Euclid Chemical, based in Cleveland, has been supplying the construction industry with products to improve the strength, appearance, and usability of concrete since 1910. Now a large, multi-national corporation, Euclid Chemical’s main offices are in a two-story, 15,000 square foot building that also contains laboratories where they develop products ranging from sealants to micro synthetic fibers.
Until recently, the building relied upon an aging VAV system with terminal reheat to keep their offices comfortable and to maintain environmental conditions in the laboratories. Even when new, records showed the system had not performed as designed. This inadequate performance was compounded by cumulative effects of years of normal wear and tear along with questionable modifications.
Ultimately, the system no longer kept people comfortable, broke down frequently and was incredibly inefficient. After analyzing the utility bills, Joe Messer, Director of Engineering for Euclid Chemical, realized that building had an average annual energy use of 38 kWh/square foot -- over twice the average consumption for offices in the same geographic area, and more than most of Euclid’s manufacturing facilities. Messer knew Euclid Chemical needed to upgrade to a dependable and efficient system that would meet their needs for years to come.
CRITERIA:
The building housed both office areas and laboratories, so throughout the facility the system had to provide individual temperature control which, at any given time, may require both heating and cooling in different areas.
In the lab, the system also had to account for the unique challenge of quickly adapting to rapidly changing make-up air requirements as laboratory fume hoods started and stopped. It also had to work in the Ohio climate where the outdoor temperature ranged from sub-zero weather in the winter to humid high-90’s in the summer. But above all else, the system had to have a manageable upfront cost and an attractive payback to the Euclid financial team.
SOLUTION:
Messer began the process of finding a new solution and reached out to trusted engineer Andy Culberson of Geisel Heating and Cooling. Culberson identified VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) technology as the optimum solution, and reached out to Peter Eno of Refrigeration Sales Corporation to collaborate on a best-in-class solution based on VRF technology from LG Electronics. Together they designed a system around LG Multi-V heat recovery systems.

The bulky 50 ton DX unit on the roof was replaced by a pair of small air-cooled outdoor units on the ground, and the VAV boxes inside the building were replaced with LG’s concealed high-static VRF indoor units. To account for the need for ventilation air and makeup air when the laboratory fume hoods were in use, a small makeup air unit with a water heating coil was added to provide ventilation air at a high-static pressure to the LG VRF indoor units. Since this was 100 percent outdoor air, the airflow could be adjusted to precisely meet the ventilation requirements as they changed. The LG Multi V is a heat recovery system, so it can heat the zones that need it while cooling others simultaneously which delivers precise temperature in all parts of the facility regardless of Ohio’s weather, including subzero winters.
After they presented the system proposal, everyone at Euclid Chemical was sold on the concept. Based on the problems and poor performance of the existing system, Messer conservatively estimated the new system would cut their utility bills by 40 percent. What’s more, they could reuse the existing distribution and supply ductwork, reducing upfront installation costs, which further sold the financial team.
RESULTS:
Once construction was completed, the system performance exceeded expectations, according to Messer. After implementation, the facility saw a 70 percent annual energy reduction compared to the average of the previous five years. (See graph.)
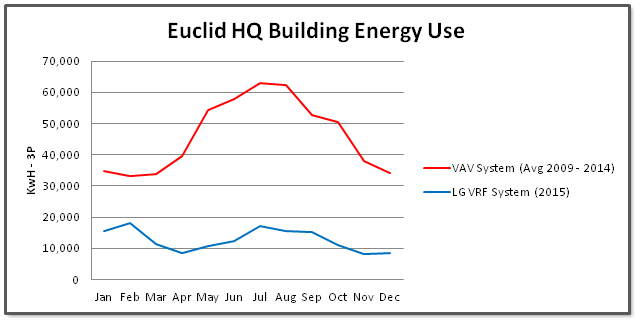
Equally important, the new system provides a quiet, comfortable environment for people to work. “Employees have definitely noticed an improvement in comfort,” said Messer. “This allowed us to focus on our core business instead of worrying about HVAC.” He is currently evaluating other buildings within the Euclid portfolio and, not surprisingly, he’s considering LG VRF solutions.
Related Stories
| Jun 1, 2011
Low-energy fans help combat disease in Rwandan clinic
Isis fans from Big Ass Fan Co. help kill airborne pathogens in Rwanda’s Butaro Health Clinic by passing air over UV lights.
| May 25, 2011
Smithsonian building $45 million green lab
Thanks to a $45 million federal appropriation to the Smithsonian Institution, the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center in Edgewater, Md., has broken ground on what is expected to be one of the most energy-efficient laboratories in the country. The 69,000-sf lab is targeting LEED Gold and is expected to use 37% less energy and emit 37% less carbon dioxide than a similar building.
| May 18, 2011
Former Bronx railyard redeveloped as shared education campus
Four schools find strength in numbers at the new 2,310-student Mott Haven Campus in New York City. The schools—three high schools and a K-4 elementary school—coexist on the 6.5-acre South Bronx campus, which was once a railyard.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
| May 16, 2011
Seattle unveils program to boost building efficiency
Seattle launched a new program that will help commercial property owners and managers assess and improve building energy efficiency. Under the program, all commercial and multifamily buildings larger than 10,000 sq. ft. will be measured for their energy performance using the EPA’s ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager.
| May 11, 2011
DOE releases guide for 50% more energy-efficient office buildings
The U.S. Department of Energy today announced the release of the first in a new series of Advanced Energy Design Guides to aid in the design of highly energy efficient office buildings. The 50% AEDG series will provide a practical approach to commercial buildings designed to achieve 50% energy savings compared to the commercial building energy code used in many areas of the country.












