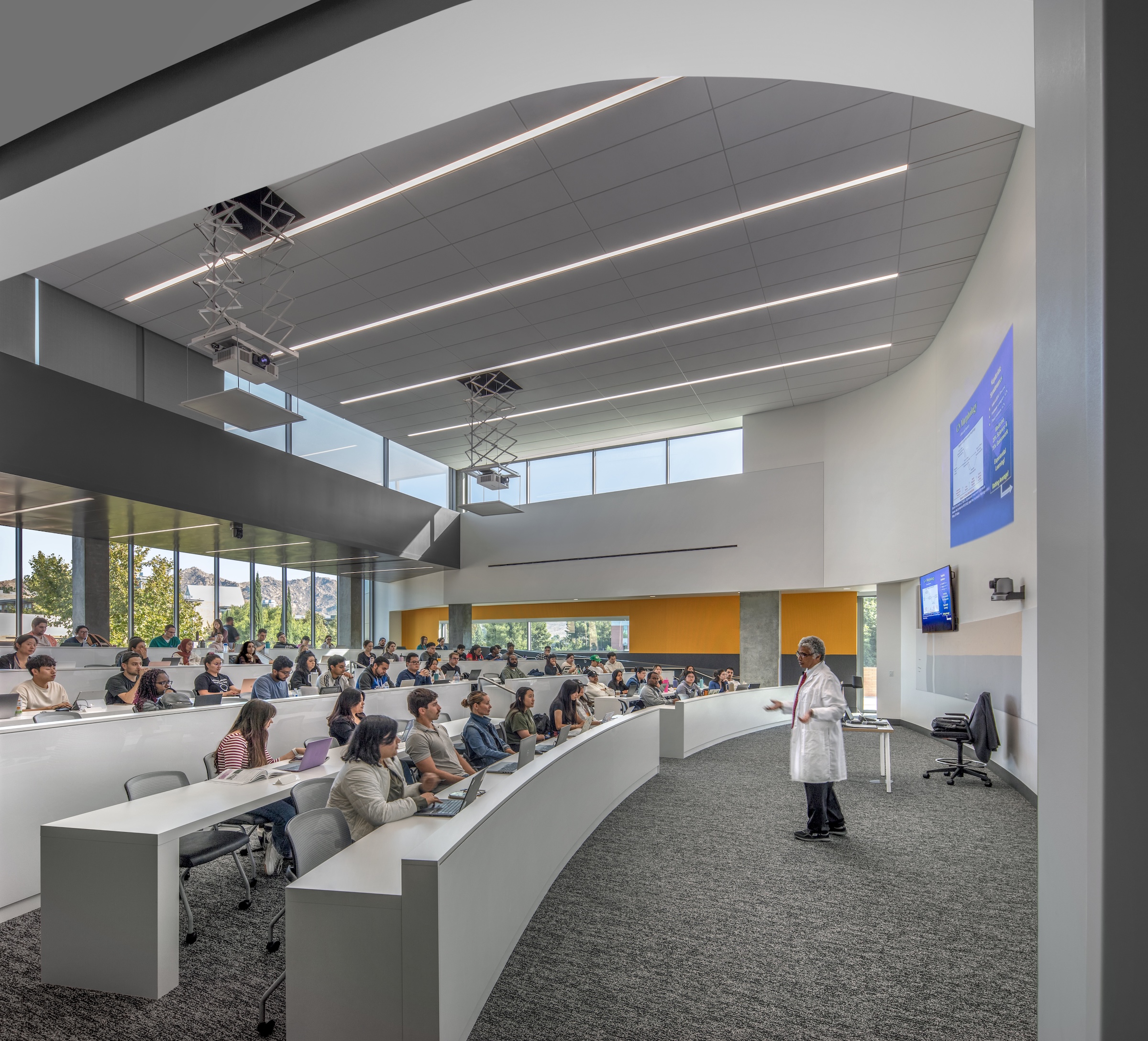
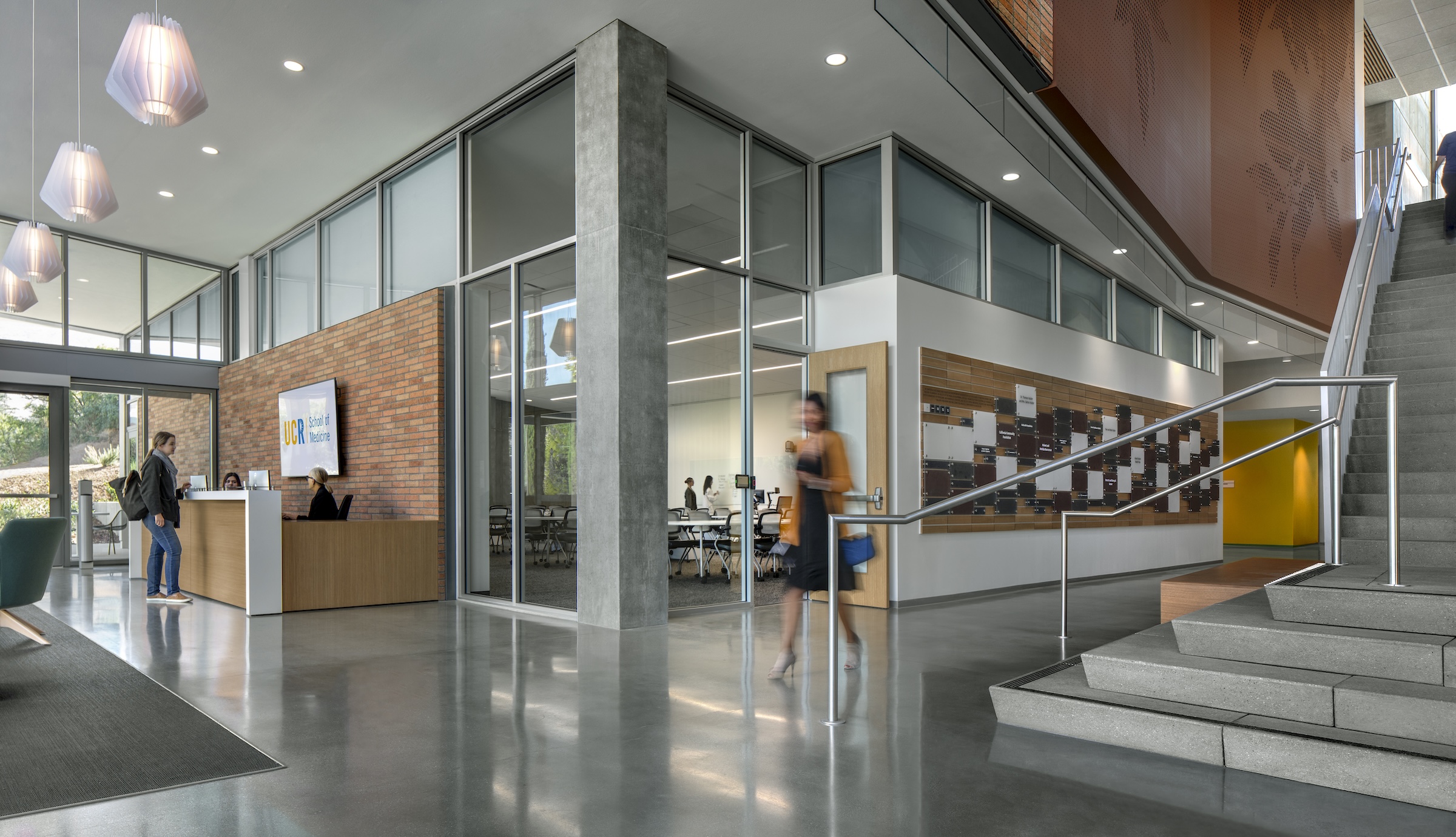
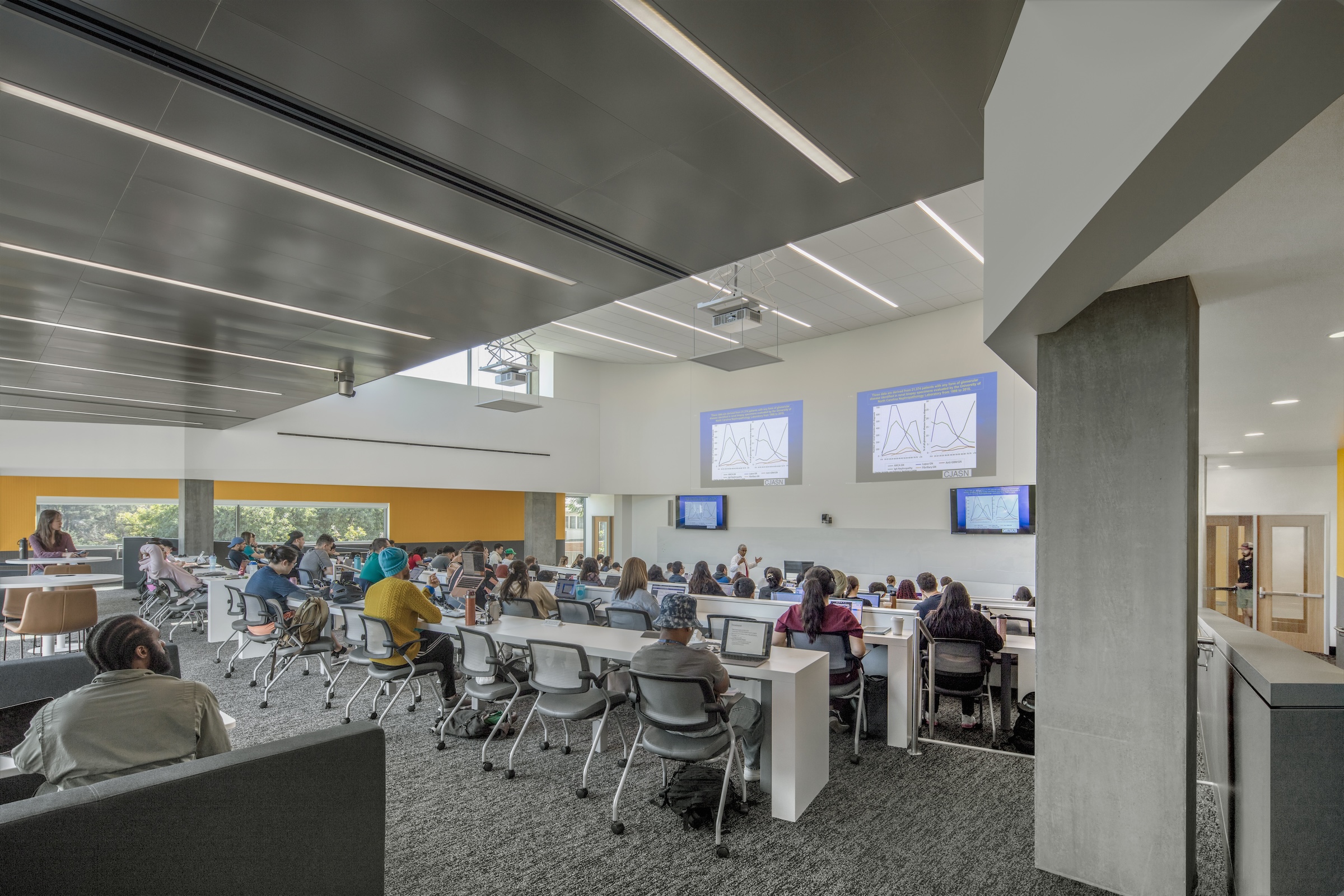
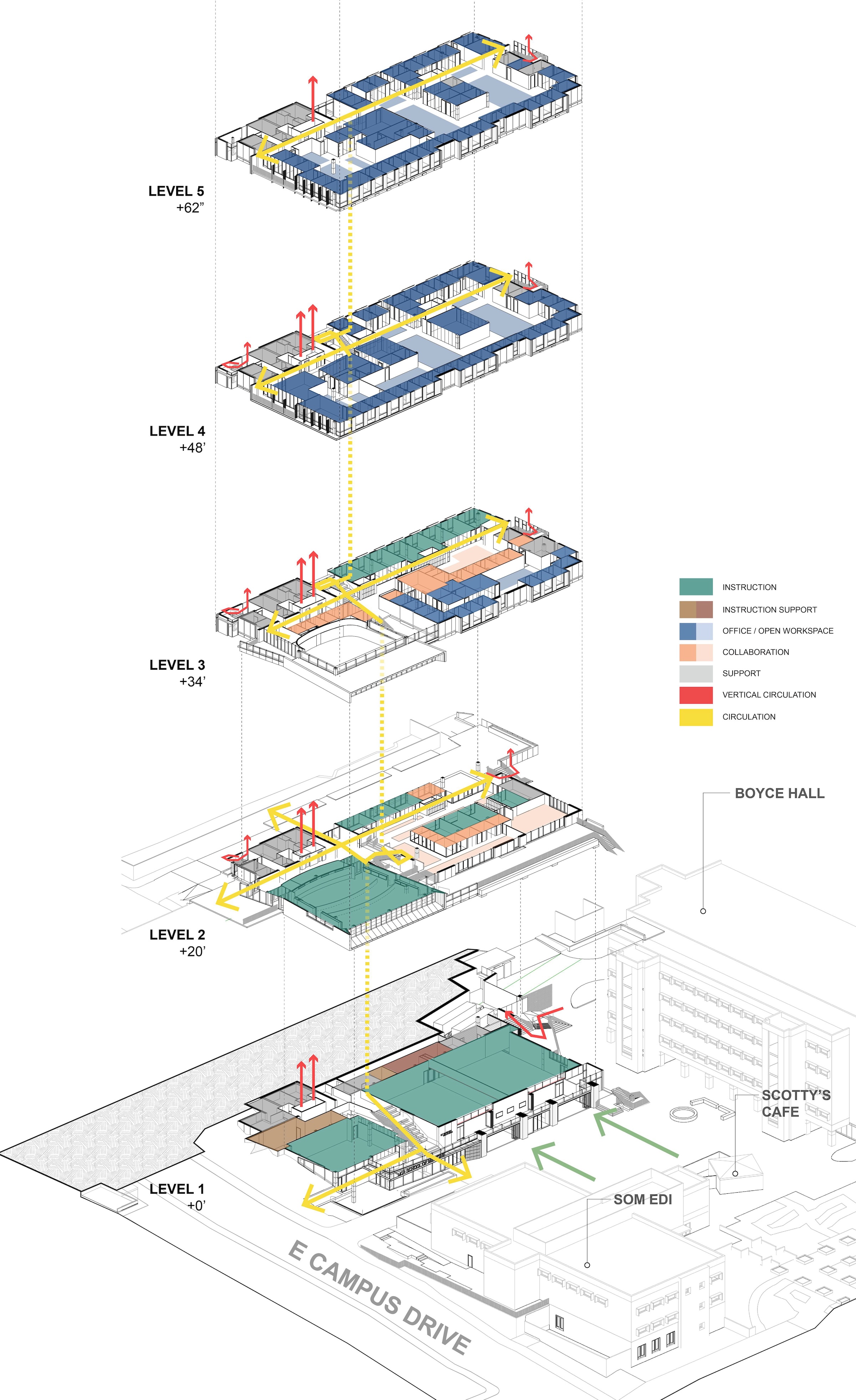
The learning spaces are located on the first three floors, while the administration and shared functions are housed on the top two floors. The building features interactive classrooms, 15 case-based group seminar rooms, variously sized study rooms, and additional study and amenity spaces.
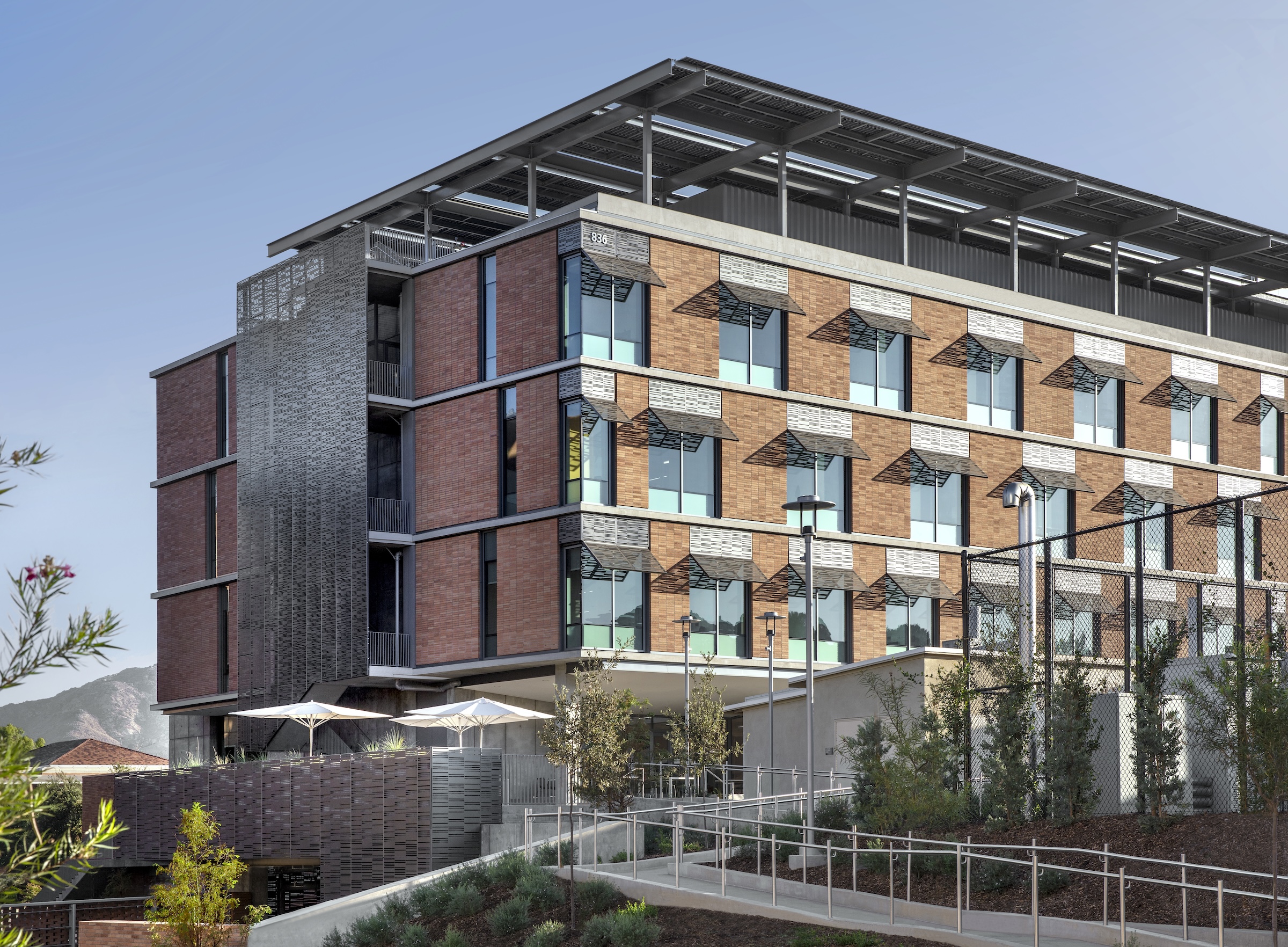
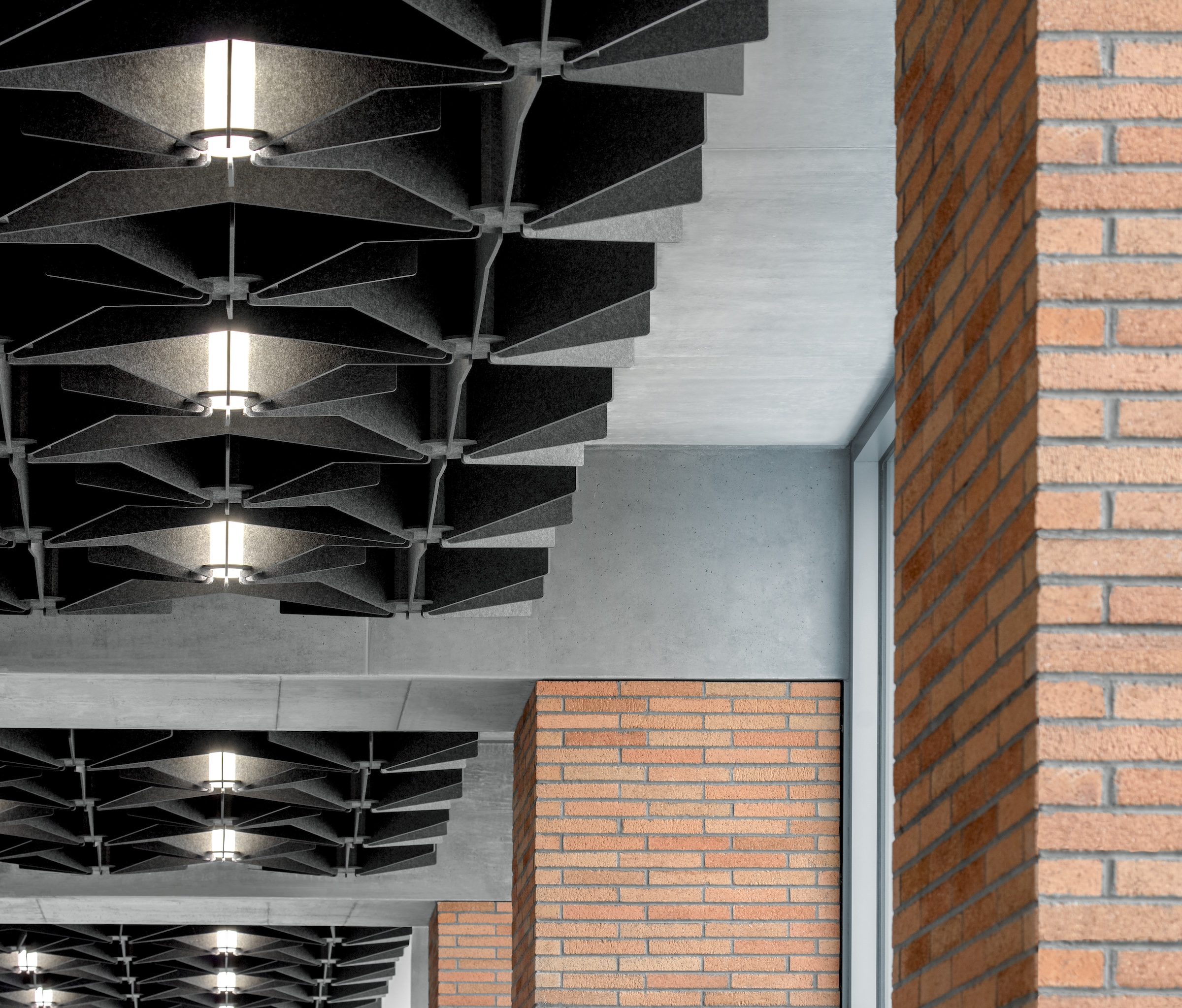
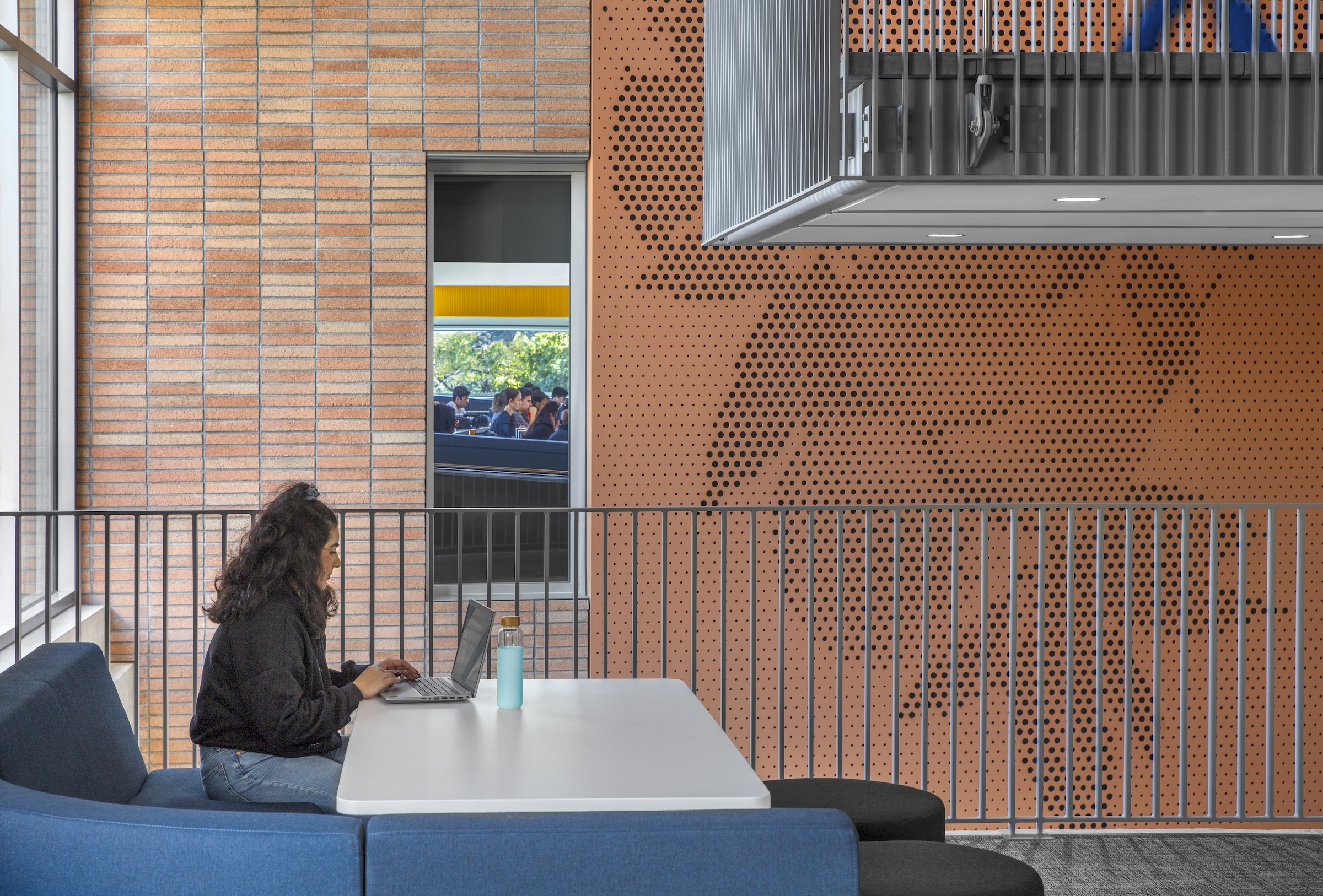
The building includes materials, such as cast-in-place concrete, brick, terracotta, and glass, that are meant to be both beautiful and durable, lasting for generations.
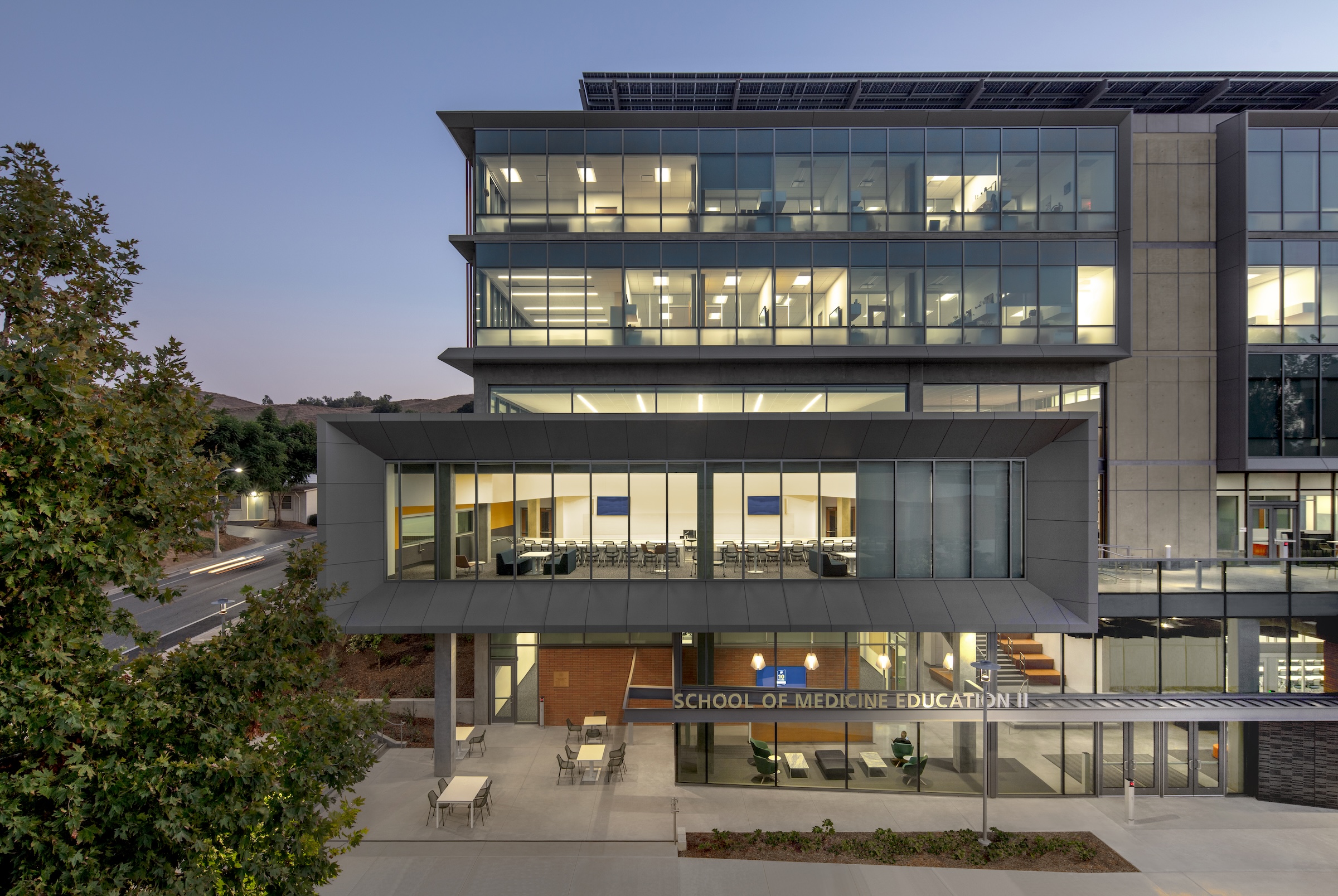

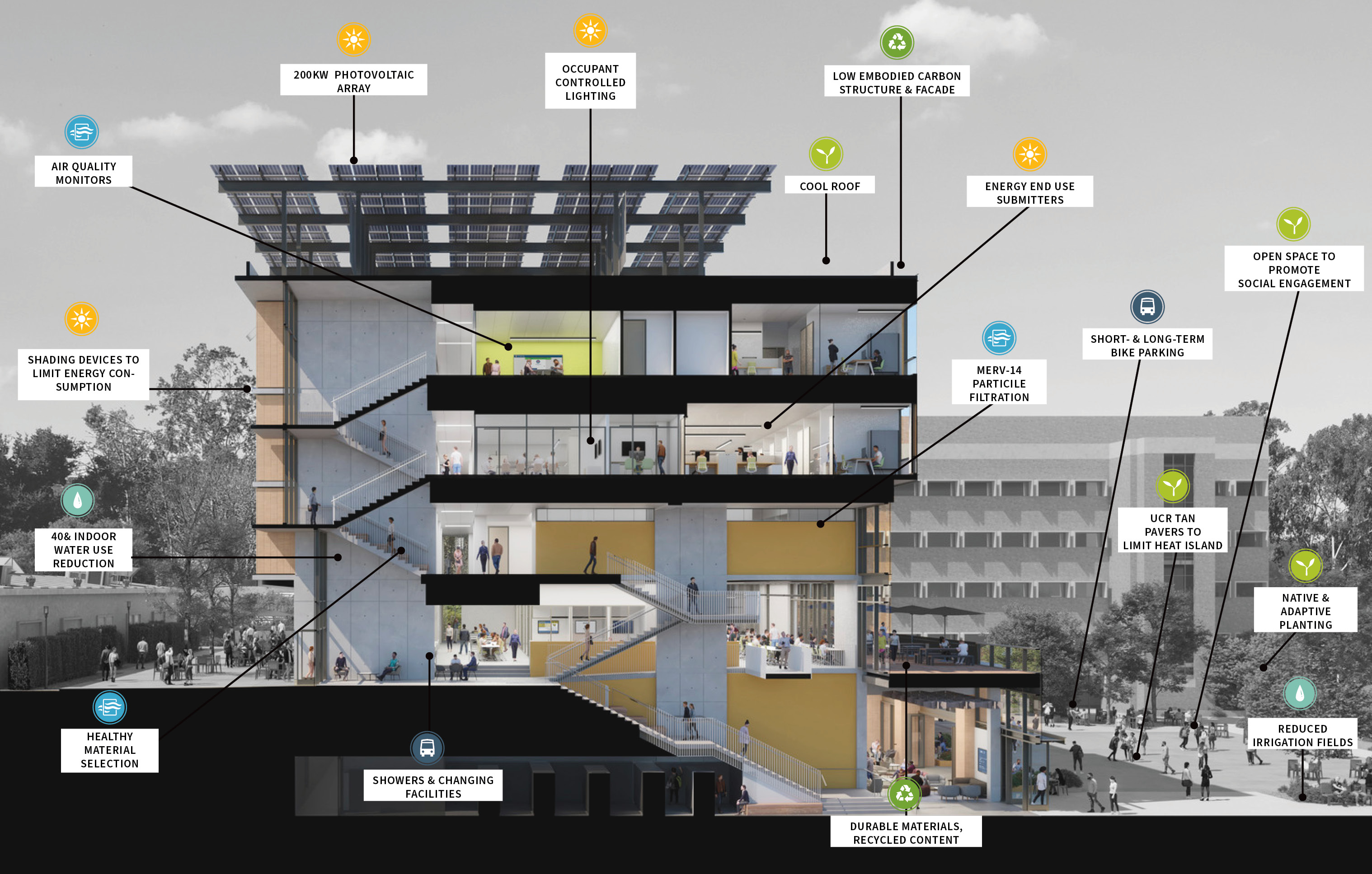
EDII’s design emphasizes transparency to help demystify medical education and welcome prospective students from diverse backgrounds. The use of transparency and shading leverages passive light, prevailing breezes, and solar heat gain. A rooftop solar array contributes to the building’s energy efficiency.
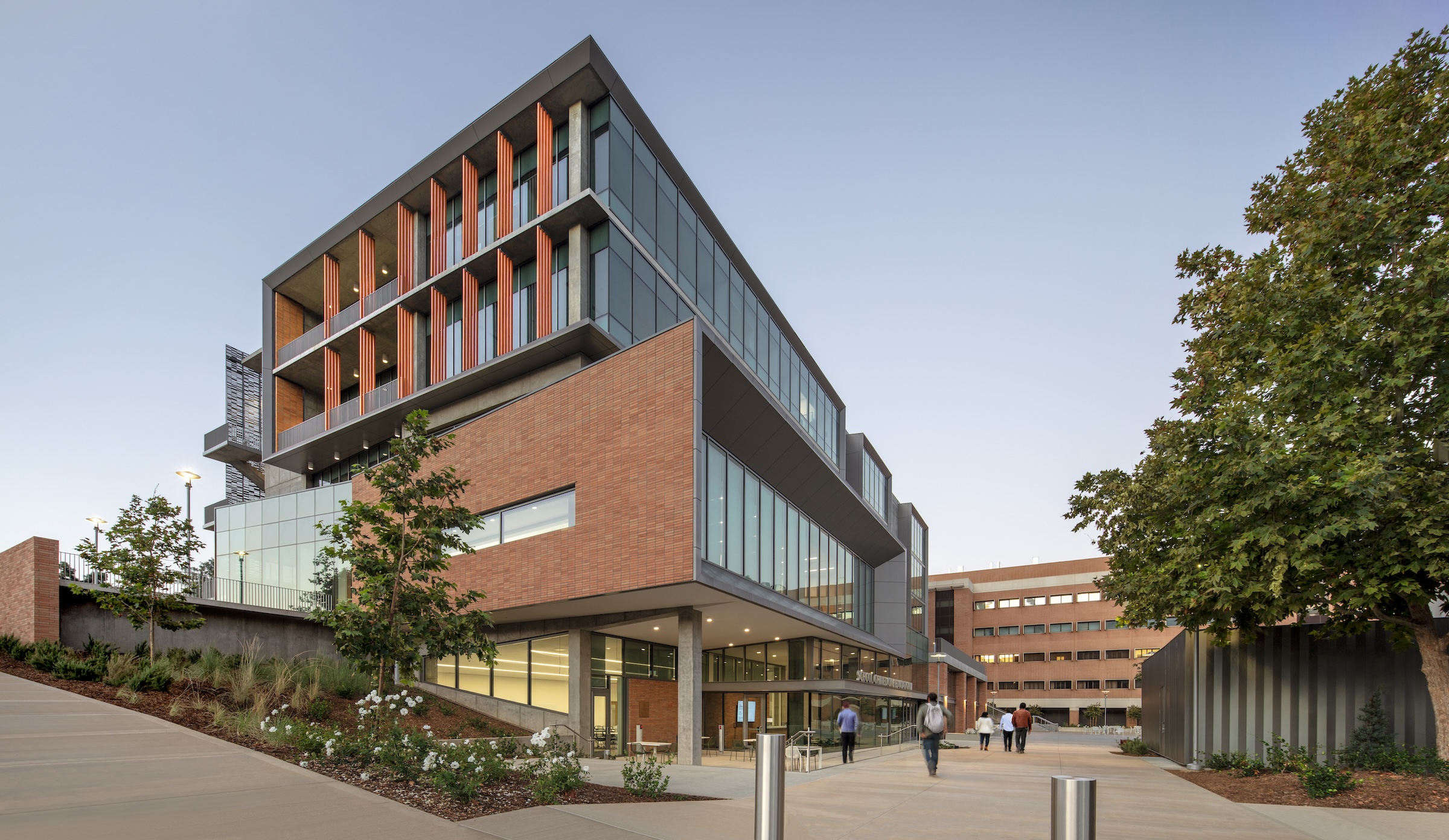
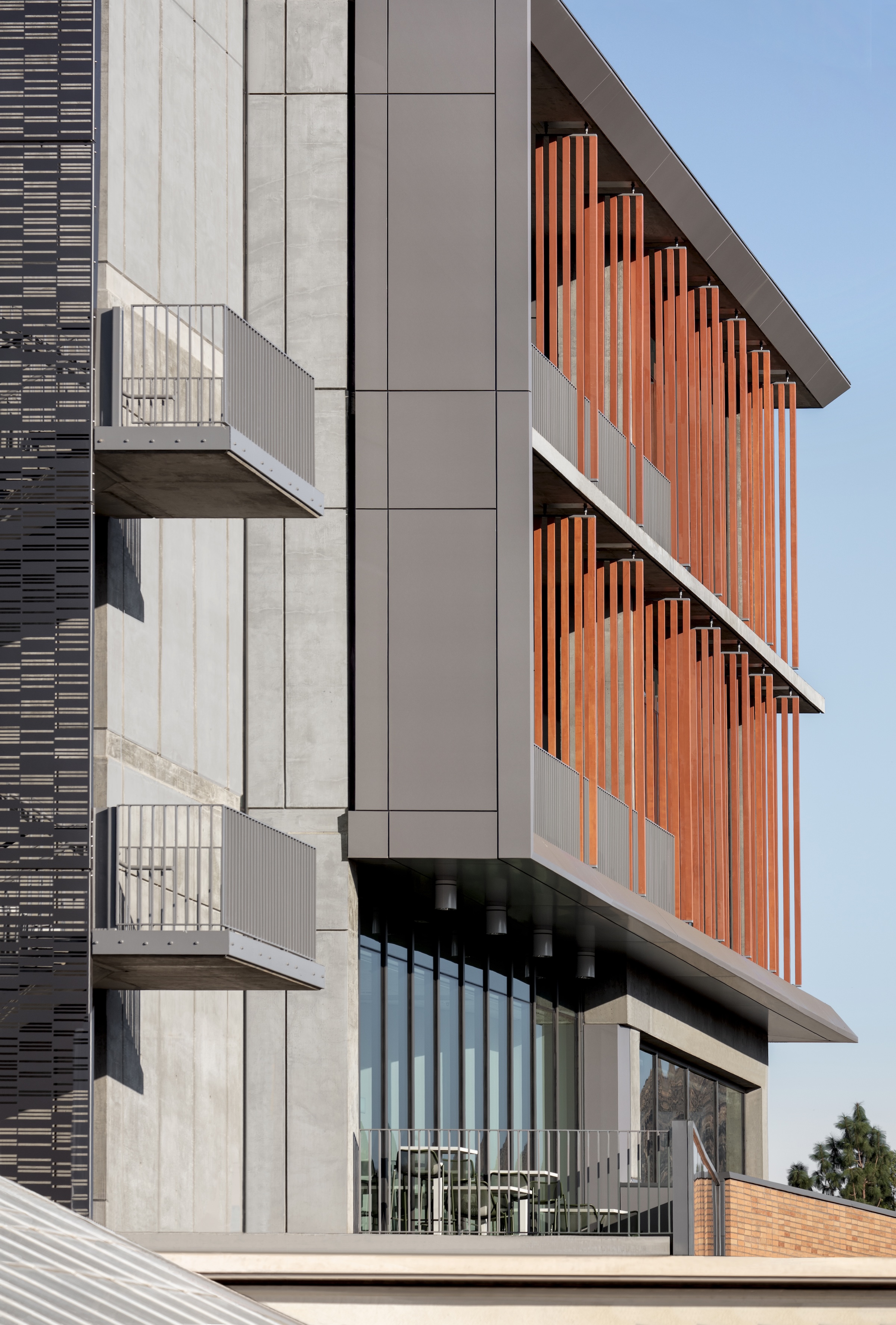
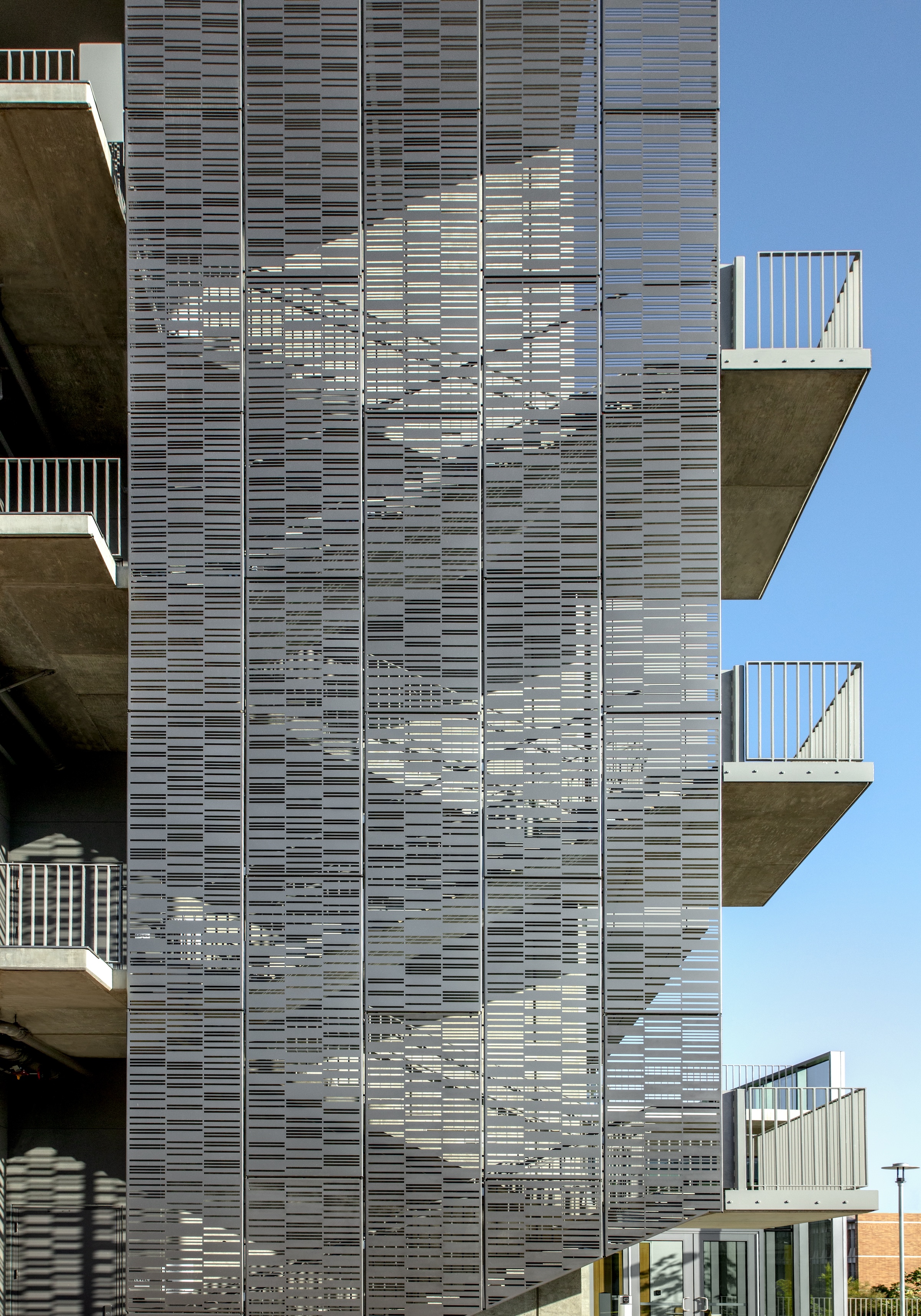
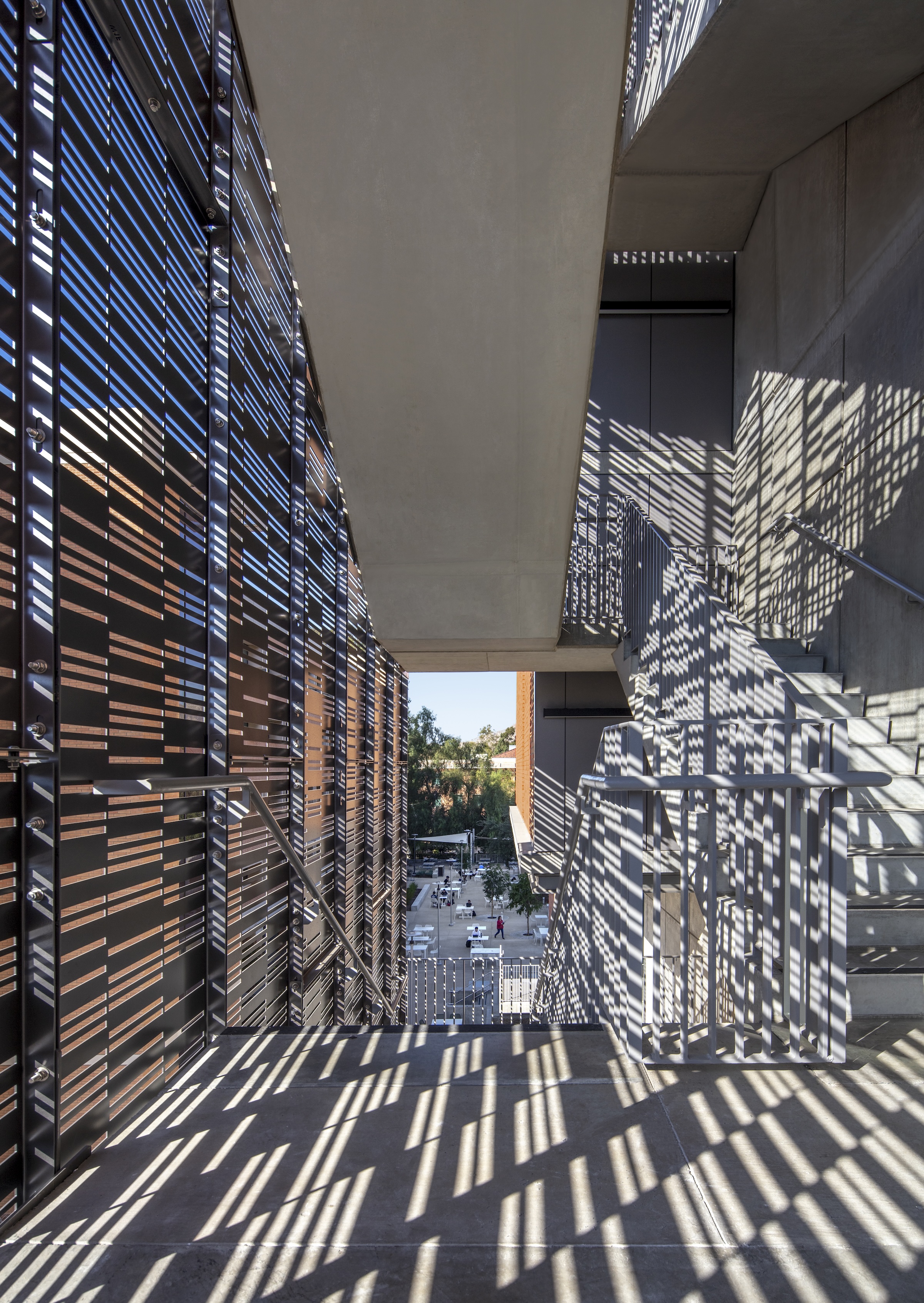
Each façade is optimized for the climate and for varying levels of sun exposure throughout the day. On the east façade, vertical glass fiber reinforced concrete (GFRC) fins create extended shadows and protect the interior from the harsh morning light. Painted perforated aluminum panels shade the east and west exit stairs as well as the south façade’s windows. The porous north façade features abundant glass and walls opening to the courtyard.
Located in a drought-prone region, the building restores the site’s natural vegetative conditions. The ground-level plaza connects the surrounding buildings.
Inside, a three-story perforated gypsum mural depicts an abstraction of orange groves, referencing the region’s history.
On the Building Team:
Owner: UCR School of Medicine
Architect/interior designer: CO Architects
Contractor: Hensel Phelps
Landscape architect: Spurlock Landscape Architects
MEP engineer: P2S, Inc.
Structural engineer, waterproofing, LEED consultant: Thornton Tomasetti
Civil engineer: Albert A. Webb Associates
Geotechnical engineer: Langan
Fire protection engineer: Woden Fire
Acoustics consultant: Arpeggio

Here is the project essay from the design-build team of Hensel Phelps and CO Architects:
The School of Medicine (SOM) Education Building II (EDII) fulfills the mission of the University of California, Riverside (UCR), to train a diverse workforce of physicians to support the medically underserved Riverside County region of Southern California. The building by the design-build partnership of Hensel Phelps + CO Architects creates a new home for the medical school by incorporating a wide range of team-based student learning, social spaces, and departmental offices for faculty and staff into one 95,476-square-foot, five-story structure. Strategically located and highly visible on campus, the EDII amplifies the SOM’s identity as a forward-thinking medical school and showcases the mission and dedication of medical education to undergraduates and community members alike.
The design team and client shared the vision of crafting a building that supports its occupants and creates an environment to empower students throughout their academic experience and into their careers. The architecture utilizes transparency to demystify medical education, welcoming prospective students from diverse backgrounds to learn about the requirements and daily activities of medical students. EDII’s design is meant to be both beautiful and durable, utilizing materials—such as cast-in-place concrete, brick, terracotta, and glass—that fit within the campus context and will last for generations.
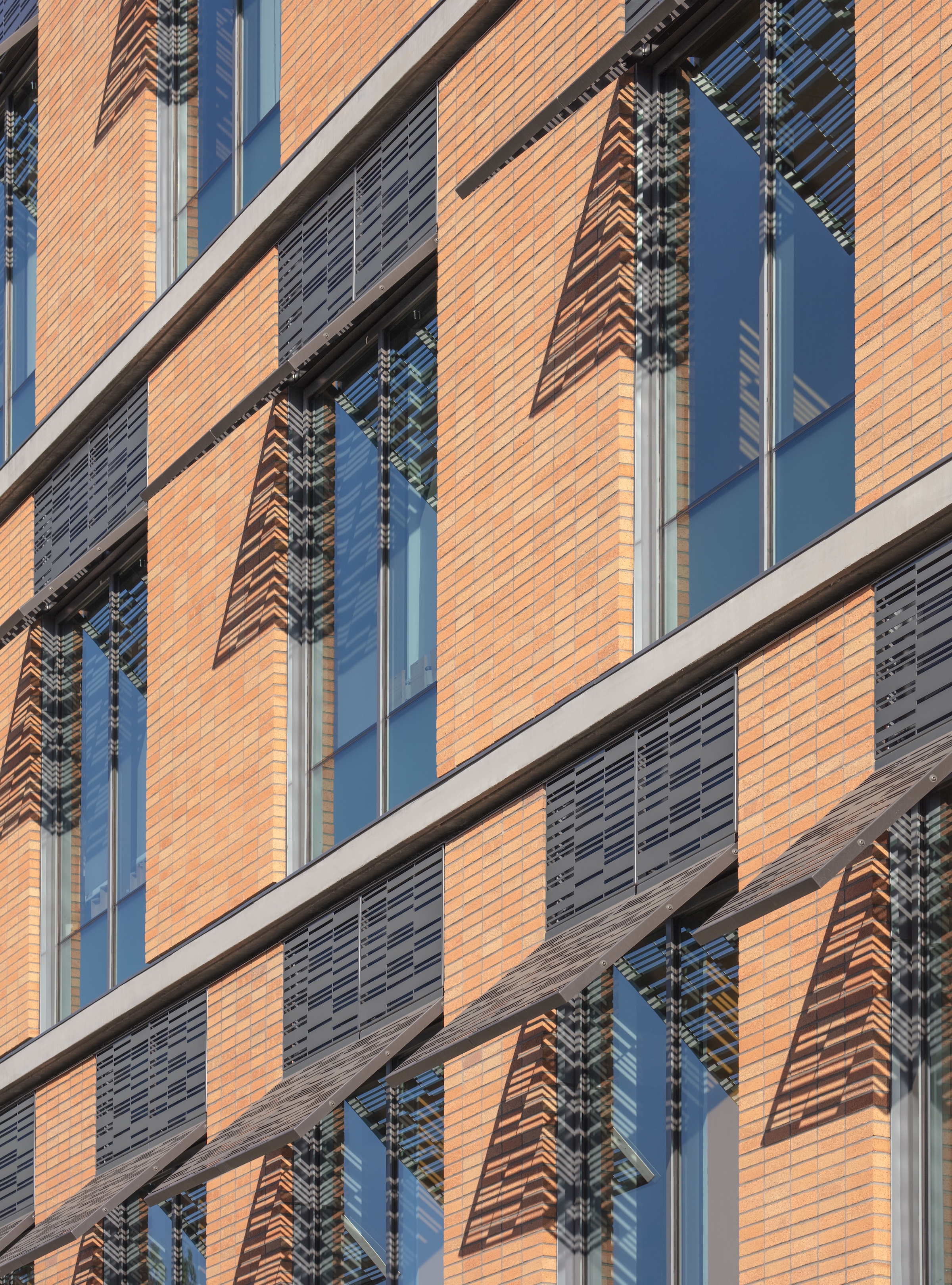
Each façade is optimized for the climate and levels of sun exposure throughout the day. Vertical glass fiber reinforced concrete (GFRC) fins on the east façade cast dramatic extended shadows while protecting interior spaces from the harsh morning light. Painted perforated aluminum panels—featuring custom patterns that resonate with the scale and pattern of the building’s brickwork—shade the east and west exit stairs, screening the stairs behind and creating a larger architectural feature on the façades.
The same panels are used on the south façade to shade individual windows. The staggered window placement is interspersed with brick infill stacked vertically in rows to signify the use of the brick as a façade skin, rather than as load-bearing elements. The north entrance face of the building is porous, both visually with abundant glass and structurally with walls opening out to the courtyard. Inside, a three-story perforated gypsum mural represents an abstraction of orange groves as a nod to the region’s history as the Orange Empire.
The materials palette provides flexibility for expansion over time and allowed construction details to be easily executed and built. During constructability review, the team modeled the different exterior connections and material intersections to digitally ensure the details were constructible and would stand the test of time with limited or no maintenance. Utilizing the design-build delivery method, the EDII was able to fit within a strict budget and a demanding schedule.
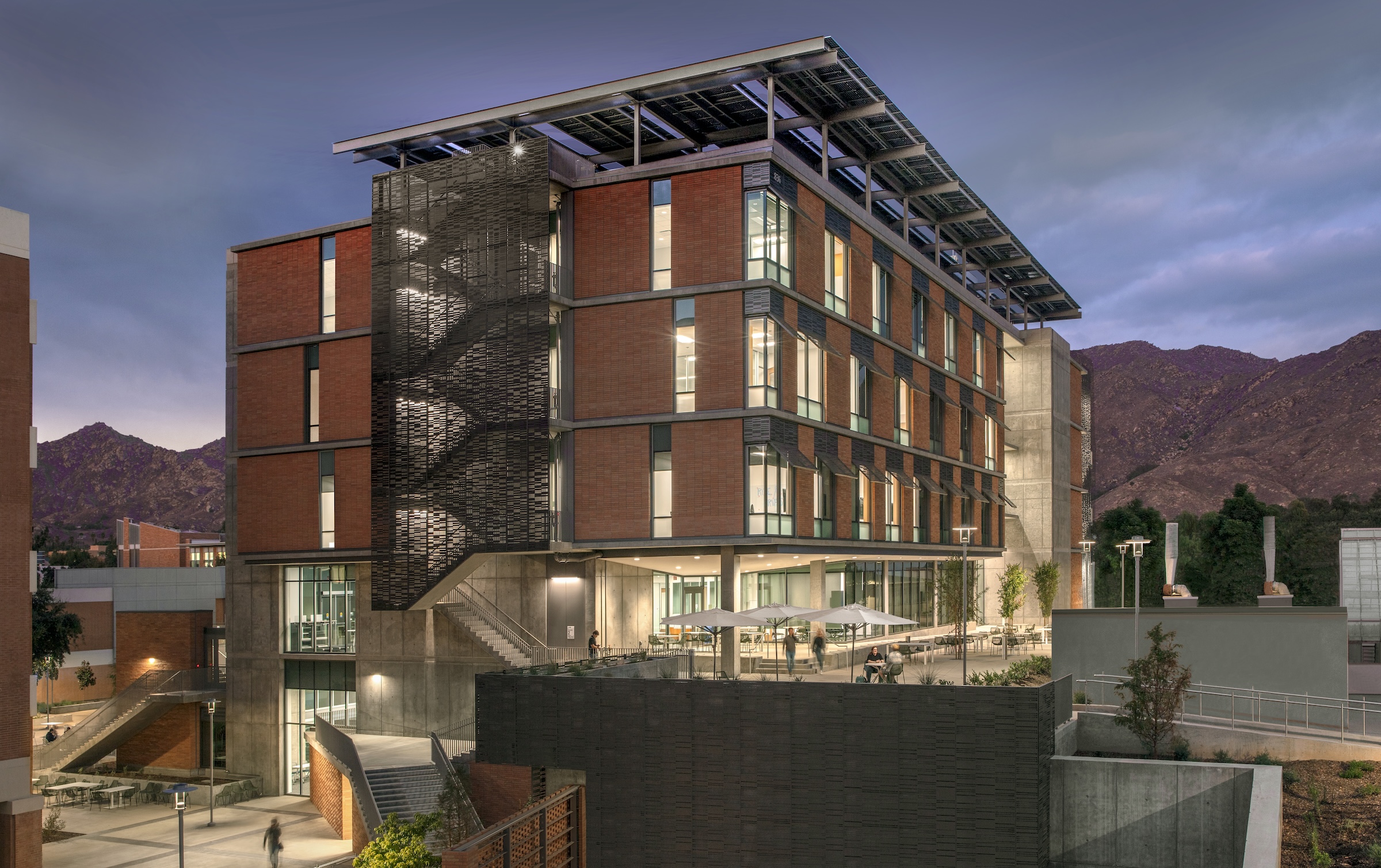

The EDII was designed with long-term sustainability in mind to ensure it will remain fully functional for generations to come while minimizing its carbon footprint. Located in a drought-prone region, the building defends and restores the natural vegetative conditions of the site. The EDII’s use of transparency and shading optimizes passive elements of light, prevailing breezes, and solar heat gain. The interiors and exteriors utilize durable, easy-to-maintain, and sustainable building materials, as well as low/no-VOC materials that promote healthy interior air quality and performance. A 200-kilowatt solar array on the roof contributes to its energy efficiency. The EDII will achieve LEED Platinum through its multiplicity of sustainability strategies in all building systems.
To maximize EDII’s lifespan, the design is flexible and adaptable to respond to growth as needs and pedagogy change. The building is organized with all the high-activity and student-centric learning spaces on the first three floors, which are more accessible and feature indoor/outdoor spaces, while administration and shared functions are located on the upper two floors. The EDII collocates most of the medical school’s staff, administrators, and faculty in the same building for the first time, creating greater efficiencies and moments for collaboration.
The medical school’s academic programs are supported by interactive classrooms, 15 case-based group seminar rooms, ample and various sized study rooms, and additional study and amenity spaces that work cohesively to integrate and support student engagement throughout the day and into the night. Throughout the building, the design team identified opportunities to enhance the program with high-profile spaces, such as an interactive tiered classroom that is universally accessible and features an abundance of daylight, state-of-the-art technology, writeup spaces, and informal lounge seating for breakout sessions.
Each level of the EDII capitalizes on the mild Southern California climate by providing outdoor environments that offer views and opportunities for collaboration, socialization, and reflection. An expansive plaza on the ground level connects and organizes the surrounding buildings, creating a new SOM Plaza for a wide variety of School of Medicine and campus events. EDII reinvigorates the area of campus in which it’s sited, creating opportunity for expansion to the south by developing a “Medical Walk”—a pathway that traverses from the health sciences library, across EDI (SOM’s first building), and through EDII, establishing an armature for future expansion.
Located on a constrained site, EDII uses the challenging terrain in innovative ways to create connections both externally to the campus and internally for users. Each grade level provides accessible opportunities to enter the building, maximizing the topographical nature of the site. By embracing the site’s challenges, EDII establishes meaningful and varied campus interfaces along all sides of the building. The design enriches the campus experience and encourages engagement with the larger campus and community of Riverside.














Related Stories
| Oct 13, 2010
Residences bring students, faculty together in the Middle East
A new residence complex is in design for United Arab Emirates University in Al Ain, UAE, near Abu Dhabi. Plans for the 120-acre mixed-use development include 710 clustered townhomes and apartments for students and faculty and common areas for community activities.
| Oct 13, 2010
New health center to focus on education and awareness
Construction is getting pumped up at the new Anschutz Health and Wellness Center at the University of Colorado, Denver. The four-story, 94,000-sf building will focus on healthy lifestyles and disease prevention.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community college plans new campus building
Construction is moving along on Hudson County Community College’s North Hudson Campus Center in Union City, N.J. The seven-story, 92,000-sf building will be the first higher education facility in the city.
| Oct 12, 2010
University of Toledo, Memorial Field House
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Memorial Field House, once the lovely Collegiate Gothic (ca. 1933) centerpiece (along with neighboring University Hall) of the University of Toledo campus, took its share of abuse after a new athletic arena made it redundant, in 1976. The ultimate insult occurred when the ROTC used it as a paintball venue.
| Oct 12, 2010
Owen Hall, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Mich.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Officials at Michigan State University’s East Lansing Campus were concerned that Owen Hall, a mid-20th-century residence facility, was no longer attracting much interest from its target audience, graduate and international students.
| Oct 12, 2010
Cell and Genome Sciences Building, Farmington, Conn.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Administrators at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington didn’t think much of the 1970s building they planned to turn into the school’s Cell and Genome Sciences Building. It’s not that the former toxicology research facility was in such terrible shape, but the 117,800-sf structure had almost no windows and its interior was dark and chopped up.
| Oct 12, 2010
Full Steam Ahead for Sustainable Power Plant
An innovative restoration turns a historic but inoperable coal-burning steam plant into a modern, energy-efficient marvel at Duke University.
| Sep 16, 2010
Green recreation/wellness center targets physical, environmental health
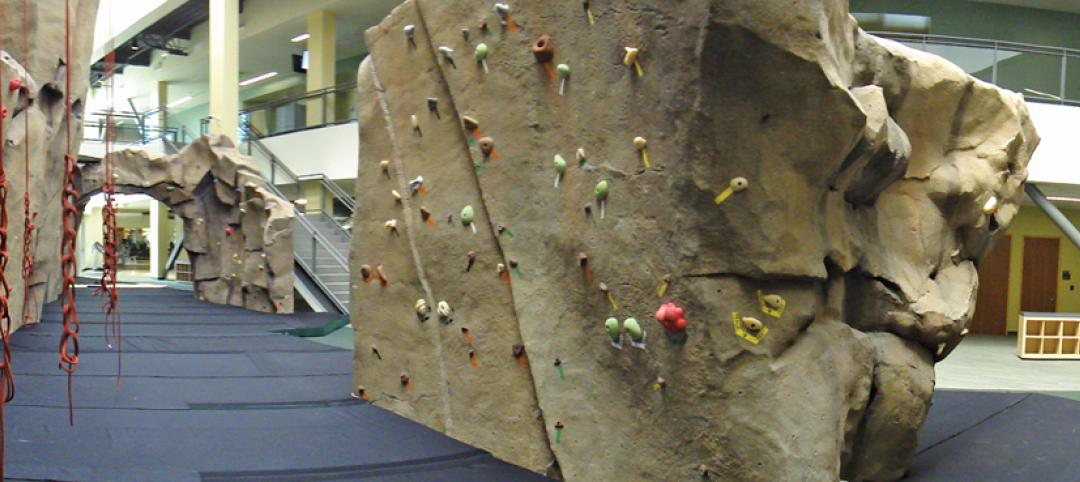
The 151,000-sf recreation and wellness center at California State University’s Sacramento campus, called the WELL (for “wellness, education, leisure, lifestyle”), has a fitness center, café, indoor track, gymnasium, racquetball courts, educational and counseling space, the largest rock climbing wall in the CSU system.
| Sep 13, 2010
Community college police, parking structure targets LEED Platinum
The San Diego Community College District's $1.555 billion construction program continues with groundbreaking for a 6,000-sf police substation and an 828-space, four-story parking structure at San Diego Miramar College.
| Sep 13, 2010
Campus housing fosters community connection
A 600,000-sf complex on the University of Washington's Seattle campus will include four residence halls for 1,650 students and a 100-seat cafe, 8,000-sf grocery store, and conference center with 200-seat auditorium for both student and community use.

















