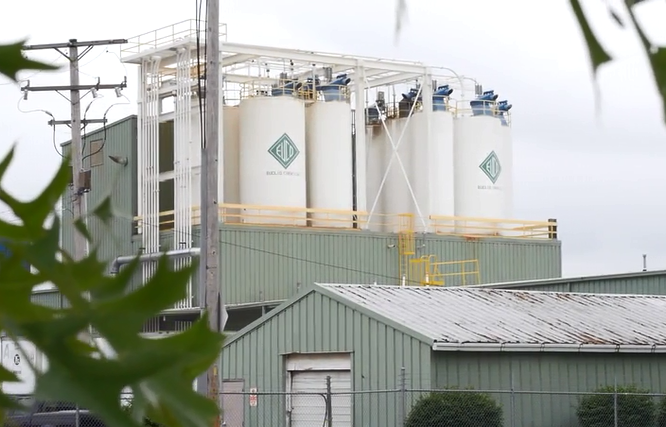
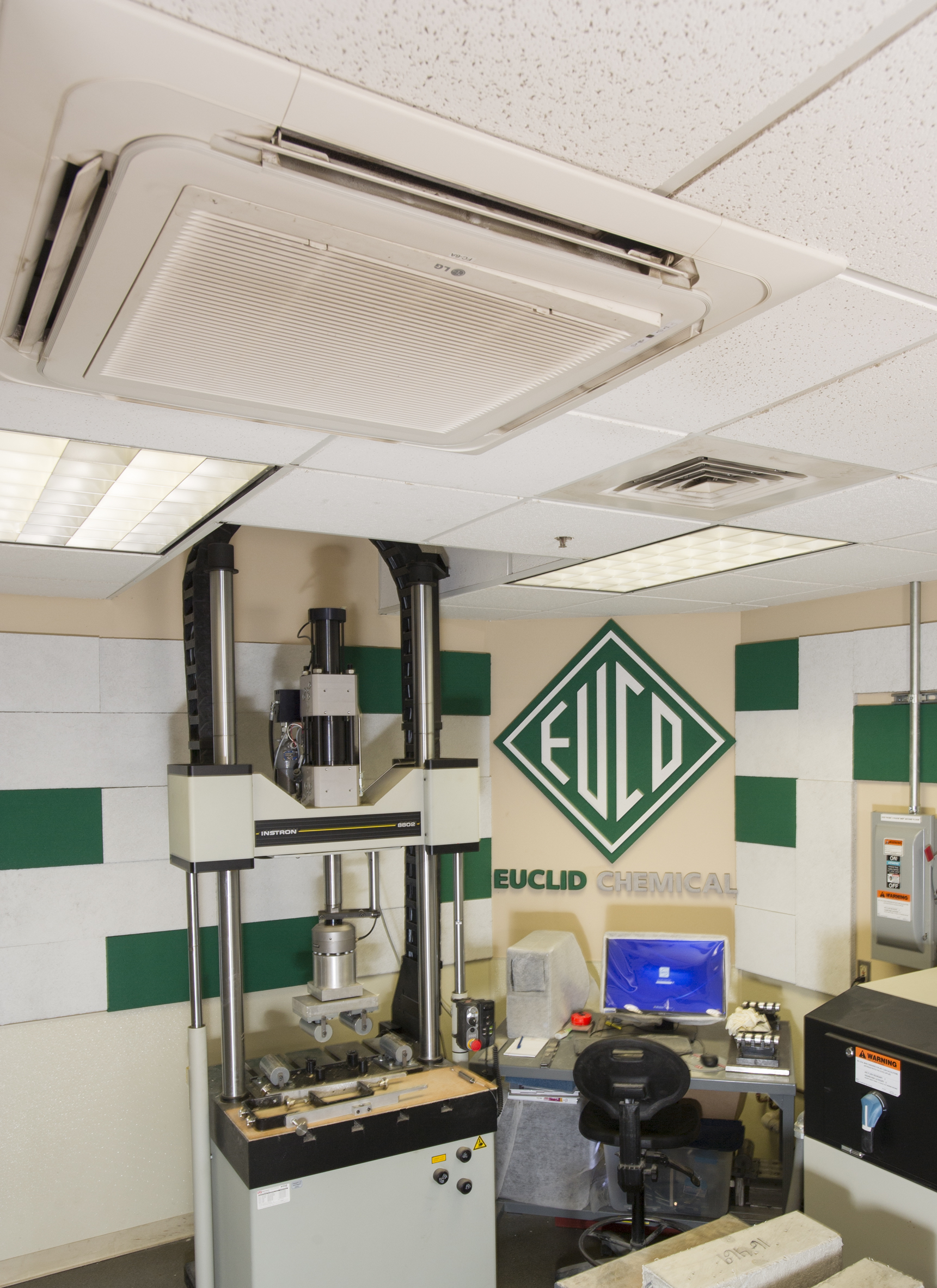
Euclid Chemical, based in Cleveland, has been supplying the construction industry with products to improve the strength, appearance, and usability of concrete since 1910. Now a large, multi-national corporation, Euclid Chemical’s main offices are in a two-story, 15,000 square foot building that also contains laboratories where they develop products ranging from sealants to micro synthetic fibers.
Until recently, the building relied upon an aging VAV system with terminal reheat to keep their offices comfortable and to maintain environmental conditions in the laboratories. Even when new, records showed the system had not performed as designed. This inadequate performance was compounded by cumulative effects of years of normal wear and tear along with questionable modifications.
Ultimately, the system no longer kept people comfortable, broke down frequently and was incredibly inefficient. After analyzing the utility bills, Joe Messer, Director of Engineering for Euclid Chemical, realized that building had an average annual energy use of 38 kWh/square foot -- over twice the average consumption for offices in the same geographic area, and more than most of Euclid’s manufacturing facilities. Messer knew Euclid Chemical needed to upgrade to a dependable and efficient system that would meet their needs for years to come.
CRITERIA:
The building housed both office areas and laboratories, so throughout the facility the system had to provide individual temperature control which, at any given time, may require both heating and cooling in different areas.
In the lab, the system also had to account for the unique challenge of quickly adapting to rapidly changing make-up air requirements as laboratory fume hoods started and stopped. It also had to work in the Ohio climate where the outdoor temperature ranged from sub-zero weather in the winter to humid high-90’s in the summer. But above all else, the system had to have a manageable upfront cost and an attractive payback to the Euclid financial team.
SOLUTION:
Messer began the process of finding a new solution and reached out to trusted engineer Andy Culberson of Geisel Heating and Cooling. Culberson identified VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) technology as the optimum solution, and reached out to Peter Eno of Refrigeration Sales Corporation to collaborate on a best-in-class solution based on VRF technology from LG Electronics. Together they designed a system around LG Multi-V heat recovery systems.

The bulky 50 ton DX unit on the roof was replaced by a pair of small air-cooled outdoor units on the ground, and the VAV boxes inside the building were replaced with LG’s concealed high-static VRF indoor units. To account for the need for ventilation air and makeup air when the laboratory fume hoods were in use, a small makeup air unit with a water heating coil was added to provide ventilation air at a high-static pressure to the LG VRF indoor units. Since this was 100 percent outdoor air, the airflow could be adjusted to precisely meet the ventilation requirements as they changed. The LG Multi V is a heat recovery system, so it can heat the zones that need it while cooling others simultaneously which delivers precise temperature in all parts of the facility regardless of Ohio’s weather, including subzero winters.
After they presented the system proposal, everyone at Euclid Chemical was sold on the concept. Based on the problems and poor performance of the existing system, Messer conservatively estimated the new system would cut their utility bills by 40 percent. What’s more, they could reuse the existing distribution and supply ductwork, reducing upfront installation costs, which further sold the financial team.
RESULTS:
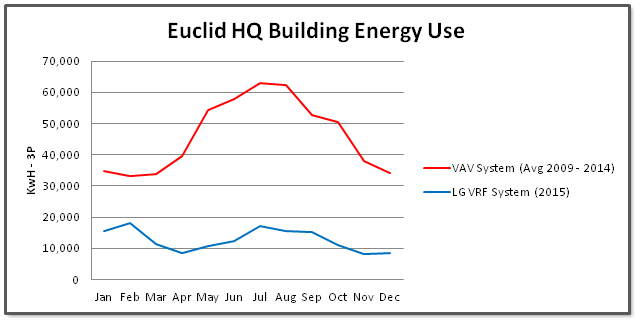
Once construction was completed, the system performance exceeded expectations, according to Messer. After implementation, the facility saw a 70 percent annual energy reduction compared to the average of the previous five years. (See graph.)
Equally important, the new system provides a quiet, comfortable environment for people to work. “Employees have definitely noticed an improvement in comfort,” said Messer. “This allowed us to focus on our core business instead of worrying about HVAC.” He is currently evaluating other buildings within the Euclid portfolio and, not surprisingly, he’s considering LG VRF solutions.
Related Stories
M/E/P Systems | Oct 30, 2024
After residential success, DOE will test heat pumps for cold climates in commercial sector
All eight manufacturers in the U.S. Department of Energy’s Residential Cold Climate Heat Pump Challenge completed rigorous product field testing to demonstrate energy efficiency and improved performance in cold weather.
Sustainable Design and Construction | Oct 10, 2024
Northglenn, a Denver suburb, opens a net zero, all-electric city hall with a mass timber structure
Northglenn, Colo., a Denver suburb, has opened the new Northglenn City Hall—a net zero, fully electric building with a mass timber structure. The 32,600-sf, $33.7 million building houses 60 city staffers. Designed by Anderson Mason Dale Architects, Northglenn City Hall is set to become the first municipal building in Colorado, and one of the first in the country, to achieve the Core certification: a green building rating system overseen by the International Living Future Institute.
Office Buildings | Sep 6, 2024
Fact sheet outlines benefits, challenges of thermal energy storage for commercial buildings
A U.S. Dept. of Energy document discusses the benefits and challenges of thermal energy storage for commercial buildings. The document explains how the various types of thermal energy storage technologies work, where their installation is most beneficial, and some practical considerations around installations.
Industrial Facilities | Aug 28, 2024
UK-based tire company plans to build the first carbon-neutral tire factory in the U.S.
ENSO, a U.K.-based company that makes tires for electric vehicles, has announced plans to build the first carbon-neutral tire factory in the U.S. The $500 million ENSO technology campus will be powered entirely by renewable energy. The first-of-its-kind tire factory aims to be carbon neutral without purchased offsets, using carbon-neutral raw materials and building materials.
Glass and Glazing | Aug 16, 2024
The next generation of thermal glazing: How improving U-value can yield energy savings and reduce carbon emissions
The standards for energy-efficient construction and design have been raised. Due to the development of advanced low-e coatings for the interior surface and vacuum insulating technologies, architects now have more choices to improve U-values wherever enhanced thermal performance is needed to create eco-friendly spaces. These options can double or even triple thermal performance, resulting in annual energy savings and a positive return on carbon.
Adaptive Reuse | Aug 14, 2024
KPF unveils design for repositioning of Norman Foster’s 8 Canada Square tower in London
8 Canada Square, a Norman Foster-designed office building that’s currently the global headquarters of HSBC Holdings, will have large sections of its façade removed to create landscaped terraces. The project, designed by KPF, will be the world’s largest transformation of an office tower into a sustainable mixed-use building.
Energy Efficiency | Aug 9, 2024
Artificial intelligence could help reduce energy consumption by as much as 40% by 2050
Artificial intelligence could help U.S. buildings to significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions, according to a paper by researchers at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Government Buildings | Aug 1, 2024
One of the country’s first all-electric fire stations will use no outside energy sources
Charlotte, N.C.’s new Fire Station #30 will be one of the country’s first all-electric fire stations, using no outside energy sources other than diesel fuel for one or two of the fire trucks. Multiple energy sources will power the station, including solar roof panels and geothermal wells. The two-story building features three truck bays, two fire poles, dispatch area, contamination room, and gear storage.
Geothermal Technology | Jul 29, 2024
Rochester, Minn., plans extensive geothermal network
The city of Rochester, Minn., home of the famed Mayo Clinic, is going big on geothermal networks. The city is constructing Thermal Energy Networks (TENs) that consist of ambient pipe loops connecting multiple buildings and delivering thermal heating and cooling energy via water-source heat pumps.
Smart Buildings | Jul 25, 2024
A Swiss startup devises an intelligent photovoltaic façade that tracks and moves with the sun
Zurich Soft Robotics says Solskin can reduce building energy consumption by up to 80% while producing up to 40% more electricity than comparable façade systems.