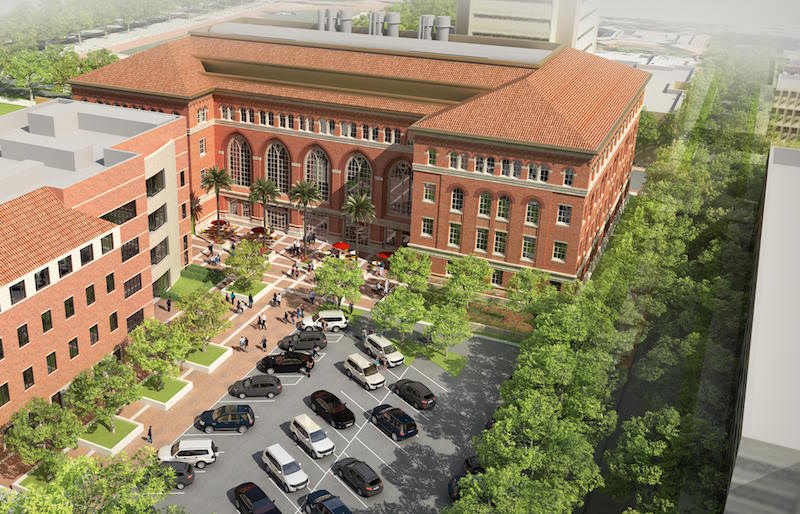
The University of Southern California (USC) has scheduled a November 1 dedication ceremony for the Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience, which at 190,000 sf is the largest academic building on the university’s Pasadena campus.
The Center will provide lab and research facilities for USC’s engineering, arts & sciences, and medical schools. The goal of the Center, according to USC, is to “fast-track detection and cure of diseases by turning biological sciences into a quantitative and predictive science.”
Over several months following the dedication, 300 people will move in. And while only 58% of the lab space has been fitted out for specific use, the infrastructure is in place and the future costs have already been accounted for the eventual fitting out of the unoccupied space, whomever the user.
More important, Michelson is designed, engineered, and constructed with an eye toward space flexibility and the accommodation of whatever equipment might need to be installed in the future, according to Alton Parks, the senior project manager. The hope, too, is that the design provokes interdisciplinary interaction.
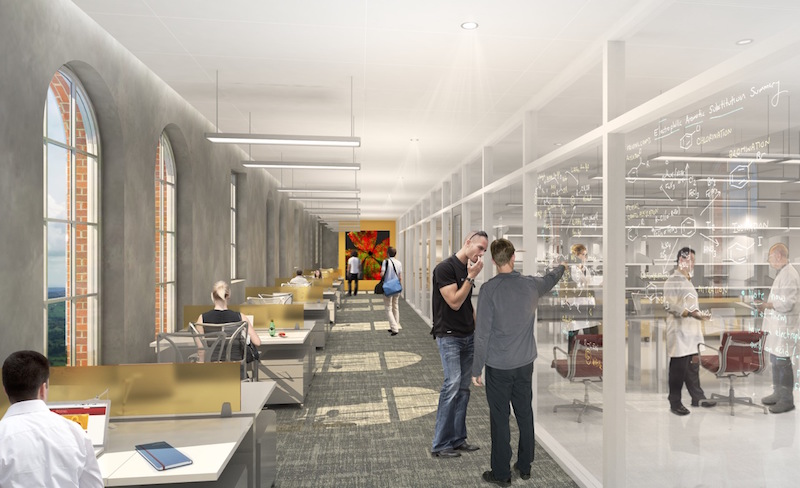

Glass walls surround the lab spaces within the Michelson Center, so that occupants can see what their coworkers are doing. The design goal is to encourage interdisciplinary “collision.” Image: USC
HOK is this project’s Executive Architect, Vanderweil Engineers its MEP/FP engineer, and DPR is GC. Construction costs were not disclosed, but in 2014 Dr. Gary K. Michelson—an orthopedic spinal surgeon who made his fortune developing implants, surgical procedures, and instruments—and his wife, Alya, donated $50 million to fund the Center.
The barbell-shaped building has labs at both ends. Right now, the engineering school takes up most of the lab space on the third and fourth floors of the building’s south end. But many of the Center’s unoccupied labs remain unfinished—literally no ceilings, just enough HVAC to meet code—so as not to hamstring any of the schools’ recruitment efforts.
“Fitouts are kind of a shell game, because you really don’t know who’s going to move in,” explained Parks.
Budget cutbacks did not impact the building’s infrastructure, said Parks, which includes 189 miles of wiring, 1 million pounds of ductwork, and is designed for a total of 80 fume hoods.
The Center, which meets California’s Title 24 energy codes, includes an air-handling system that can deliver air over any area of the building, at whatever air-exchange rate is called for. The HVAC system also has the flexibility to service “the outer limits of machines themselves, to their maximum capacity forever,” said Parks.
The Center aggregates several departments that had been spread across campus, and is designed, said Parks, to encourage “collision” among different academic disciplines within the building.
“We needed to do something about silo-ing,” said Parks. So the central areas of the building include conferences rooms on the second and fourth floors. The third floor is dominated by a large central social space called “the living room” that has varied seating, huddle and meeting rooms, and a 22-ft-long community table in the middle. This central space is supported by a kitchen/pantry with refrigerators, vending machines, and sinks.
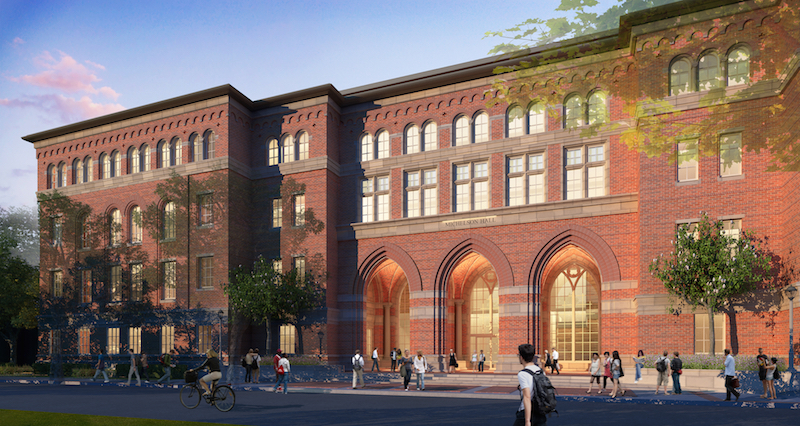

More than 250,000 bricks were used for the exterior facade of the Michelson Center, which also includes 312 exterior windows and doors. Image: USC
The goal, explained Parks, is to get people working within the building’s north and south wings to mingle and talk on a regular basis in the middle of the Center. There are lots of glass walls throughout, so people working in the building can see what’s going on along its north-south and east-west circulation axes. Interactive video screens adorn the west wall. “Monumental stairs” in front of the building’s entries are meant to stimulate human movement between floors.
Furniture can contribute to convergence, too, said Parks. Two people can work together at the rise-up desks throughout the building. And the Center is the first science building to install a new piece of furniture, designed by Herman Miller, which is kind of a pop-up office: The freestanding, conical module, stationed in the hallways, includes a round table, marker boards, and seating for four or five people. Its curved design dissipates sound.
“This furniture synchronizes with Michelson’s [convergent] intent,” said Parks.
Related Stories
University Buildings | May 5, 2023
New health sciences center at St. John’s University will feature geothermal heating, cooling
The recently topped off St. Vincent Health Sciences Center at St. John’s University in New York City will feature impressive green features including geothermal heating and cooling along with an array of rooftop solar panels. The geothermal field consists of 66 wells drilled 499 feet below ground which will help to heat and cool the 70,000 sf structure.
Mass Timber | May 1, 2023
SOM designs mass timber climate solutions center on Governors Island, anchored by Stony Brook University
Governors Island in New York Harbor will be home to a new climate-solutions center called The New York Climate Exchange. Designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM), The Exchange will develop and deploy solutions to the global climate crisis while also acting as a regional hub for the green economy. New York’s Stony Brook University will serve as the center’s anchor institution.
University Buildings | Apr 24, 2023
Solving complicated research questions in interdisciplinary facilities
University and life science project owners should consider the value of more collaborative building methods, close collaboration with end users, and the benefits of partners who can leverage sector-specific knowledge to their advantage.
Green | Apr 21, 2023
Top 10 green building projects for 2023
The Harvard University Science and Engineering Complex in Boston and the Westwood Hills Nature Center in St. Louis are among the AIA COTE Top Ten Awards honorees for 2023.
Higher Education | Apr 13, 2023
Higher education construction costs for 2023
Fresh data from Gordian breaks down the average cost per square foot for a two-story college classroom building across 10 U.S. cities.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
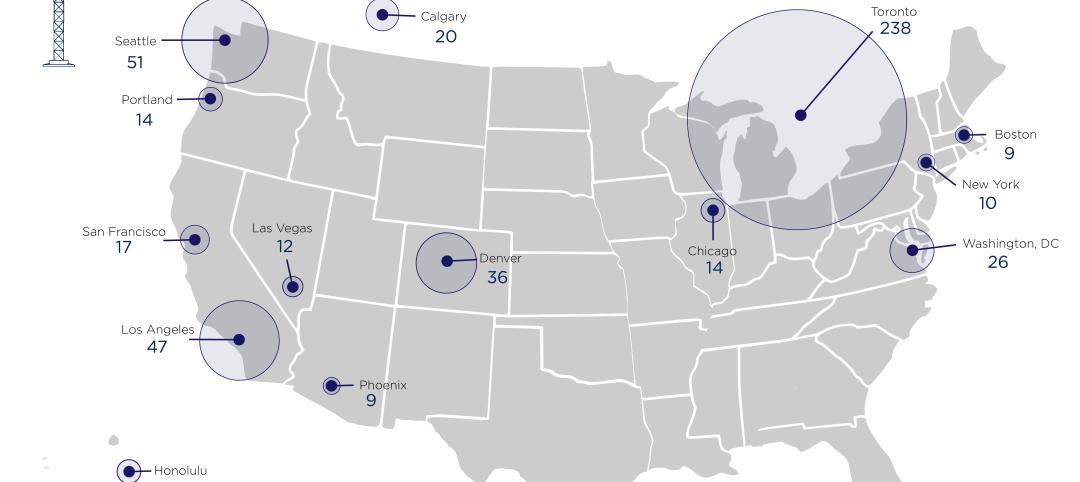
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
University Buildings | Apr 11, 2023
Supersizing higher education: Tracking the rise of mega buildings on university campuses
Mega buildings on higher education campuses aren’t unusual. But what has been different lately is the sheer number of supersized projects that have been in the works over the last 12–15 months.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
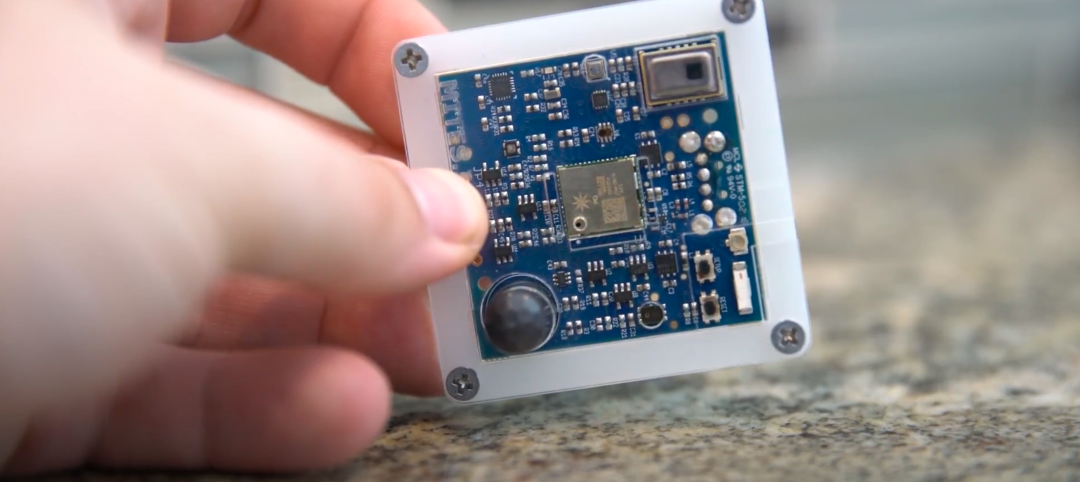
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.