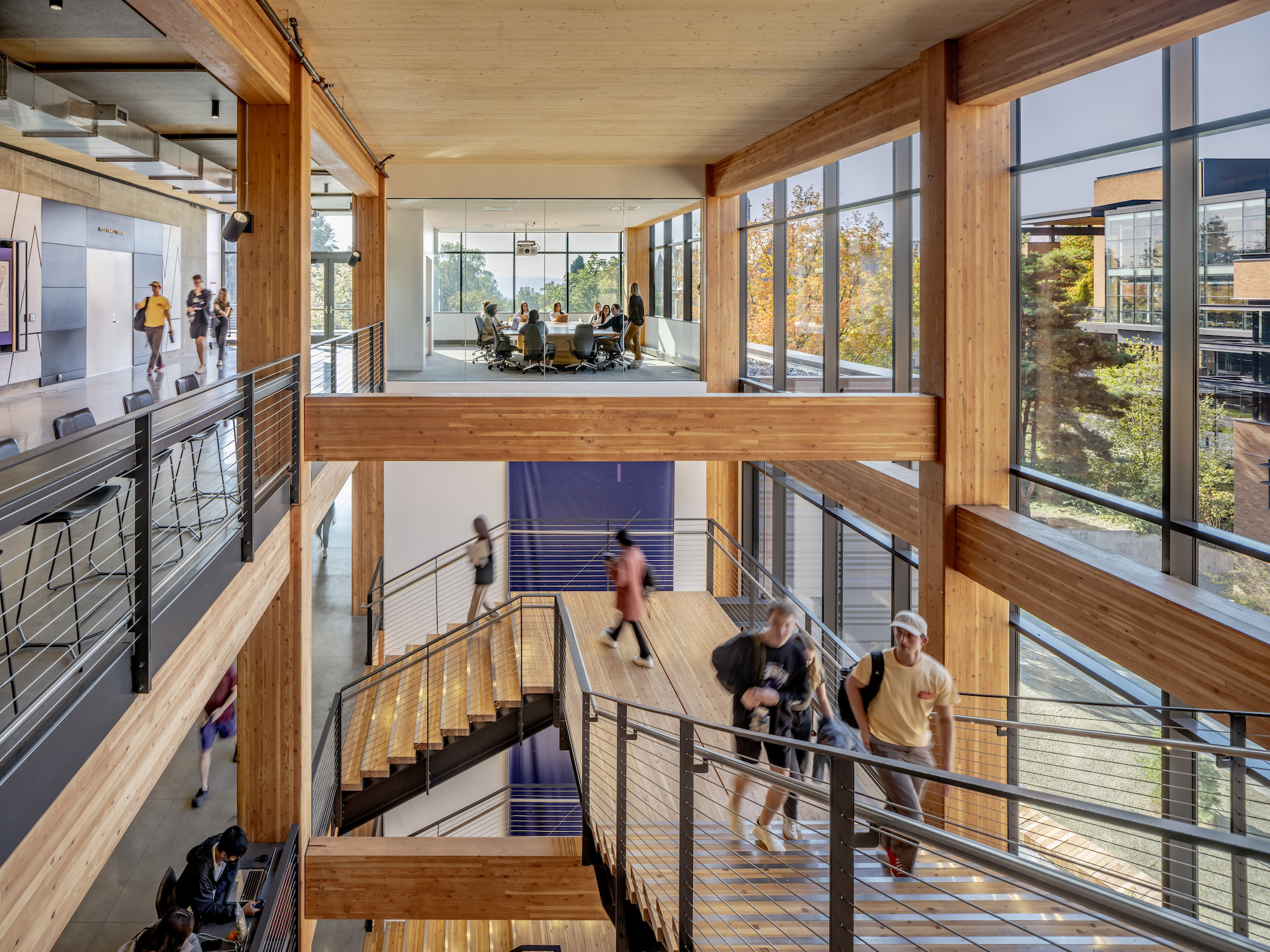
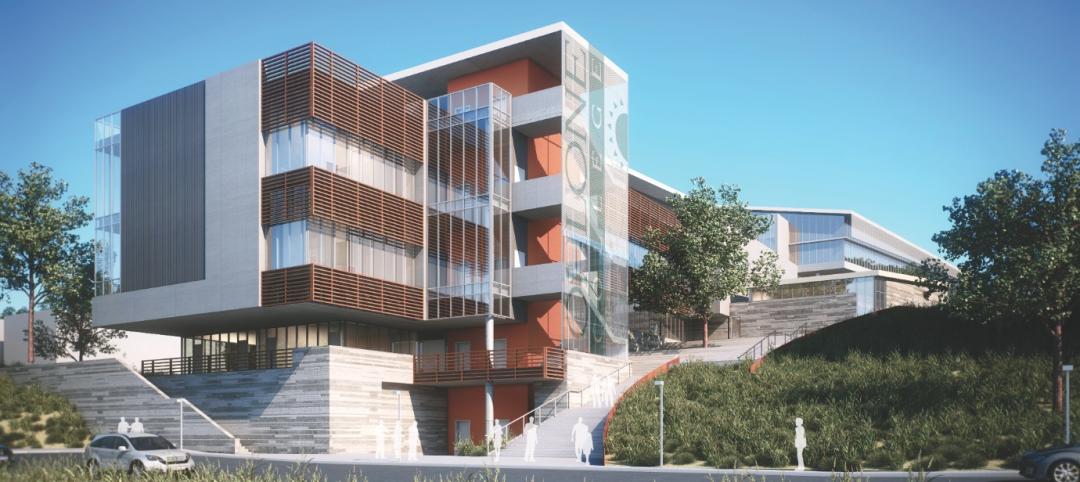
Founders Hall at the University of Washington Foster School of Business, the first mass timber building at Seattle campus of Univ. of Washington, was recently completed. The 84,800-sf building creates a new hub for community, entrepreneurship, and innovation, according the project’s design architect LMN Architects.
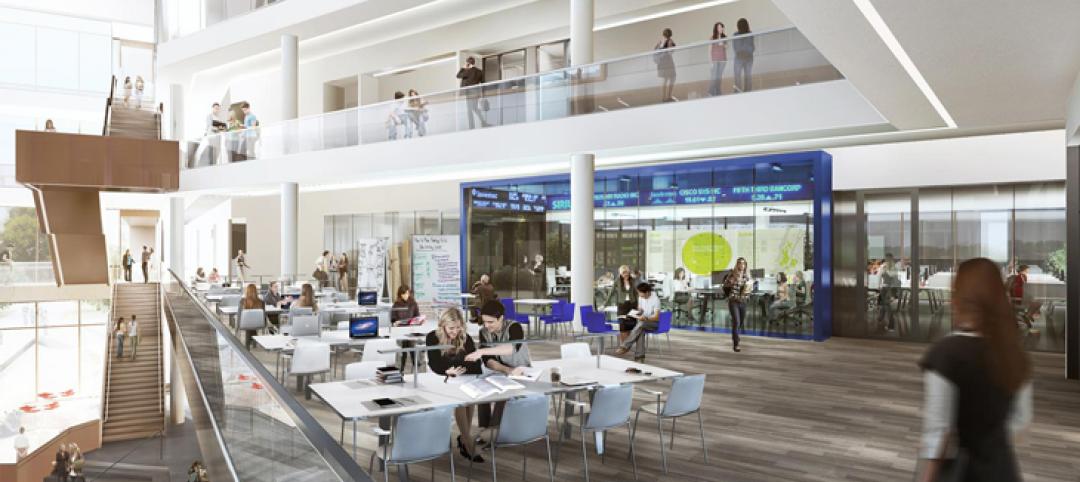
The design creates an intersection of three volumes hosting student-focused team collaboration spaces, program offices, classrooms, and gathering spaces, all connected by a five-story steel and wood feature stair that weaves through the mass timber structure.
The community connector houses the feature stair, circulation spaces, pre-function spaces, and two tiered classrooms that can be set for 65 or 135 students. The team bar provides 28 team and interview rooms, four executive conference rooms, a student commons with an outdoor terrace, and a rooftop event forum.
The building was organized to foster spontaneous and open interaction between staff, business professionals, and students by positioning program offices, alumni offices, and career services offices adjacent to student spaces on every level. With meeting spaces accessible to all for shared use, students and program staff will be able to interact with one another daily.
Mass timber construction cuts embodied carbon
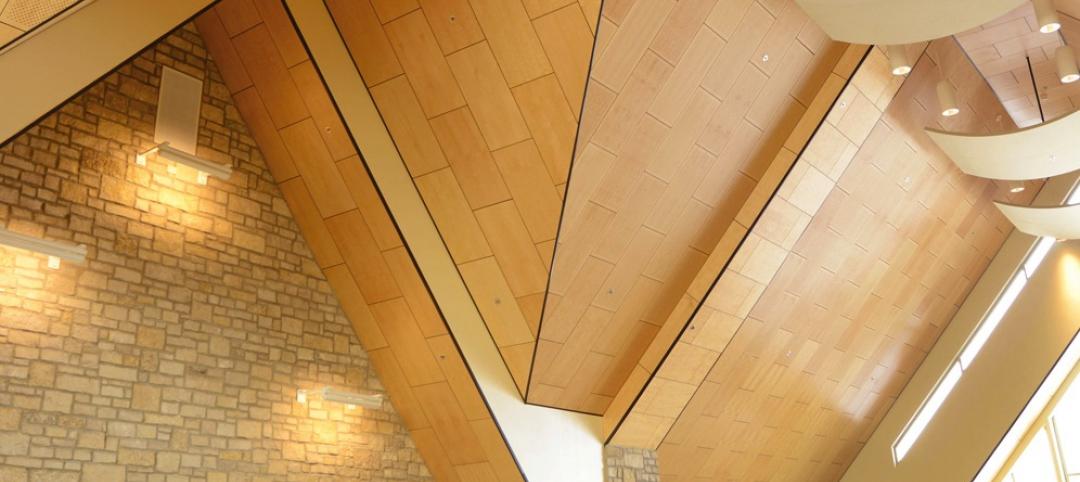
The use of mass timber lowers the project’s embodied carbon substantially with the use of Douglas fir creating a warm and inviting interior atmosphere. The exterior architectural expression draws from the material palette established by other Foster School buildings and reveals moments of the mass timber structure.
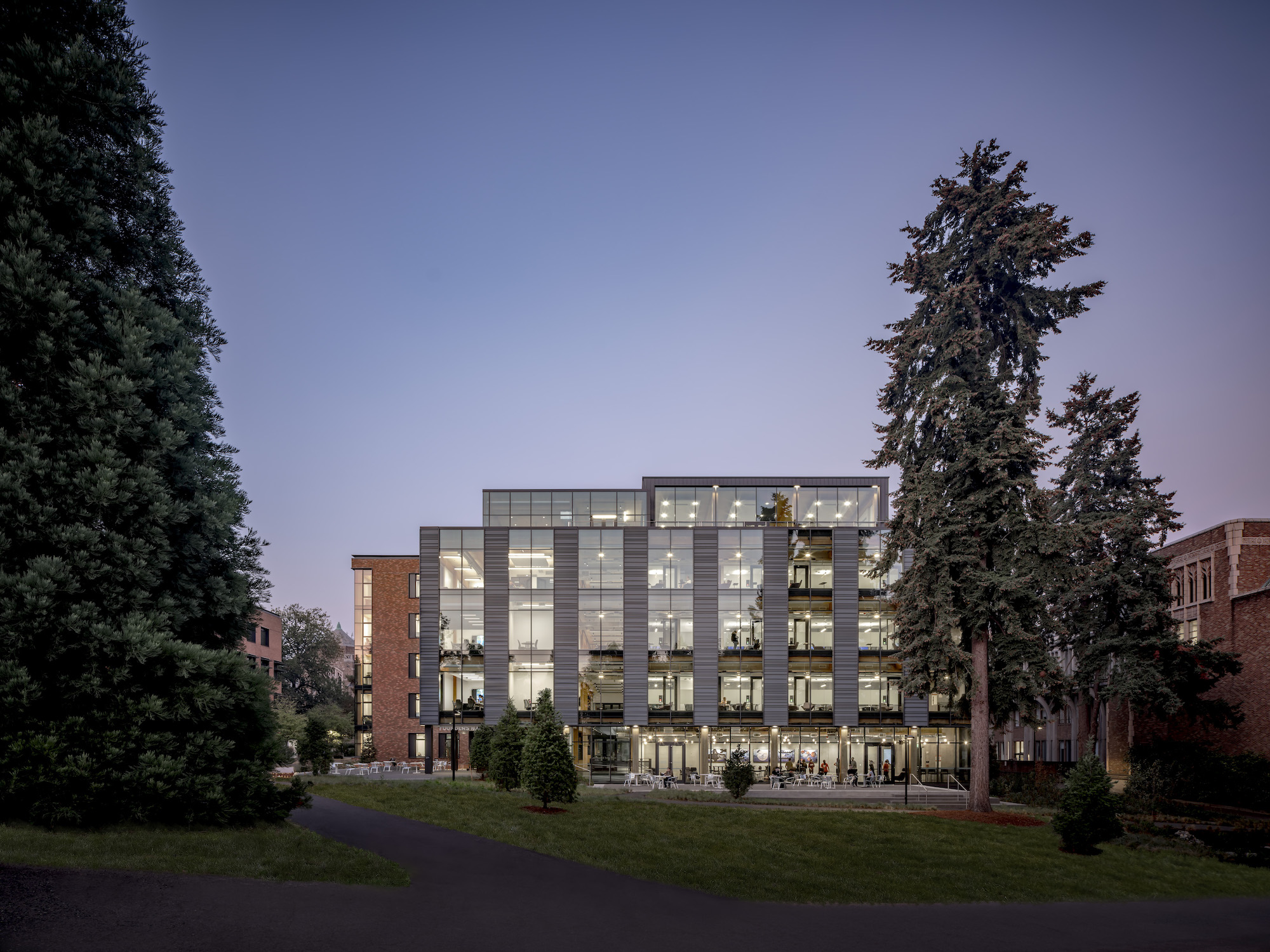

Founders Hall is the first new building to meet the University of Washington Green Building Standards, reducing carbon emissions by over 90%. The design takes advantage of Seattle’s weather by integrating natural and mechanical ventilation to provide a comfortable environment for users with minimal reliance on conditioned air. As an integrated element in both the interior and exterior expression, the building incorporates a mass timber structure with cross-laminated timber decking. This reflects the Foster School’s connection to the Northwest and the local wood products industry, also reducing the building’s embodied carbon by almost 60%.
Many of the existing nearby Douglas fir and sequoia trees on site were preserved. The peeled-away brick façade paired with carefully placed glazing exposes the timber inside the building while providing views of the Douglas firs, giving the higher floors of the building an immersive Northwest forest experience.
The project partnered with Aureus Earth, a provider of carbon offsetting incentive programs, to create a proof of concept for long-term biogenic carbon storage in a mass timber building. The building will store more than 1,000 tons of CO2 for decades, keeping carbon out of the atmosphere for the lifetime of the building.
On the project team:
Owner and/or developer: The University of Washington
Design Architect: LMN Architects
Design-Builder: Hoffman Construction
MEP engineer: PAE Consulting Engineers
Structural engineer: Magnusson Klemencic Associates
Related Stories
| Nov 3, 2014
An ancient former post office in Portland, Ore., provides an even older art college with a new home
About seven years ago, The Pacific Northwest College of Art, the oldest art college in Portland, was evaluating its master plan with an eye towards expanding and upgrading its campus facilities. A board member brought to the attention of the college a nearby 134,000-sf building that had once served as the city’s original post office.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 14, 2014
Proven 6-step approach to treating historic windows
This course provides step-by-step prescriptive advice to architects, engineers, and contractors on when it makes sense to repair or rehabilitate existing windows, and when they should advise their building owner clients to consider replacement.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
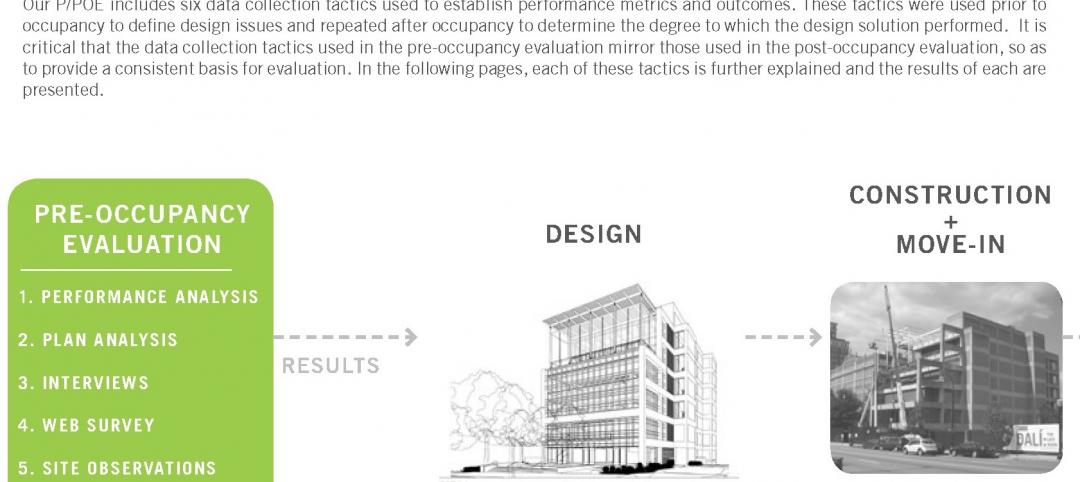
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 17, 2014
New hub on campus: Where learning is headed and what it means for the college campus
It seems that the most recent buildings to pop up on college campuses are trying to do more than just support academics. They are acting as hubs for all sorts of on-campus activities, writes Gensler's David Broz.