Euclid Chemical, based in Cleveland, has been supplying the construction industry with products to improve the strength, appearance, and usability of concrete since 1910. Now a large, multi-national corporation, Euclid Chemical’s main offices are in a two-story, 15,000 square foot building that also contains laboratories where they develop products ranging from sealants to micro synthetic fibers.
Until recently, the building relied upon an aging VAV system with terminal reheat to keep their offices comfortable and to maintain environmental conditions in the laboratories. Even when new, records showed the system had not performed as designed. This inadequate performance was compounded by cumulative effects of years of normal wear and tear along with questionable modifications.
Ultimately, the system no longer kept people comfortable, broke down frequently and was incredibly inefficient. After analyzing the utility bills, Joe Messer, Director of Engineering for Euclid Chemical, realized that building had an average annual energy use of 38 kWh/square foot -- over twice the average consumption for offices in the same geographic area, and more than most of Euclid’s manufacturing facilities. Messer knew Euclid Chemical needed to upgrade to a dependable and efficient system that would meet their needs for years to come.
CRITERIA:
The building housed both office areas and laboratories, so throughout the facility the system had to provide individual temperature control which, at any given time, may require both heating and cooling in different areas.
In the lab, the system also had to account for the unique challenge of quickly adapting to rapidly changing make-up air requirements as laboratory fume hoods started and stopped. It also had to work in the Ohio climate where the outdoor temperature ranged from sub-zero weather in the winter to humid high-90’s in the summer. But above all else, the system had to have a manageable upfront cost and an attractive payback to the Euclid financial team.
SOLUTION:
Messer began the process of finding a new solution and reached out to trusted engineer Andy Culberson of Geisel Heating and Cooling. Culberson identified VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) technology as the optimum solution, and reached out to Peter Eno of Refrigeration Sales Corporation to collaborate on a best-in-class solution based on VRF technology from LG Electronics. Together they designed a system around LG Multi-V heat recovery systems.

The bulky 50 ton DX unit on the roof was replaced by a pair of small air-cooled outdoor units on the ground, and the VAV boxes inside the building were replaced with LG’s concealed high-static VRF indoor units. To account for the need for ventilation air and makeup air when the laboratory fume hoods were in use, a small makeup air unit with a water heating coil was added to provide ventilation air at a high-static pressure to the LG VRF indoor units. Since this was 100 percent outdoor air, the airflow could be adjusted to precisely meet the ventilation requirements as they changed. The LG Multi V is a heat recovery system, so it can heat the zones that need it while cooling others simultaneously which delivers precise temperature in all parts of the facility regardless of Ohio’s weather, including subzero winters.
After they presented the system proposal, everyone at Euclid Chemical was sold on the concept. Based on the problems and poor performance of the existing system, Messer conservatively estimated the new system would cut their utility bills by 40 percent. What’s more, they could reuse the existing distribution and supply ductwork, reducing upfront installation costs, which further sold the financial team.
RESULTS:
Once construction was completed, the system performance exceeded expectations, according to Messer. After implementation, the facility saw a 70 percent annual energy reduction compared to the average of the previous five years. (See graph.)
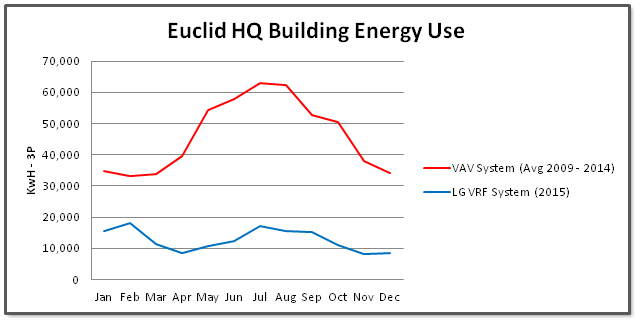
Equally important, the new system provides a quiet, comfortable environment for people to work. “Employees have definitely noticed an improvement in comfort,” said Messer. “This allowed us to focus on our core business instead of worrying about HVAC.” He is currently evaluating other buildings within the Euclid portfolio and, not surprisingly, he’s considering LG VRF solutions.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Pella introduces BIM models for windows and doors
Pella Corporation now offers three-dimensional (3D) window and door models for use in Building Information Modeling (BIM) projects by architects, designers, and others looking for aesthetically correct, easy-to-use, data-rich 3D drawings.
| Aug 11, 2010
Draft NIST report on Cowboys practice facility collapse released for public comment
A fabric-covered, steel frame practice facility owned by the National Football League’s Dallas Cowboys collapsed under wind loads significantly less than those required under applicable design standards, according to a report released today for public comment by the Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
| Aug 11, 2010
ASHRAE releases free BIM introductory guide
A newly released guide from ASHRAE on building information models and building information modeling (BIM) serves as a resource for professionals considering BIM tools and applications for their businesses. According to "An Introduction to Building Information Modeling," BIM is “a digital representation of the physical and the functional characteristics of a facility.” Unlike 2D or 3D CAD, BIM software utilizes intelligent objects to create models.
| Aug 11, 2010
An Innovative Energy-Absorbing Anti-Terrorism Crash Barrier for Homeland Security
Anti-terrorism physical barrier techniques and applications have become highly desired to protect critical facilities and human lives in recent years. Based on in-depth review and practices, the systemic criteria are proposed here for selection of security barriers specifically against terrorist attacks with truck-borne explosives.
| Aug 11, 2010
NoricF4 custom metal ICF frames receive fire ratings, comply with antiterrorism standards for buildings
Reward Wall Systems' NoricF4 Custom Metal ICF Frames have received fire ratings of 1.5 hours to 3 hours and they have been evaluated to be in compliance with the prescriptive requirements of the Department of Defense Minimum Antiterrorism Standards for Buildings for blast/force protection.
| Aug 11, 2010
Embassy's dual façades add security and beauty
The British government's new 46,285-sf embassy building in Warsaw, Poland's diplomatic quarter houses the ambassador's offices, the consulate, and visa services on three floors. The $20 million Modernist design by London-based Tony Fretton Architects features a double façade—an inner concrete super structure and an outer curtain wall.
| Aug 11, 2010
Cost of HVAC equipment to remain flat in 2009, says Turner
While some manufacturers have announced slight increases in facilities equipment pricing for 2009, the average cost of equipment is expected to remain flat in 2009, according to the 2009 Turner Logistics Equipment Cost Index. However, equipment pricing could face increased pressure if there is a further decline in market demand.
| Aug 11, 2010
Toronto mandates green roofs
The city of Toronto late last month passed a new green roof by-law that consists of a green roof construction standard and a mandatory requirement for green roofs on all classes of new buildings. The by-law requires up to 50% green roof coverage on multi-unit residential dwellings over six stories, schools, nonprofit housing, and commercial and industrial buildings.







