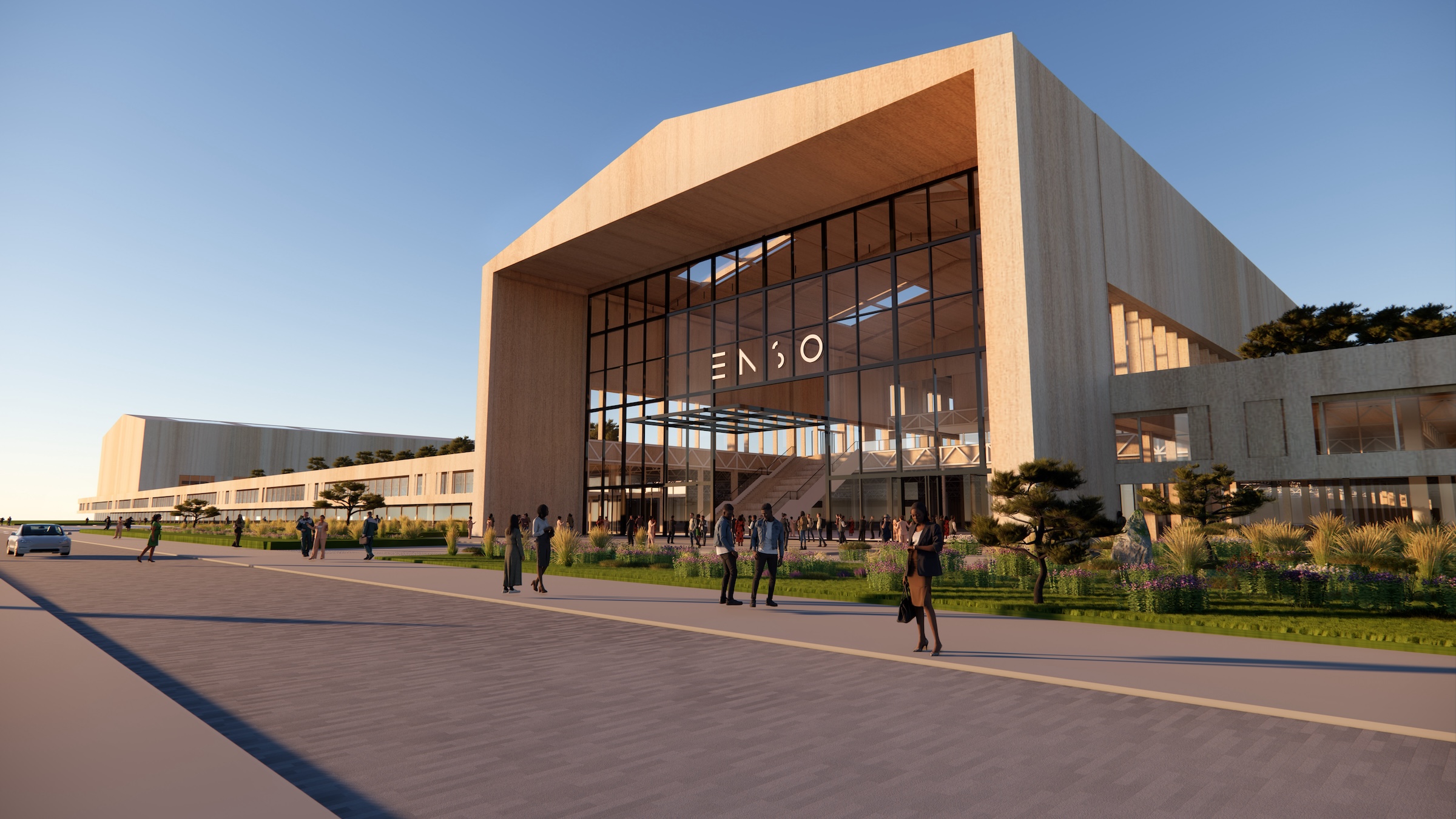
ENSO, a U.K.-based company that makes tires for electric vehicles, has announced plans to build the first carbon-neutral tire factory in the U.S.
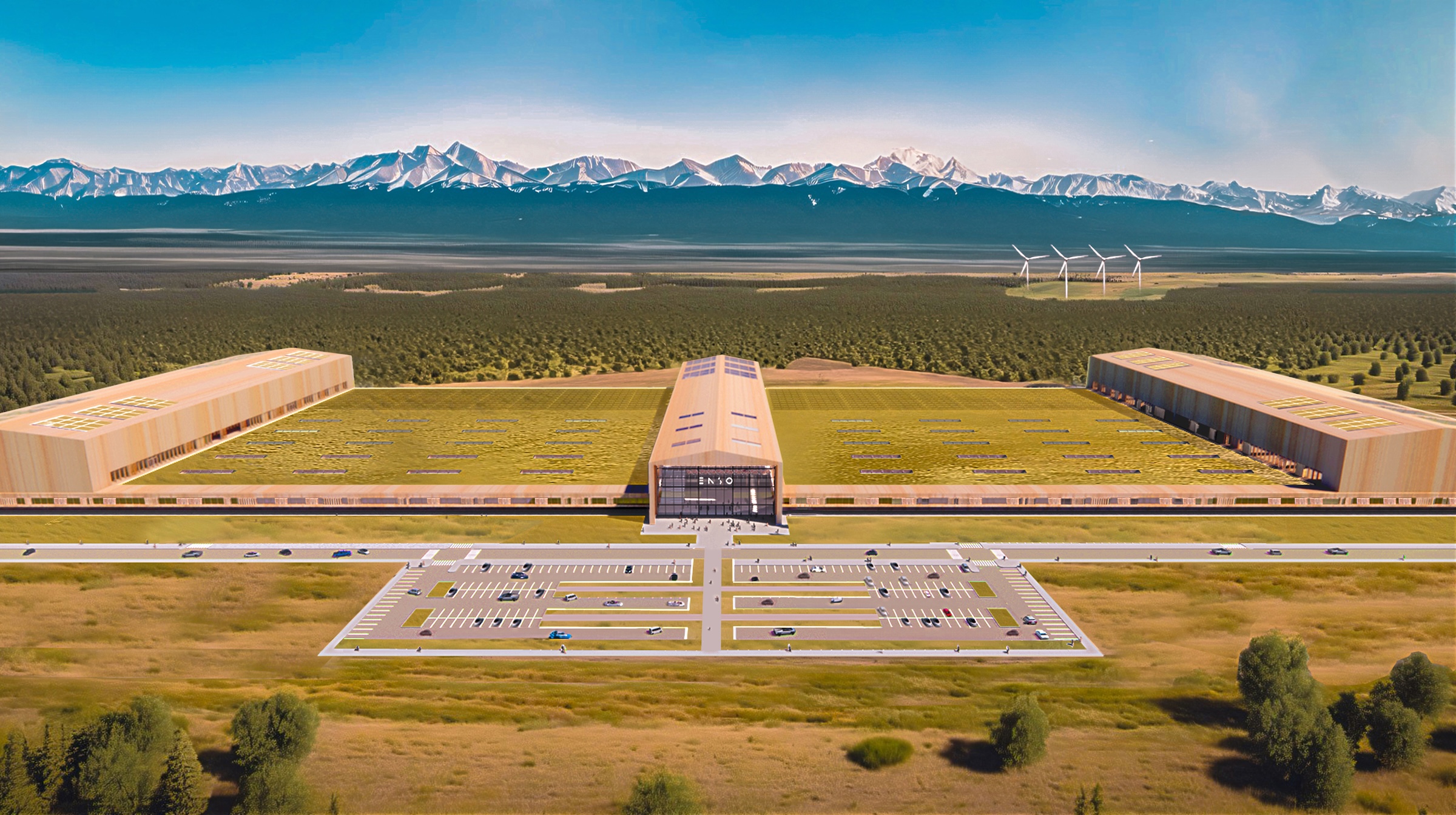
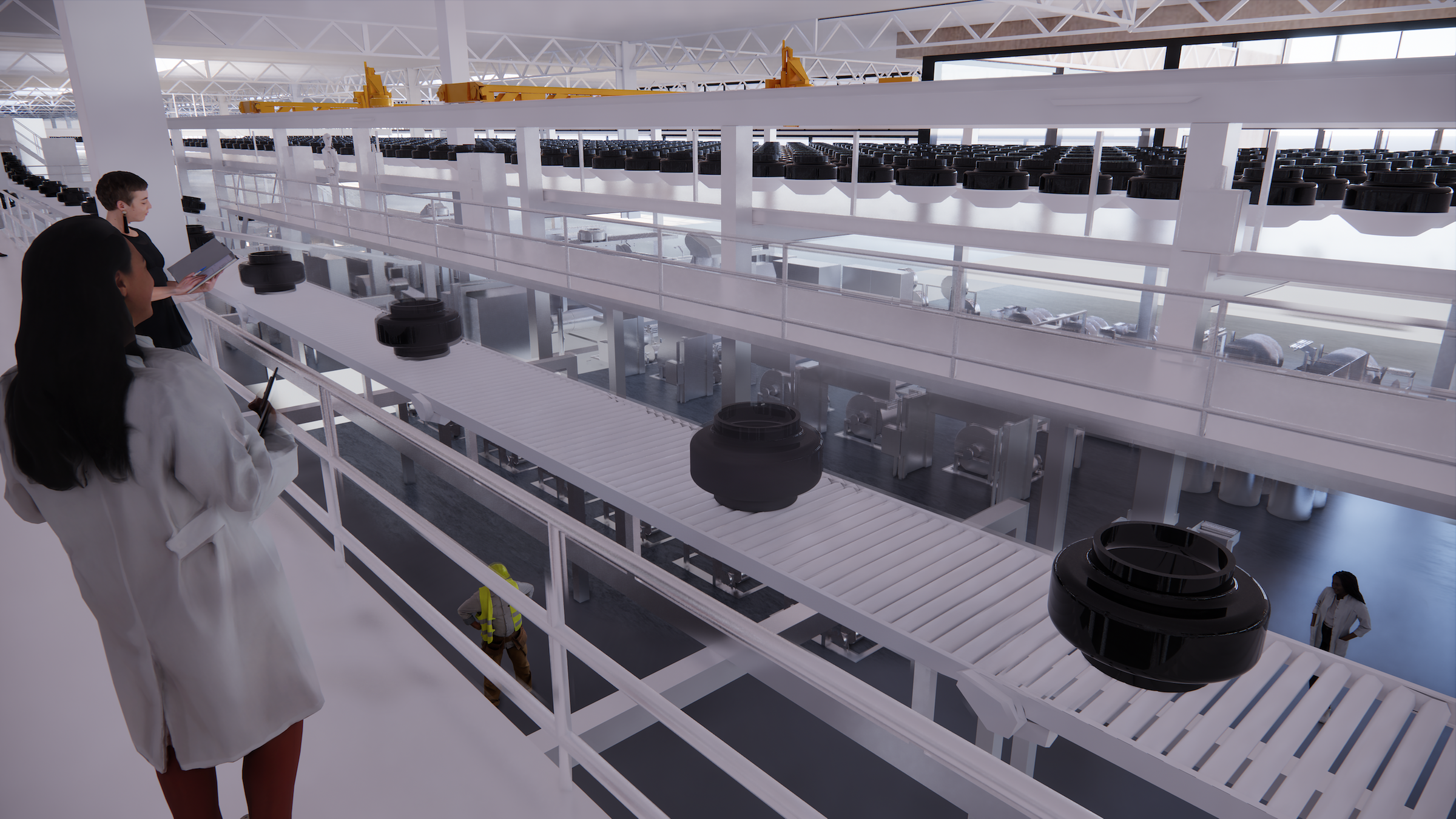
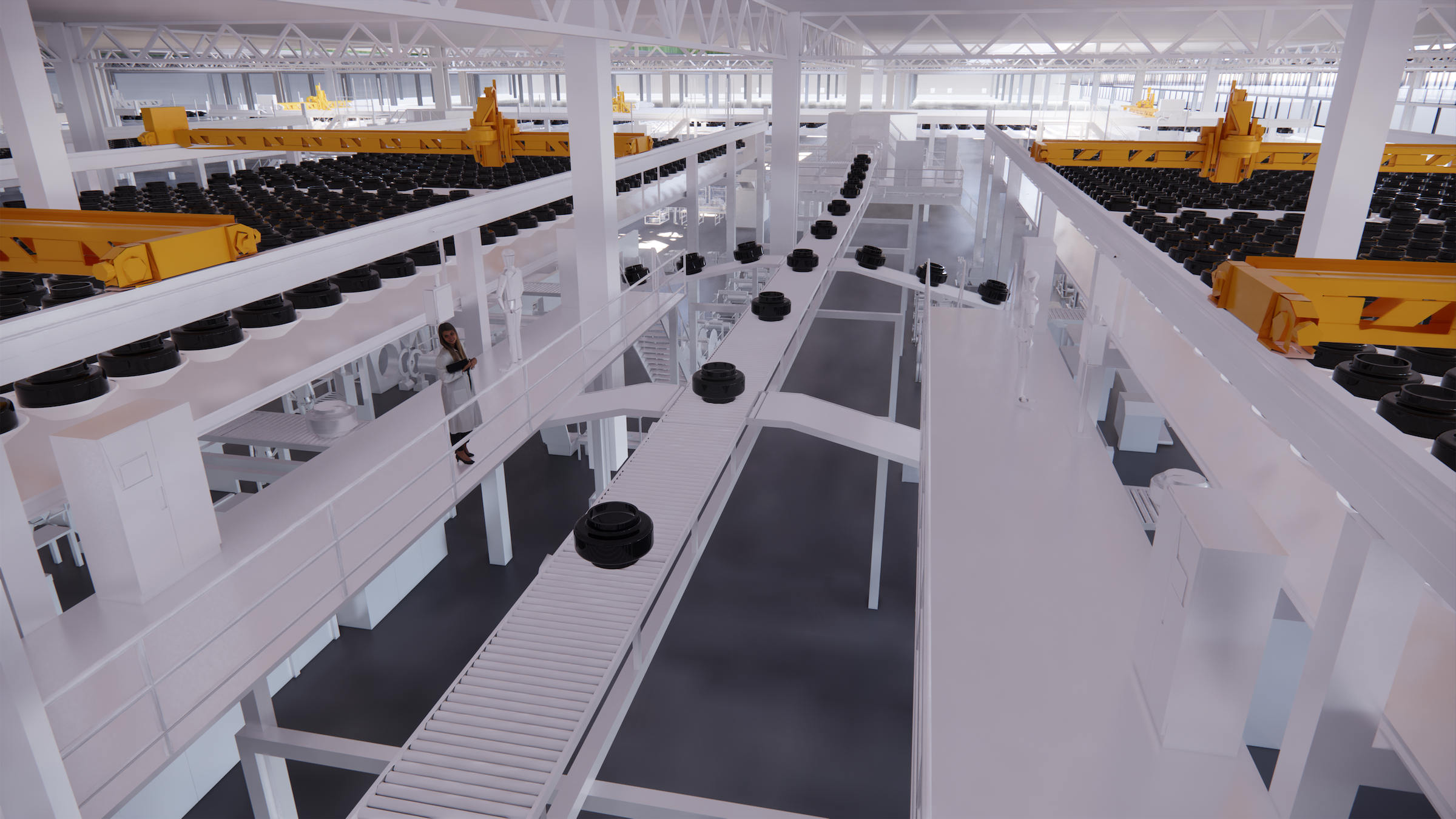
The $500 million ENSO technology campus will be powered entirely by renewable energy. The first-of-its-kind tire industrial campus aims to be carbon neutral without purchased offsets, using carbon-neutral raw materials and building materials.
In its first phase, the factory will produce five million EV tires annually by 2027 and create 600 jobs. The factory will expand to 2,400 jobs when built out to its full production capacity of 20 million tires, which ENSO says is 8% of the total annual U.S. tire market. To accelerate and scale innovation, the ENSO technology campus will integrate research and development production under one roof.
Most tires sold in the U.S. today are imported, ENSO reports. The factory aims to reduce U.S. reliance on imports and enhance domestic production. Possible factory locations include Colorado, Georgia, Nevada, and Texas, among other states.
“The U.S. is the best place for ENSO to establish its first carbon-neutral tire factory,” ENSO CEO Gunnlaugur Erlendsson said in a press statement. “With strong regulatory support and a significant market opportunity, we are committed to bringing our innovative, low-emission, low-cost tires to American consumers. This factory will make tires more affordable, reduce tire pollution, create great jobs, and drive sustainability in the U.S. tire industry.”
ENSO says it has signed a letter of interest with the Export-Import Bank of the United States to establish the factory in the U.S. Technology partner Rockwell, development firm Arup, and investors 8090 Industries and Galway Sustainable Capital are also supporting the project.
ENSO’s mission is to make EVs more successful and reduce tire pollution, which is responsible for 6 million tons of particulate matter emitted globally, per the statement. The company says its tires increase EV range by 10% and reduce particulate matter emissions by 35%. ENSO plans to phase out all fossil fuel-based raw materials from its products by 2030, replacing them with bio-based renewable and low-carbon alternatives.

Here is the full press release from ENSO:
ENSO, the tire technology company that makes better tires for electric vehicles (EVs), has signed a Letter of Interest (LOI) with the Export-Import Bank of the United States (U.S. EXIM Bank) to establish a groundbreaking carbon-neutral tire factory in America. U.S.-based technology partners Rockwell, global sustainable development firm Arup and US-based investors 8090 Industries and Galway Sustainable Capital, are supporting ENSO.
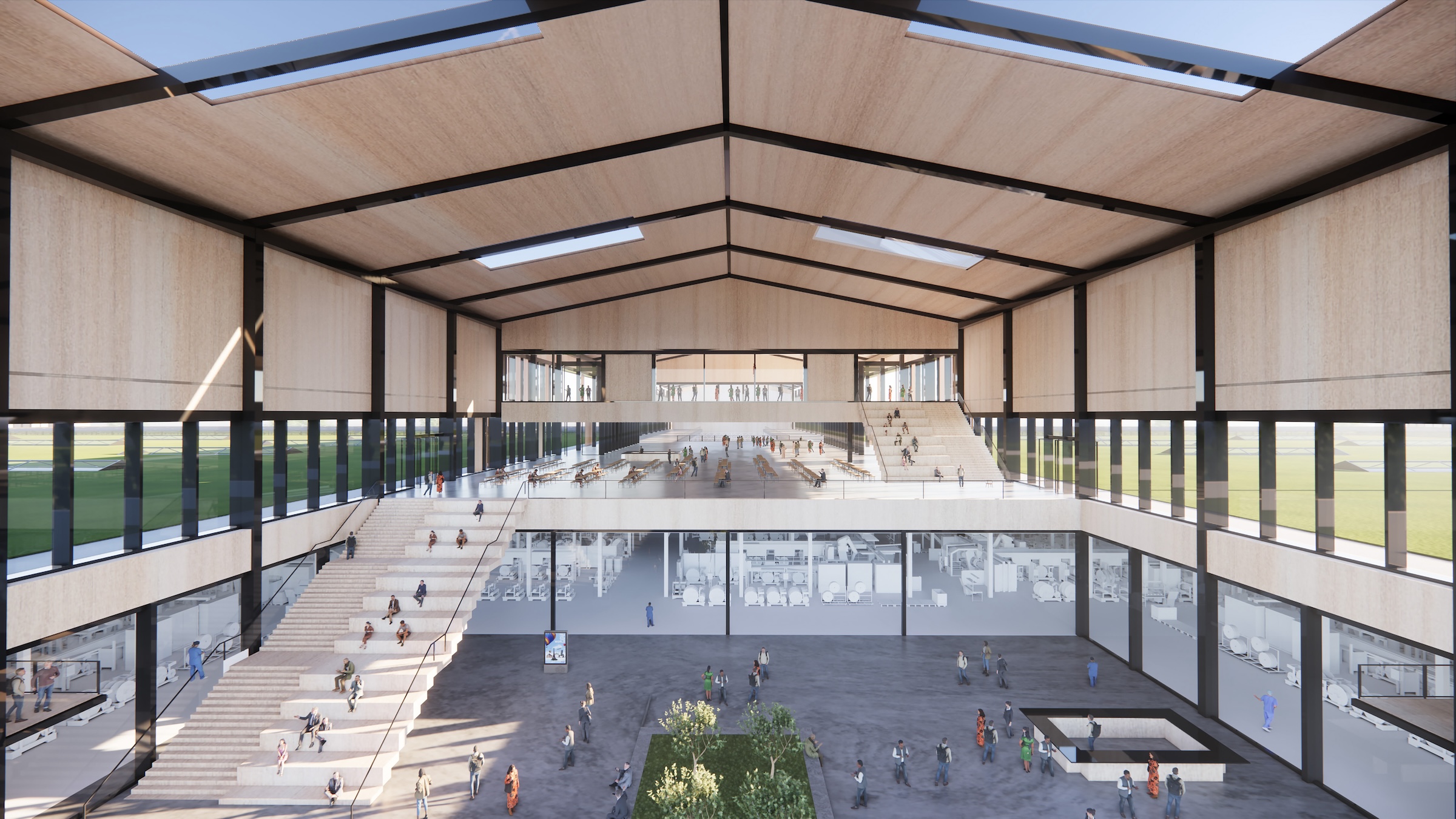
The first-of-its-kind tire factory will be carbon-neutral without purchased offsets, utilizing carbon-neutral raw materials, building materials and 100% renewable energy. In its first phase, the factory will produce 5 million EV tires by 2027 and create 600 jobs, rising to 2,400 jobs when built out to full production capacity of 20 million tires – 8% of America’s total annual tire market. The ENSO technology campus will integrate research and development with production under one roof to accelerate and scale innovation.
Announced at the SelectUSA Investment Summit in Washington DC, potential factory locations include Colorado, Nevada, Texas, and Georgia, with other states in consideration. The U.S., particularly California, has a significant EV consumer base and is leading efforts to regulate tire efficiency and emissions, making the U.S. the ideal market for ENSO.
ENSO CEO Gunnlaugur Erlendsson said, "The U.S. is the best place for ENSO to establish its first carbon-neutral tire factory. With strong regulatory support and a significant market opportunity, we are committed to bringing our innovative, low-emission, low-cost tires to American consumers. This factory will make tires more affordable, reduce tire pollution, create great jobs and drive sustainability in the U.S. tire industry.”

The U.S. regulatory environment strongly supports ENSO’s move to America. Initiatives like the Inflation Reduction Act have transformed the automotive sector and enabled more ambitious EPA (Environment Protection Act) emissions standards, paving the way for similar advancements in the tire industry. Programs such as the California Energy Commission’s (CEC) Replacement Tire Efficiency Program and the California Environmental Protection Agency’s (CalEPA) efforts to control toxic chemicals such as 6PPD in tires align with ENSO's goals, by setting out minimum efficiency and environmental standards for both new and aftermarket tires.
Tires are critical to keeping America’s economy moving. Without tires, all 275 million vehicles in the U.S. would grind to halt. Currently, the majority of tires sold in the U.S. are imported. This factory will help reduce America’s reliance on imports, enhancing domestic production capabilities. There is a big consumer appetite in the U.S. for ENSO’s tire innovation. Nearly half (47%) of Americans would be more encouraged to buy a set of tires if they were made in the U.S., 46% if they used fewer toxic materials, 43% if they produced fewer emissions, and 41% if they were made from recycled materials.
ENSO’s mission is to make EVs more successful and reduce tire pollution, saving costs for every American. ENSO’s tires already increase EV range by 10% and reduce particulate matter emissions by 35%. By producing fewer, longer-lasting tires with better technology, ENSO aims to cut tire pollution.
Tire pollution is a significant issue, responsible for six million tons of particulate matter emitted globally each year. Tire pollution is a major contributor to ocean microplastic pollution and local air pollution, while tire production is carbon intensive and creates huge amounts of waste at the end of life. ENSO, a finalist in the ‘Clean Our Air’ category of The Earthshot Prize, the prestigious annual environmental award established by Prince William, is leading the way on environmental standards in the tire industry. ENSO is leading efforts to decarbonize the tire industry and is committed to completely phase out all fossil fuel based raw materials from its products by 2030, replacing them with bio-based renewable and low-carbon alternatives.
The U.S. has a major market opportunity to lead the transformation of the tire industry and to incentivize EV adoption. America doesn't make enough tires, and ENSO’s factory will be a major step toward achieving these goals, ensuring economic benefits and environmental sustainability for American consumers. This factory therefore represents a significant investment in setting a new standard for the future of American tire manufacturing.



Related Stories
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 14, 2014
Slash energy consumption in data centers with liquid-based ‘immersive-cooling’ technology
A new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency by using liquid instead of air to cool the servers.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 9, 2014
Beyond the bench: Meet the modern laboratory facility
Like office workers escaping from the perceived confines of cubicles, today’s scientists have been freed from the trappings of the typical lab bench, writes Perkins+Will's Bill Harris.
| Oct 1, 2014
4 trends shaping the future of data centers
As a designer of mission critical facilities, I’ve learned that it’s really difficult to build data centers to keep pace with technology, yet that’s a reality we face along with our clients, writes Gensler's Jackson Metcalf.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
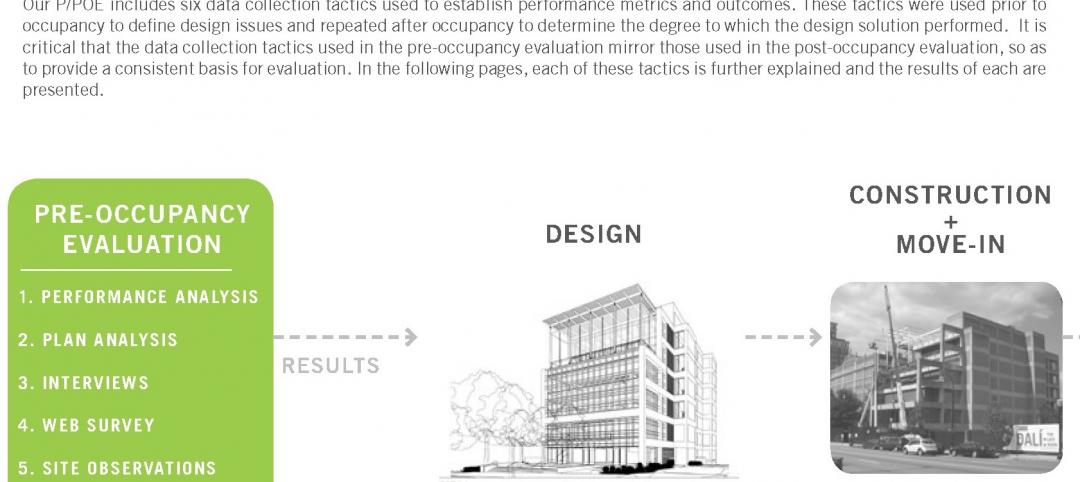
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 19, 2014
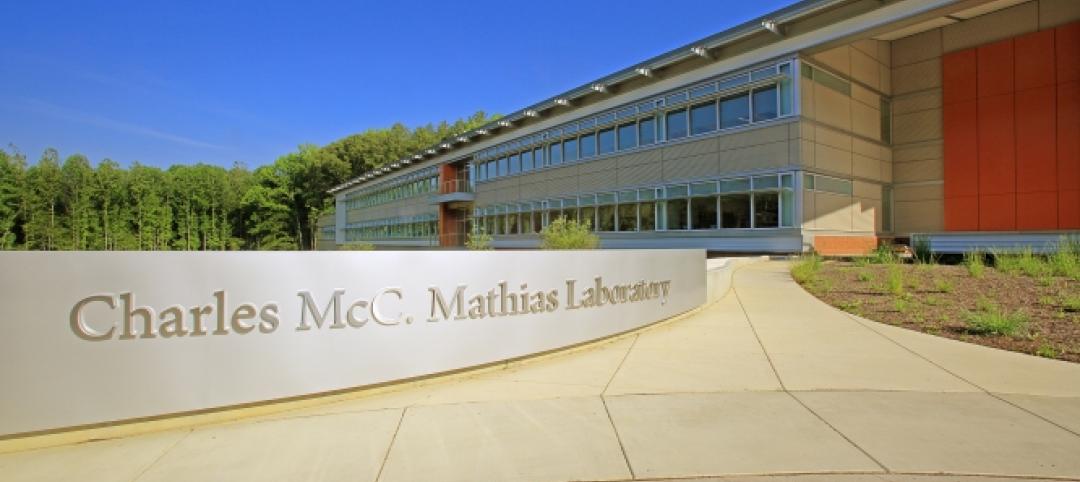
Smithsonian Institution opens LEED Platinum lab facility
The Charles McC. Mathias Laboratory will emit 37% less CO2 than a comparable lab that does not meet LEED-certification standards.