The University of Pennsylvania’s Biomedical Library was built on the southern portion of the school’s campus in Philadelphia in the late 1960s. Much has changed in the ensuing decades: Penn has expanded and transformed that part of its campus with research and clinically focused buildings. And digitization has altered the function and purpose of libraries in general to where they are less about being repositories of past knowledge and more about contributing to a dynamic future.
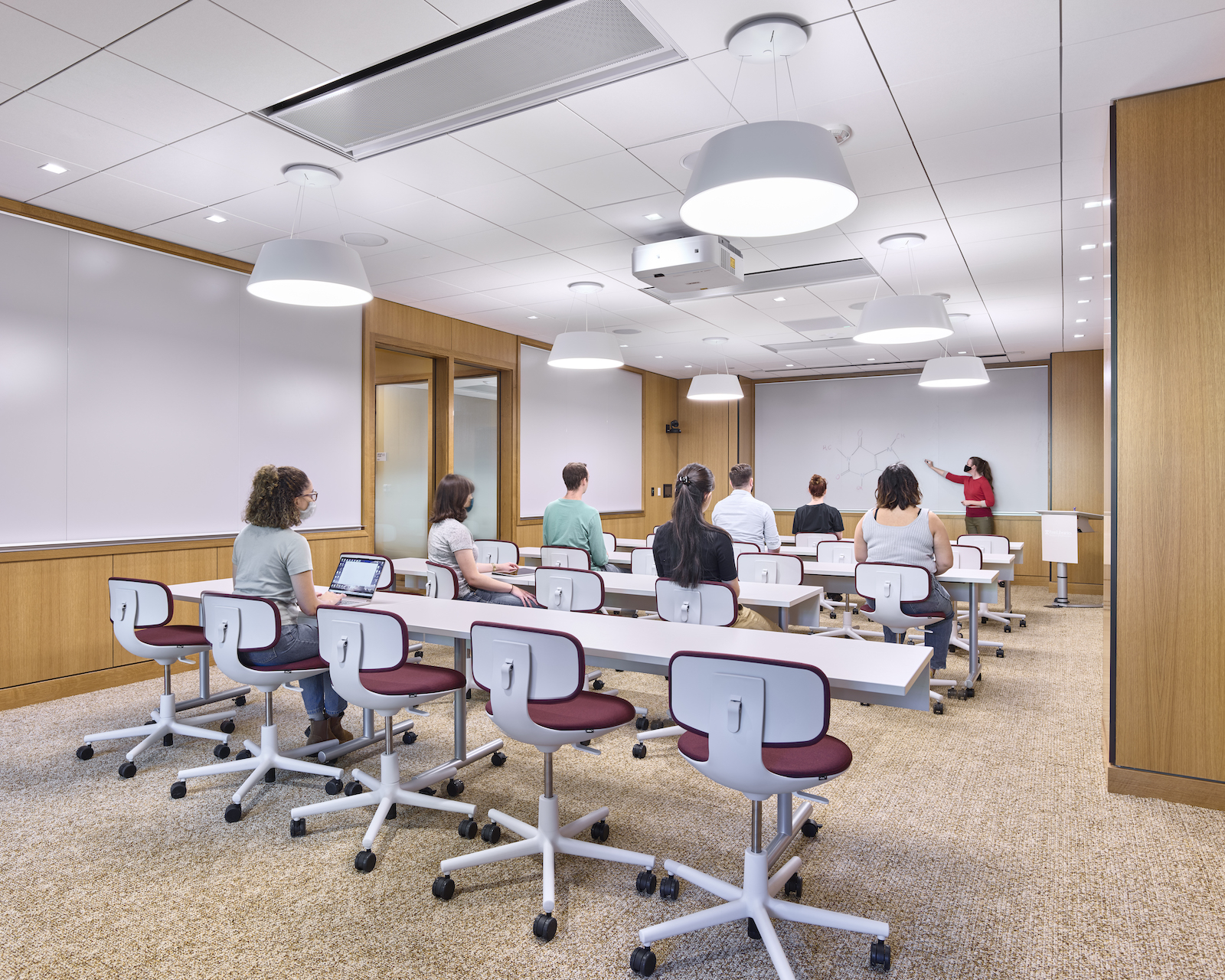
On September 20, 2021, Penn reopened its renovated and expanded library as an open center for cross-disciplinary learning, prototyping, and collaboration. Now called Biotech Commons, the 17,000-sf building supports new modes of research by offering a range of spaces and services—from conference centers to fabrication shops—that is free to be scheduled by any student or faculty member.
“No place is as interdisciplinary as a library space, and the reimagined Biotech Commons takes this to the next level,” Constantia Constantinou, the H. Carton Rogers III Vice Provost and Director of the Penn Libraries, told Penn Today. She predicted that the facility “will enhance the intellectual vitality of Penn as a whole by providing an extraordinary user experience for all.”
The Biotech Commons unites the medical and scientific campus to the north and the core campus to the south, said the university in a statement it sent to BD+C in early January. “It is intended to provide a high-tech, community-building hub that integrates resources and brings together students, faculty, researchers, and staff from multiple disciplines.” The Biotech Commons also serves as “a powerful magnet” for communities from across campus.
“The facility is very clearly research oriented, and the research is more technologically advanced,” observes Daniela Voith, FAIA, LEED AP BD+C, IIDA, Founding Partner and Director of Design with Voith & Mactavish Architects (VMA), the design architect on the Biotech Commons renovation, which began in December 2020. Voith says that Associate Principal Sennah Loftus, VMA’s project manager, is this firm’s go-to person when it comes to integrating high-level technology into its academic facility designs.
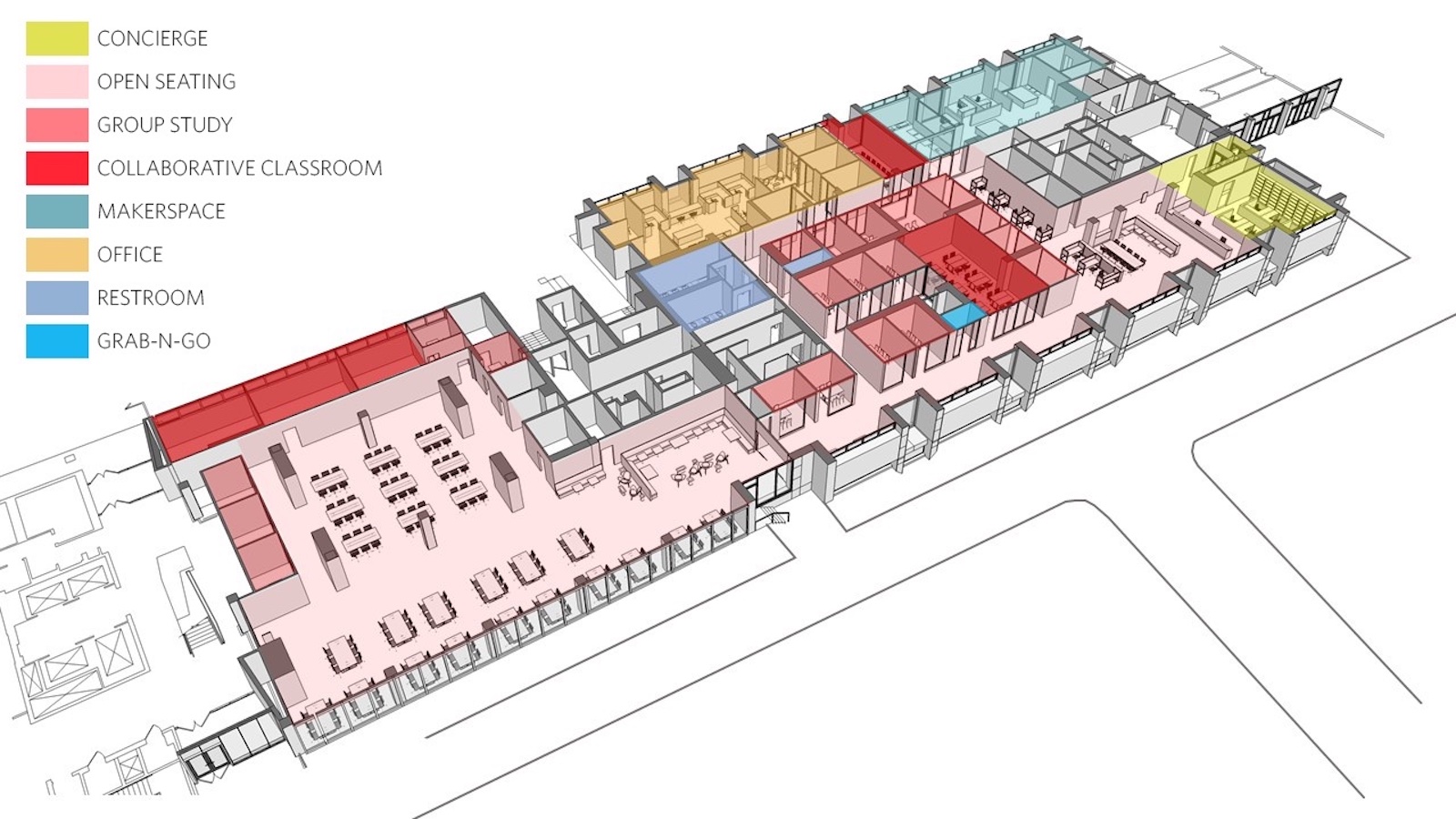
The Judith and William Bollinger Digital Fabrication Lab within Biotech Commons is equipped with nine high-end 3D printers and two 3D scanners, a laser cutter, and plotters for scientific poster printing. The first-of-its-kind anatomy visualization system, called an Anatomage Table, is available for use by all members of the Penn community, allowing for the virtual dissection and review of life-size virtual cadavers outside of clinical lab coursework.
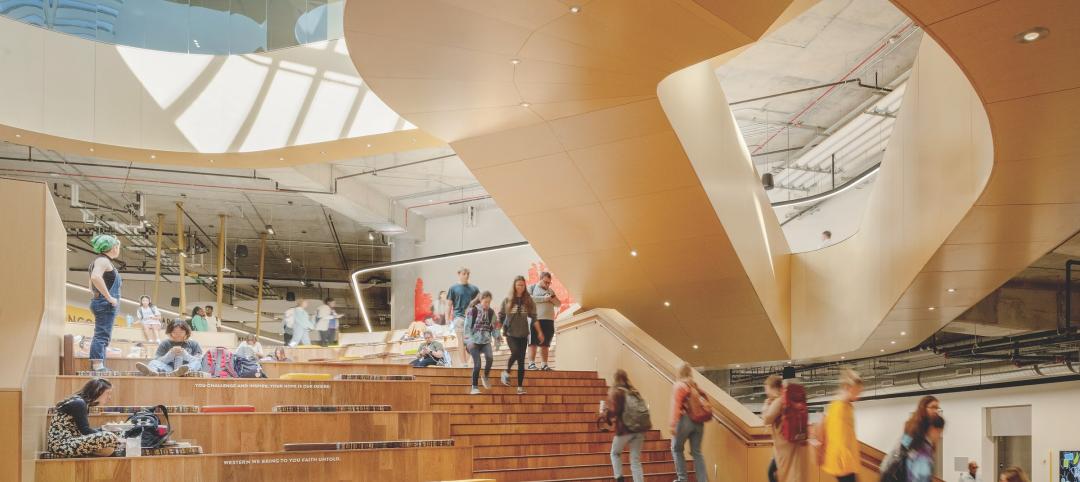
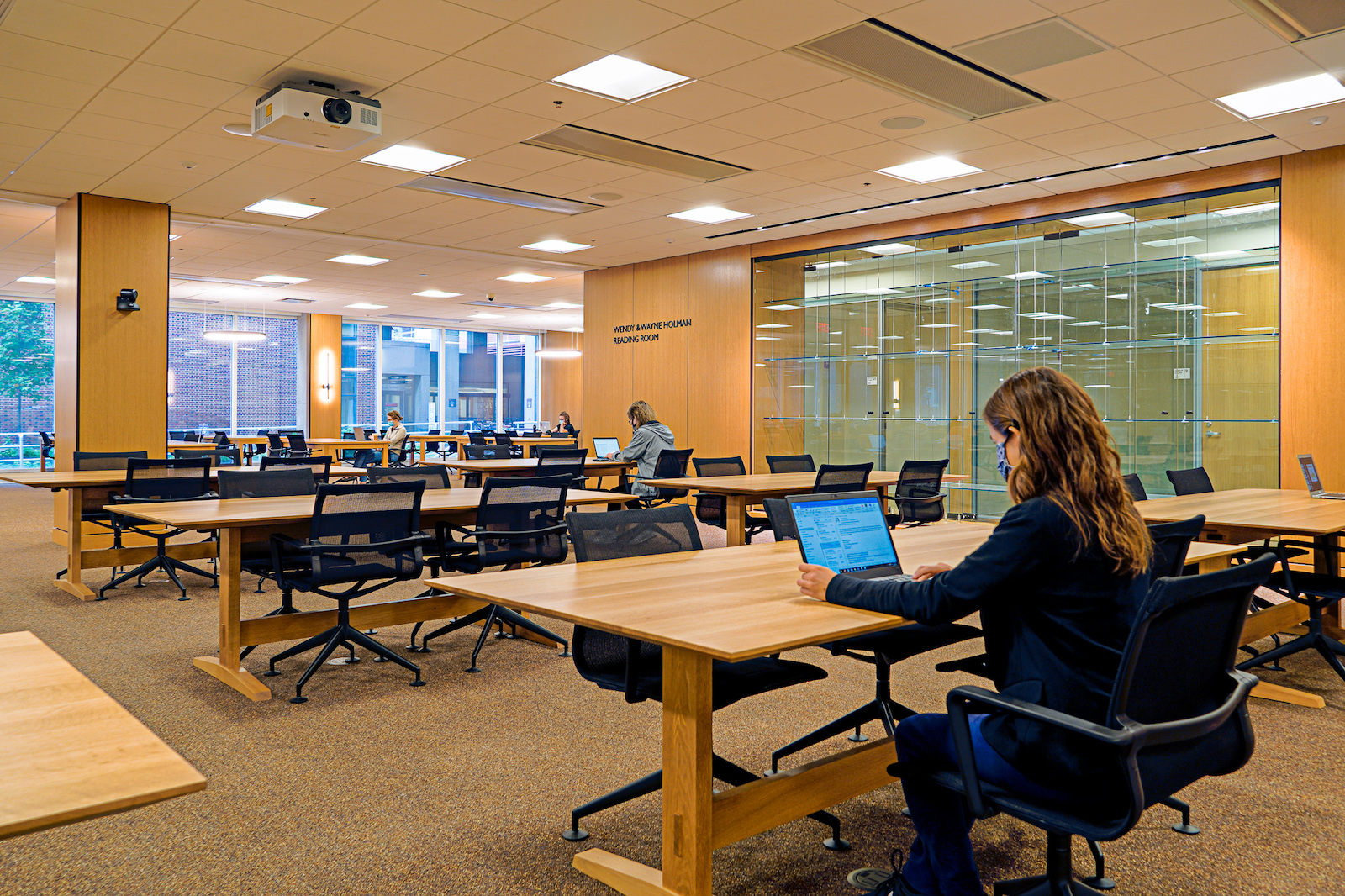
At the heart of Biotech Commons are clusters of adaptable group workspaces. Accommodating anywhere from four to 12 people, these allow students to have impromptu breakout sessions and meetings. A spacious, natural-light-filled reading room offers places for individual study. Various seating options encourage different formats of collaboration, and 20 group study rooms accommodate eight people each. The group studies are acoustically treated, allowing students to work together freely without disrupting others.
The reading room doubles as a multipurpose event space with moveable furniture; a Design Thinking Studio has wall-mounted whiteboards, supplies, and mobile, writable tables; and a Mixed Reality Lab is where faculty and students experiment with virtual and augmented reality. A conference room showcases the libraries’ historic collections. And the flexibly furnished Gershwind & Bennett Family Collaboration Classroom hosts seminars, lecture-style presentations, and active, flipped-classroom style instruction.
Most of the books in the library remained in the stacks on the lower levels, which were outside the renovation area.
Bureaucratic Stalling at the university level
The building team on this $11.5 million project included Wolfe Scott Associates (CM), Burns Engineering, and KMK Consulting (AV/IT). Voith says that about half of what is now Biotech Commons was renovated, and the other half had been used previously as shelf space for Stemmler Hall of the university’s Perelman School of Medicine. The library’s renovation had to be planned around sensitive lab space that included a basement which hosts Zebrafish aquariums with very low tolerances for sound vibration.

Before VMA came on board for this project, Penn Libraries—that oversees a network of 17 campus buildings—had conducted a feasibility study for the Biomedical Library renovation. VMA proposed several changes, including a new main entrance. Several master plans were bandied about to give the medical school, which is part of this complex, a better entrance, too. However, these changes would have put the project between $5 million and $6 million over budget, says Voith. It took another year to come up with an alternative plan that everyone agreed on.
Related Stories
Libraries | Oct 30, 2024
Reasons to reinvent the Midcentury academic library
DLR Group's Interior Design Leader Gretchen Holy, Assoc. IIDA, shares the idea that a designer's responsibility to embrace a library’s history, respect its past, and create an environment that will serve student populations for the next 100 years.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 18, 2024
7 design lessons for future-proofing academic medical centers
HOK’s Paul Strohm and Scott Rawlings and Indiana University Health’s Jim Mladucky share strategies for planning and designing academic medical centers that remain impactful for generations to come.
University Buildings | Oct 15, 2024
Recreation and wellness are bedfellows in new campus student centers
Student demands for amenities and services that address their emotional and mental wellbeing are impacting new development on college campuses that has led to recreation centers with wellness portfolios.
Higher Education | Oct 14, 2024
Higher education design for the first-gen college student
In this Design Collaborative blog, Yogen Solanki, Assoc. AIA, shares how architecture and design can help higher education institutions address some of the challenges faced by first-generation students.
University Buildings | Oct 9, 2024
Des Moines University Medicine and Health Sciences opens a new 88-acre campus
Des Moines University Medicine and Health Sciences has opened a new campus spanning 88 acres, over three times larger than its previous location. Designed by RDG Planning & Design and built by Turner Construction, the $260 million campus features technology-rich, flexible educational spaces that promote innovative teaching methods, expand research activity, and enhance clinical services. The campus includes four buildings connected with elevated pathways and totaling 382,000 sf.
University Buildings | Oct 4, 2024
Renovations are raising higher education campuses to modern standards
AEC higher ed Giants report working on a variety of building types, from performing arts centers and libraries to business schools. Hybrid learning is seemingly here to stay. And where possible, these projects address wellness and mental health concerns.
Museums | Oct 1, 2024
UT Dallas opens Morphosis-designed Crow Museum of Asian Art
In Richardson, Tex., the University of Texas at Dallas has opened a second location for the Crow Museum of Asian Art—the first of multiple buildings that will be part of a 12-acre cultural district. When completed, the arts and performance complex, called the Edith and Peter O’Donnell Jr. Athenaeum, will include two museums, a performance hall and music building, a grand plaza, and a dedicated parking structure on the Richardson campus.
Higher Education | Sep 30, 2024
Studio Gang turns tobacco warehouse into the new home of the University of Kentucky’s College of Design
Studio Gang has completed the Gray Design Building, the new home of the University of Kentucky’s College of Design. In partnership with K. Norman Berry Associates Architects, Studio Gang has turned a former tobacco warehouse into a contemporary facility for interdisciplinary learning and collaboration.
University Buildings | Sep 24, 2024
Texas Christian University opens new medical school building
The facility is designed and programmed to anticipate advances in medicine and technology.
Designers | Sep 20, 2024
The growing moral responsibility of designing for shade
Elliot Glassman, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP BD+C, CPHD, Building Performance Leader, CannonDesign, makes the argument for architects to consider better shade solutions through these four strategies.

















