I am an architect. I am also a woman of color.
As a brown woman, and now a citizen who emigrated to the United States from India 17 years ago, the recent unrest in our country following the death of George Floyd has made me pause and think about the role of architecture and architects in building a world that not only encourages but demands equity through design.
I was reminded of that day almost two decades ago when I made the 9,000-mile journey from my home in Thiruvananthapuram, the capital of the southwestern state of Kerala, to San Francisco with my younger sister in tow. My mother, who had always been my biggest champion, passed away when I was 15; my father – recently retired from the Indian army – had remarried and was living in San Francisco with my new stepmother and stepsiblings.
As a 19-year-old in charge of a 14-year-old, travelling across continents, I was anxious about all the layovers and connections I had to make, nervous about misplacing the $100 bill my father had entrusted me with, afraid of ordering the wrong meals and drinks on the flight, curious about my new family, but most of all excited about new beginnings. I didn’t stop to consider things like my accent, the color of my skin, the way that I pronounced certain words (my Vs have always sounded like Ws), and my minimal knowledge of American culture.
'I HAD OPPORTUNITIES, AN EDUCATION, A CAREER'
I have been fortunate, even with my differences, to avoid the depth of discrimination so many in this country face. I had opportunities that not everyone does. My parents worked hard to make sure we had comfortable lives and were able to pay for college, even if it meant we had to work hard for scholarships and supplement their contributions with employment while we attended school. Having studied English in schools in India, my transition into American life was smoother than for many who immigrate to this country. I had an education that led me toward a career in architecture, one that is fulfilling and allows great vertical growth. Not everyone is as fortunate.
Even with all the benefits I had, I continued to confront and stand up against the multitude of insidious forms of discrimination – in India and here in the U.S. In India where fairer complexioned women are sought out for marriage, it was the color of my skin. Being naturally darker in complexion, I can still remember the snide comments comparing me to my fairer sister. In India, my independence as a woman was seen as an affront to the patriarchal system that still rears its ugly head. In the U.S., I initially ignored the seemingly small but telling instances of sexism and ageism, later vowing to stand up against it. But I never experienced racism.
As we speak of the systemic racism against minorities in our country, let us consider the true meaning of humanity: our ability to love, show compassion, and use creativity to advance the human race. Every one of us can express this humanity in many different ways. I express mine through my profession.
ARCHITECTURE AS 'A PLACE OF HUMANITY'
Throughout history, the one thing architecture has always represented is a place of humanity. Architects and engineers are tasked with designing spaces that in the very root of their existence strive to provide for those in need of comfort, respite, healing, faith, and justice.
Too often, the true essence of design gets lost or ignored in the milieu. In many communities, disenfranchised people of color are the least served, be it in adequate healthcare facilities and services, housing that they can afford, or educational opportunities. It is time for us to fight for equity.
The profession of architecture uses data, statistics, and information, translating these factors into a creative, visual homage to life on earth. Our profession also takes the basic psychological and safety components of Maslow’s hierarchy – shelter, personal security, resources, and health – and transforms them into love and belonging, esteem, and ultimately self-actualization.
When we deprive people of their basest needs, we are wrenching away their hopes of achieving all the higher needs. Without the feeling of belonging, esteem, and the drive to become our best selves, we can become consumed by an eternal cycle of disenfranchisement and dissolution.
'WE MUST USE OUR VOICES TO EDUCATE AND ADVOCATE'
As architects, we must use our voices to educate, advocate, and demand a say in the future of our world. We are leaving legacies that define a narrative too important to ignore. The buildings we design become vessels of a collective consciousness.
To see architecture in the sum of its parts is paramount. Here’s how we can do that:
1. DESIGN FOR THE PEOPLE
We have been taught to design to the context, a varied array of constraints, and to the site. But let us also start designing to those who use the space. For example, in certain economically impoverished areas, it is important to provide larger waiting areas in clinics than is the industry standard. This allows larger families with siblings and grandparents to attend appointments with the primary patient when childcare is too expensive or not available.
Understanding the people who use the space and the way the space will be used has such value in design, yet it is often overlooked for aesthetics, budget constraints, or schedule demands.

2. EMPOWER THE PEOPLE
We must inspire neighborhoods to take pride in improving their quality of life. Instead of allowing gentrification that forces out a community’s indigenous residents, we must add resources that allow them to invest in the future of their neighbors and their community.
Programs such as urban farms operated and used by the community, sustainable initiatives providing green energy sources at a discount, increased access to education specific to preventive healthcare and well-being, and community art and upgrade programs allowing neighbors to define their surroundings are all great means to accomplish this. This is how self-worth can be nurtured. Architecture is one important tool that can help accomplish this.

3. STAY INVESTED IN THE COMMUNITY
More often than not, architects and designers are removed from the job once the project is complete and occupied. Like doctors’ follow-up visits, we should endeavor to conduct post-occupancy evaluations – particularly in impoverished neighborhoods and on projects that deeply affect the community, such as clinics, hospitals, schools, and housing – and take any necessary corrective action to make sure our buildings serve all the people for whom they were designed, not just owners or clients.

4. STRIVE FOR INCLUSION
We must locate and design accessible public spaces for people of all races and economic standings. Instead of using parks and plazas as a tool to separate, we must see these as opportunities to engage and integrate. Design has the power to address concerns regarding safety and security. We must not allow these concerns to prevent us from doing what is right.
It is our responsibility as architects to empower neighborhoods, those we live in and those we touch through our work. Imagine the collective power of a group that weaves a community’s and a nation’s urban fabric. Let’s understand the importance of established minority neighborhoods. Let’s learn how to work with the local community by providing the proper resources and support to enhance a community and meet its needs. Let’s help every human being achieve his or her best self.
I cannot wait for the day when, regardless of race, sex, gender, or economic status, we all have equal rights to safety, security, a sense of belonging, and self-value. The very first words of our Constitution are “We the People of the United States.” Our country cannot move forward until there is equity for all of its citizens. At the very foundation of our democracy is the right to shape our future for the betterment of all the people. As leaders in the building industry, we have a professional and moral obligation to use our skills and training to achieve this goal, now more than ever.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR: MELANIE HARRIS, AIA
Melanie Harris, AIA (mharris@bsalifestructures.com), is the National Healing Practice Director for BSA LifeStructures, a full-service architecture and engineering firm. She is a graduate of Texas A&M University and when not in Tampa, she travels the world in search of new experiences, unique foods, and architecture.
Related Stories
| Nov 9, 2010
Designing a library? Don’t focus on books
How do you design a library when print books are no longer its core business? Turn them into massive study halls. That’s what designers did at the University of Amsterdam, where they transformed the existing 27,000-sf library into a study center—without any visible books. About 2,000 students visit the facility daily and encounter workspaces instead of stacks.
| Nov 9, 2010
Turner Construction report: Green buildings still on the agenda
Green buildings continue to be on the agenda for real estate owners, developers, and corporate owner-occupants, according to the Turner 2010 Green Building Market Barometer. Key findings: Almost 90% of respondents said it was extremely or very likely they would incorporate energy-efficiency improvements in their new construction or renovation project, and 60% expected to incorporate improvements to water efficiency, indoor environmental quality, and green materials.
| Nov 5, 2010
New Millennium’s Gary Heasley on BIM, LEED, and the nonresidential market
Gary Heasley, president of New Millennium Building Systems, Fort Wayne, Ind., and EVP of its parent company, Steel Dynamics, Inc., tells BD+C’s Robert Cassidy about the Steel Joist Manufacturer’s westward expansion, its push to create BIM tools for its products, LEED, and the outlook for the nonresidential construction market.
| Nov 3, 2010
First of three green labs opens at Iowa State University
Designed by ZGF Architects, in association with OPN Architects, the Biorenewable Research Laboratory on the Ames campus of Iowa State University is the first of three projects completed as part of the school’s Biorenewables Complex. The 71,800-sf LEED Gold project is one of three wings that will make up the 210,000-sf complex.
| Nov 3, 2010
Park’s green education center a lesson in sustainability
The new Cantigny Outdoor Education Center, located within the 500-acre Cantigny Park in Wheaton, Ill., earned LEED Silver. Designed by DLA Architects, the 3,100-sf multipurpose center will serve patrons of the park’s golf courses, museums, and display garden, one of the largest such gardens in the Midwest.
| Nov 3, 2010
Public works complex gets eco-friendly addition
The renovation and expansion of the public works operations facility in Wilmette, Ill., including a 5,000-sf addition that houses administrative and engineering offices, locker rooms, and a lunch room/meeting room, is seeking LEED Gold certification.
| Nov 3, 2010
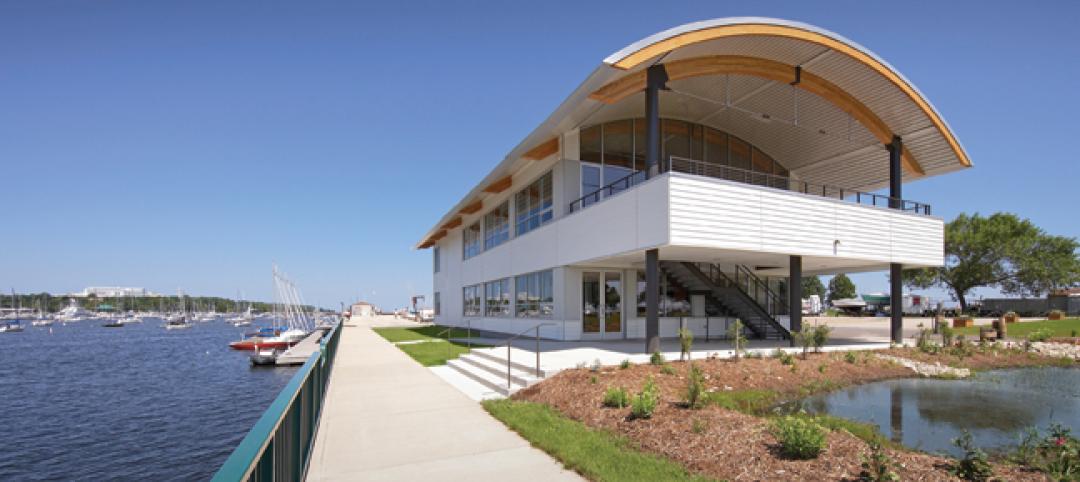
Sailing center sets course for energy efficiency, sustainability
The Milwaukee (Wis.) Community Sailing Center’s new facility on Lake Michigan counts a geothermal heating and cooling system among its sustainable features. The facility was designed for the nonprofit instructional sailing organization with energy efficiency and low operating costs in mind.
| Nov 3, 2010
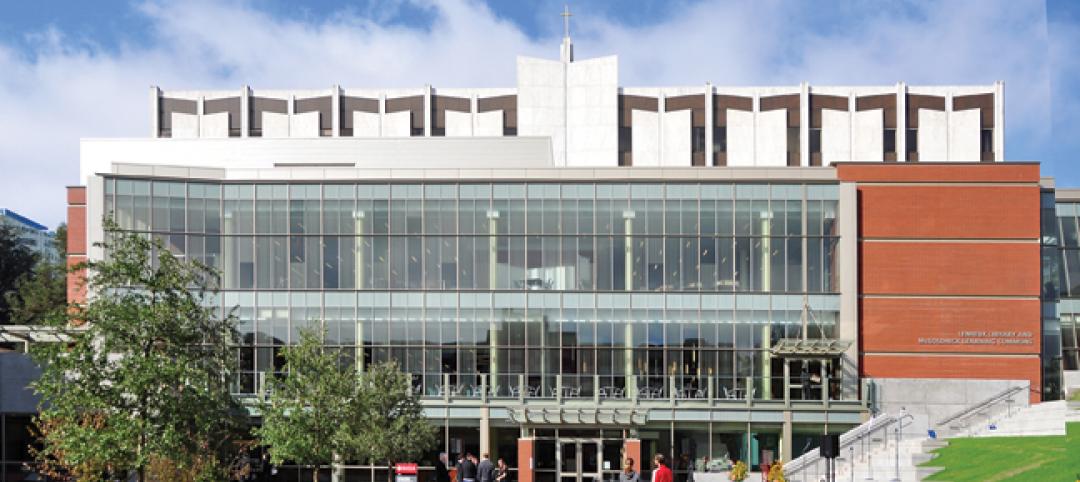
Seattle University’s expanded library trying for LEED Gold
Pfeiffer Partners Architects, in collaboration with Mithun Architects, programmed, planned, and designed the $55 million renovation and expansion of Lemieux Library and McGoldrick Learning Commons at Seattle University. The LEED-Gold-designed facility’s green features include daylighting, sustainable and recycled materials, and a rain garden.
| Nov 3, 2010
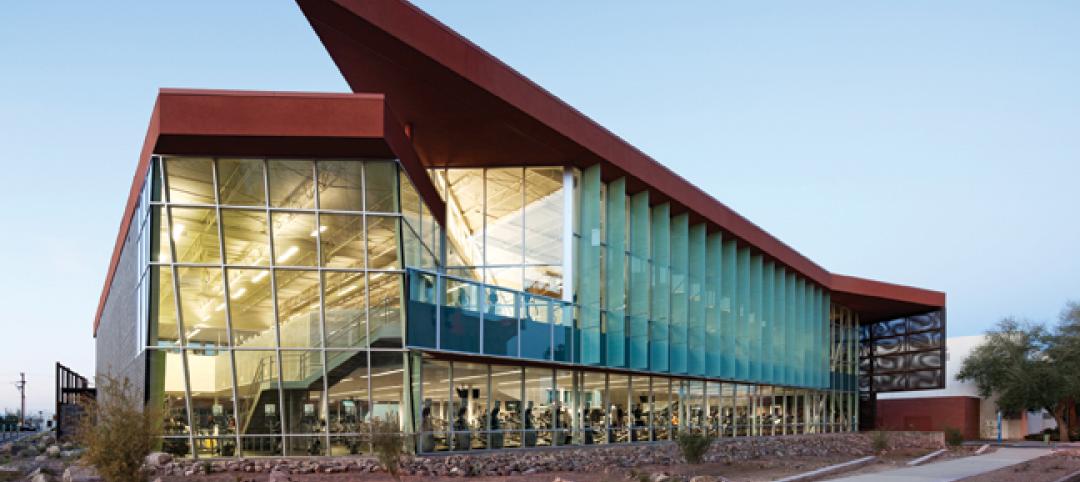
Recreation center targets student health, earns LEED Platinum
Not only is the student recreation center at the University of Arizona, Tucson, the hub of student life but its new 54,000-sf addition is also super-green, having recently attained LEED Platinum certification.
| Nov 3, 2010
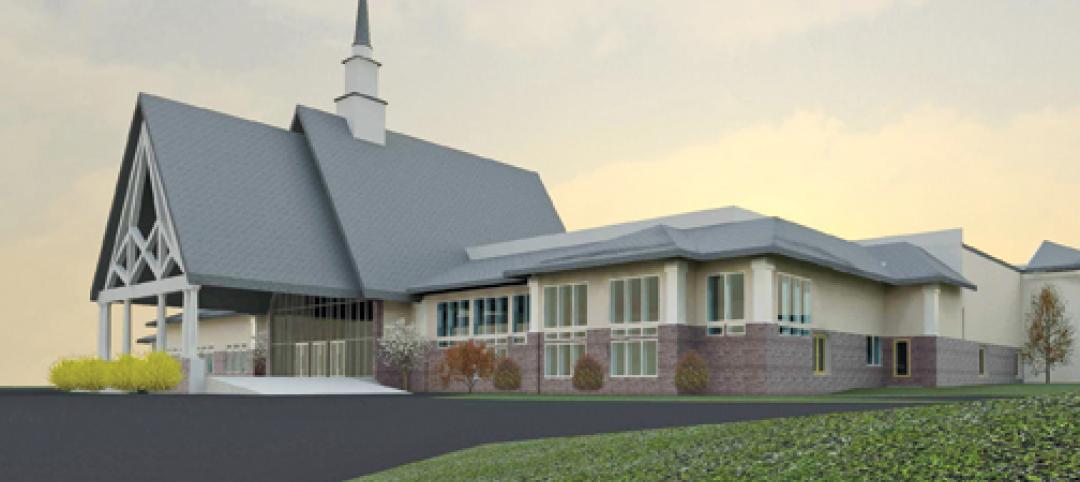
New church in Connecticut will serve a growing congregation
Tocci Building Companies will start digging next June for the Black Rock Congregational Church in Fairfield, Conn. Designed by Wiles Architects, the 103,000-sf multiuse facility will feature a 900-person worship center with tiered stadium seating, a children’s worship center, a chapel, an auditorium, a gymnasium, educational space, administrative offices, commercial kitchen, and a welcome center with library and lounge.
















