The U.S. Energy Information Administration has posted preliminary results from its periodic Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption survey. Data for the project were collected in 2012 and detailed analyses of energy consumption will be released beginning next spring. The project includes buildings >1,000 sf that devote more than half of their floorspace to activity that is not residential, manufacturing, industrial, or agricultural.
The preliminary results from the Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey (CBECS) show that there were 5.6 million commercial buildings in the United States in 2012, comprising 87.4 billion square feet of floorspace. This represents a 14% increase in the number of buildings and a 22% increase in floorspace since 2003, the last year for which CBECS results are available.
The preliminary data can be found in this summary table of building counts and total square footage by building size category, principal building activity, year of construction category, Census region, and Census division. The first tab provides the estimates; the second tab on the table provides relative standard errors (RSEs) for the estimates.
For comparison, there is a similar summary table from the 2003 CBECS. Other file formats for the same table can be accessed from the 2003 CBECS data page.
The size, use, vintage, and geographic region of a building are among the key determinants that influence its energy use. Subsequent releases will show more detailed characteristics and crosstabulations among key categories. This is the first release of many reports and data releases expected for the 2012 CBECS; these preliminary tables provide a first look at the building stock and the attributes that drive commercial energy use.
Trends – 1979 to 2012: Growth in building size outpaces increases in building stock
Since the first CBECS was conducted in 1979 to the current 2012 CBECS, the number of buildings has increased from 3.8 million to 5.6 million, and the amount of commercial floorspace has increased from 51 billion to 87 billion square feet.

HOW DOES EIA PRODUCE RELIABLE RESULTS FROM A SAMPLE SURVEY?
The CBECS is a national sample survey. See How Were Buildings Selected for the 2012 CBECS? for an overview of the sampling process. After the sample was selected, preparations for the interviewing phase began. In April 2013, about 250 field interviewers were trained to visit buildings across the United States and recruit respondents knowledgeable about energy use in the buildings. After recruiting a respondent at a building, the field interviewer’s job was to conduct an interview on a laptop computer asking questions about the building’s structure, use, energy equipment, and energy use. Between April and November 2013, interviews were conducted in-person or by telephone at over 6,500 buildings nationwide. Because every building had a chance to be selected and that chance is known, a sample weight can be assigned to each case. The resulting dataset is representative of the entire U.S. commercial building population.
Principal building activities: The most prevalent building types account for the majority of the total buildings and floorspace, while the building types with the largest average buildings are less common in the building stock
The commercial building sector is characterized by diversity. The 2012 survey identified more than 100 subcategories of building activity, which are aggregated into the 14 principal building activities shown in the summary table and in the figures below. CBECS includes buildings as small and singular in activity as a freestanding bank or fast food restaurant, to buildings as large and complex as an office building with hundreds of tenants or a major airport terminal. CBECS also includes vacant buildings; some vacant buildings use energy, either for maintenance purposes or because a small amount of space is still used in the building1.

Among the general building activities, lodging, education, and health care are the largest buildings, on average. The health care category's average is greatly affected by the size of inpatient health care buildings (i.e., hospitals), which have an average size of 247,700 square feet per building, compared to outpatient health care buildings, which have an average size of 12,100 square feet.

Figure 4 tracks changes in the building stock over the past 10 years by comparing the number of buildings for each principal building activity from 2003 to 2012. The highest percent of growth was in vacant buildings and other types of buildings, which includes buildings such as airplane hangars, laboratories and data centers. Warehouses, food service buildings, public assembly, and office buildings also increased between 2003 and 2012, while food sales buildings (e.g., grocery and convenience stores) showed a decrease,2 and mercantile (retail and malls) showed a decrease, although it is not statistically significant. Because CBECS is a sample survey, each estimate has sampling error associated with it, which should be considered when comparing estimates. See What is an RSE? and Estimation of Standard Errors for more information.

Size of buildings: Although there are relatively few very large buildings (over 100,000 square feet of floorspace), they account for more than one-third of total commercial building floorspace
Commercial buildings are often depicted showing a skyline of towering buildings. However, the vast majority of commercial buildings are relatively small. Just less than half of buildings are 5,000 square feet in size or smaller, and nearly three-fourths are 10,000 square feet or smaller. The median building size is 5,100 square feet (i.e., half the buildings are larger than this and half are smaller), while the average size is 15,700 square feet. The average is larger than the median because of the influence of a small number of very large buildings; buildings over 100,000 square feet make up only about 2% of the building count but about 35% of the total floorspace.

Year constructed: The commercial building stock is middle-aged, and newer buildings are larger than older ones
Commercial buildings remain in use for many decades. Although about 12% of commercial buildings (comprising 14% of commercial floorspace) were built in the past 10 years, the commercial building stock is still fairly old, with about half of all buildings constructed at least 35 years ago. However, in the existing building stock, there are more buildings built in the 2000s than buildings built prior to 1946.

Newer buildings tend to be larger than older buildings. The average building size for those constructed before 1960 is 12,000 square feet; buildings constructed between 1960 and 1999 average 16,300 square feet; and buildings constructed in the 2000s average 19,100 square feet. The differences between these average building sizes are statistically significant.

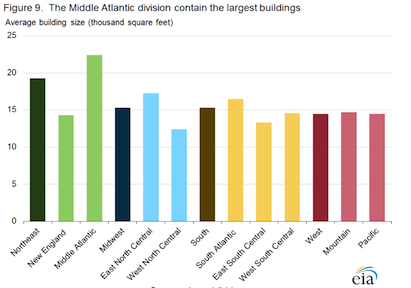
Census region and division (see map): The South has the most commercial buildings, but the Northeast has the largest commercial buildings
The South Census region, the most populous of the four Census regions, has the largest percentage of commercial buildings and commercial floorspace, with about 40% of both total buildings and floorspace. The Midwest and West regions each account for more than one-fifth of commercial buildings and floorspace.

Buildings in the Northeast region are, on average, 4,000 to 5,000 square feet larger than buildings in the other regions. The Northeast region includes the Middle Atlantic division (New York, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey), where buildings average 22,400 square feet.

Footnote
1 CBECS principal building activity is defined as the activity occupying the most floorspace. Respondents are first asked if there is one activity that occupies 75% or more of the floorspace. If not, CBECS collects the top three building activities and their corresponding percents and the principal activity is assigned as the one comprising the most floorspace.
2 Estimates for number of food sales buildings can be somewhat misleading because grocery stores and convenience stores are often part of strip malls and therefore included in the "Enclosed and strip malls" category in CBECS. "Enclosed and strip malls" is a subcategory of "Mercantile" and is shown in the summary table.
Specific questions on this product may be directed to Joelle Michaels.
Related Stories
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Women in Design+Construction | Mar 21, 2023
Two leading women in construction events unite in 2023
The new Women in Residential + Commercial Construction Conference (WIR+CC) will take place in Nashville, Tenn., October 25-27, 2023. Combining these two long-standing events aligns with our mission to create an event most impactful for women in the $1.4 trillion U.S. commercial and residential design and construction industry.
Mass Timber | Mar 19, 2023
A 100% mass timber construction project is under way in North Carolina
An office building 100% made from mass timber has started construction within the Live Oak Bank campus in Wilmington, N.C. The 67,000-sf structure, a joint building venture between the GCs Swinerton and Wilmington-headquartered Monteith Construction, is scheduled for completion in early 2024.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 17, 2023
Aurora, Colo., recreation center features city’s first indoor field house, unobstructed views of the Rocky Mountains
In January, design firm Populous and the City of Aurora, Colo. marked the opening of the Southeast Aurora Recreation Center and Fieldhouse. The 77,000-sf facility draws design inspiration from the nearby Rocky Mountains. With natural Douglas Fir structure and decking, the building aims to mimic the geography of a canyon.
Architects | Mar 16, 2023
HKS launches partner diversity program to create a more diverse workforce and partnership network
Design firm HKS has launched a new partner diversity program that will work to build a more diverse AEC ecosystem. The HKS xBE program will give xBE firms (a term encompassing all disadvantaged businesses) and their members “access to opportunities to build relationships, pursue new work, and bolster innovation within the architecture and design professions,” according to HKS.
Sustainability | Mar 16, 2023
Lack of standards for carbon accounting hamper emissions reduction
A lack of universally accepted standards for collecting, managing, and storing greenhouse gas emissions data (i.e., carbon accounting) is holding back carbon reduction efforts, according to an essay published by the Rocky Mountain Institute.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
Georgia State University Convocation Center revitalizes long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood
Georgia State University’s new Convocation Center doubles the arena it replaces and is expected to give a shot in the arm to a long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood. The new 200,000 sf multi-use venue in the Summerhill area of Atlanta is the new home for the university’s men’s and women’s basketball teams and will also be used for large-scale academic and community events.
Sponsored | Cladding and Facade Systems | Mar 15, 2023
Metal cladding trends and innovations
Metal cladding is on a growth trajectory globally. This is reflected in rising demand for rainscreen cladding and architectural metal coatings. This course covers the latest trends and innovations in the metal cladding market.
Education Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
DLR Group’s Campus Planning Studio defines new leadership
Linsey Graff named Campus Planning Leader. Krisan Osterby transitions to Senior Planner.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.