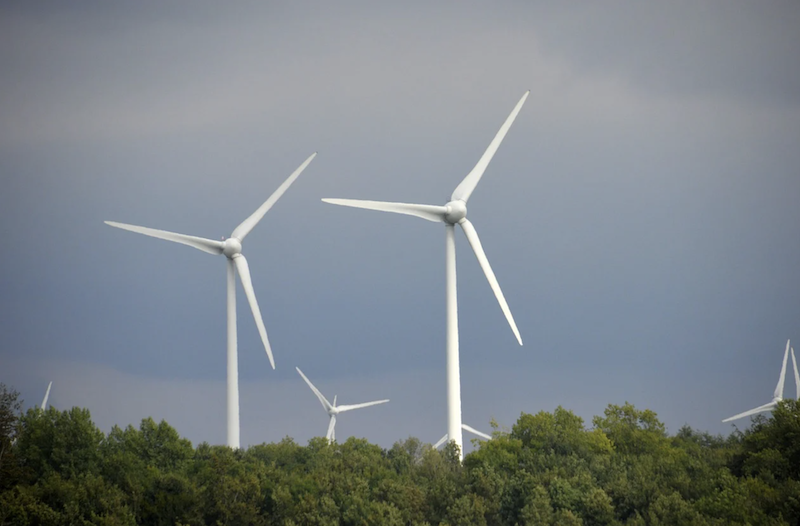
The U.S. electric grid is making significant progress to zero-carbon status, according to a report from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Greenhouse-gas emissions from the electricity sector last year were 52% lower in 2020 than the U.S. Energy Information Administration predicted they would be back in 2005, the report says. Power-sector emissions fell 40% from 2005 to 2020, with much of the drop driven by cheap natural gas supplanting coal as the dominant fuel for U.S. power plants.
Further emissions cuts will require greater adoption of clean technologies such as energy storage, and that is achievable with the declining cost of solar and wind power generation, and battery storage, the report says. Low-carbon resources could reliably meet as much as 70%–90% of power supply needs at low incremental cost.
Other sectors, including the built environment, have made less progress in cutting emissions. Residential building emissions declined 29% from 2005 to 2020. Commercial building emissions dipped 32% during the same period.
Grid-interactive efficient buildings could help to make the grid more efficient by reducing the need for new supply and delivery infrastructure and providing another form of demand flexibility.
Related Stories
| Sep 14, 2012
To create more pedestrian-friendly neighborhoods, Chicago unveils safety plan
As more urban mixed-use and residential developments aim to encourage residents to walk and use mass transit, cities are addressing pedestrian safety.
| Sep 14, 2012
Worker killed in Brooklyn building collapse; overloaded floor decking blamed
One worker was killed after he and others plunged 40 feet through an unfinished upscale Brooklyn townhouse building.
| Sep 14, 2012
NRCA University offers photovoltaic class
NRCA University will offer a class called “Photovoltaic Roof Systems: Energizing Your Business” Oct. 16 in Philadelphia.
| Sep 14, 2012
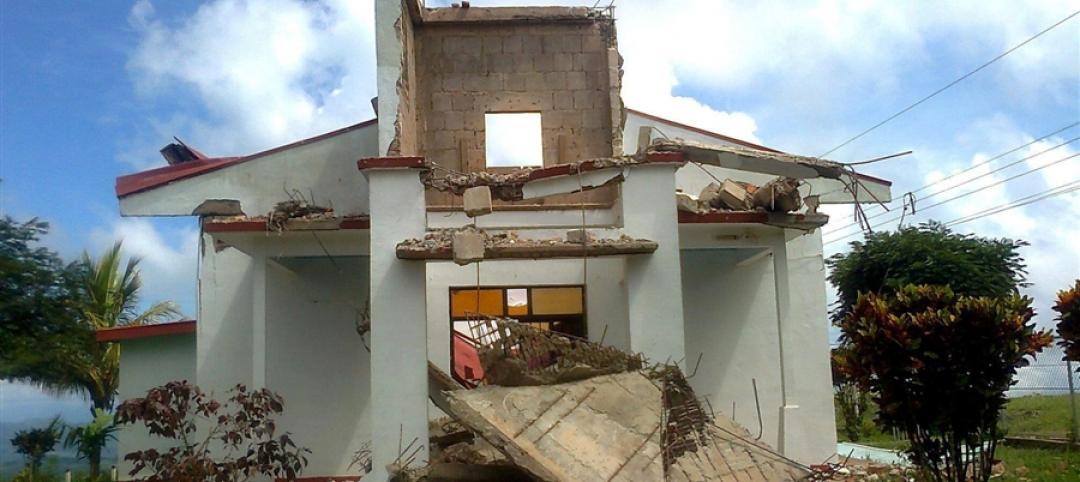
Costa Rica’s strict building codes prevent major damage in powerful quake
The relatively little damage from a 7.6 earthquake was due in large part to strict building codes in Costa Rica, a country that has long enjoyed more stability, better governance, and stronger economic development than many of its Central American neighbors.
| Sep 14, 2012
Building codes should require continuous connection from roof to foundation, says IBHS chief
“One of the most effective ways to greatly increase a building’s strength and safety during hurricanes, tornadoes and straight-line windstorms is to be sure the building is tied together properly,” says Julie Rochman, president and CEO of the Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety (IBHS).
| Sep 7, 2012
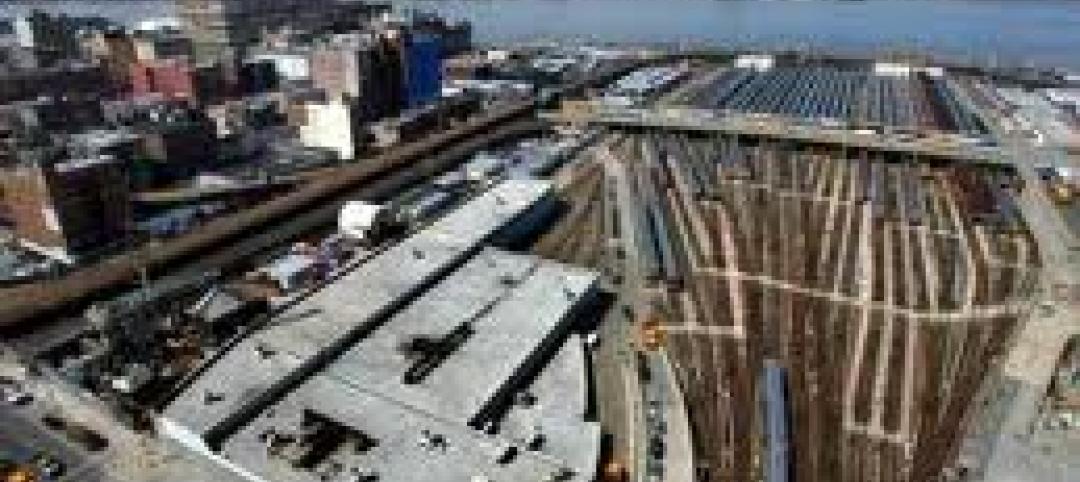
Related Companies and unions agree to wage-cutting deal on Hudson Yards
The Related Companies has won wage-cutting agreements with four dozen construction unions in its efforts to save money on the $15 billion development of Hudson Yards.
| Sep 7, 2012
Lorain, Ohio considers halting downtown construction while it works out development plan
Construction would stop downtown for six months while Lorain, Ohio officials consider a development plan for the city, according to new legislation.
| Sep 7, 2012
Business, labor groups push for easing of California’s Environmental Quality Act
Business and labor groups have combined forces to push for a change to California's Environmental Quality Act, specifically its complex review process for building and construction projects.
| Sep 7, 2012
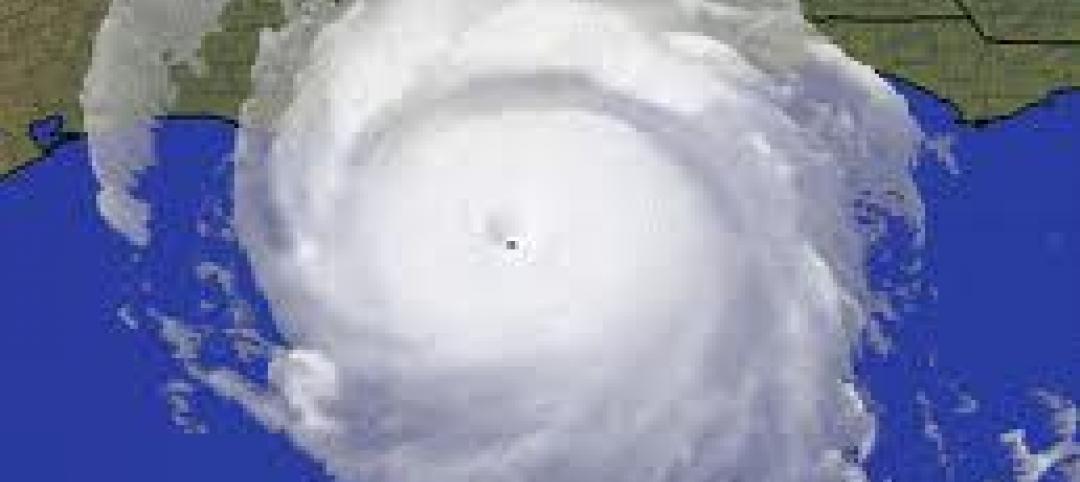
Twenty years later, Florida contractors cite Hurricane Andrew as construction game-changer
Remarking on the 20th anniversary of Hurricane Andrew, which devastated south Florida; contractors are noting the storm’s impact on their industry—including the state’s adoption of tougher building codes.
| Sep 7, 2012
At risk for nine types of natural disasters, Texas trails most coastal states on building codes
Texas has the most diverse weather risk in the country, with exposure to nine different types of natural disasters.