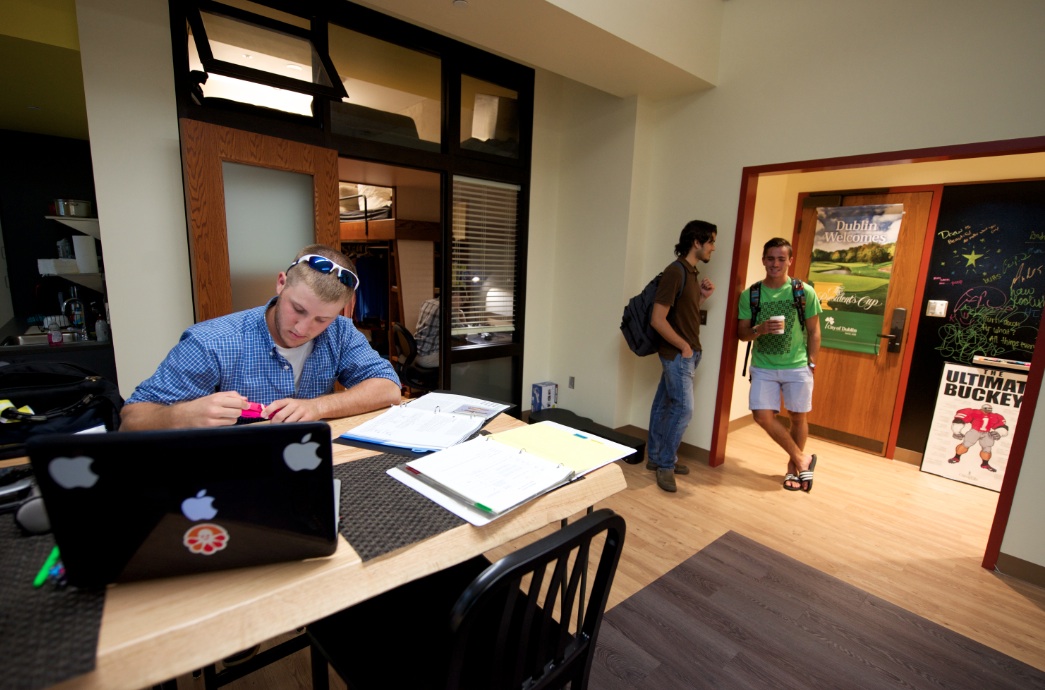
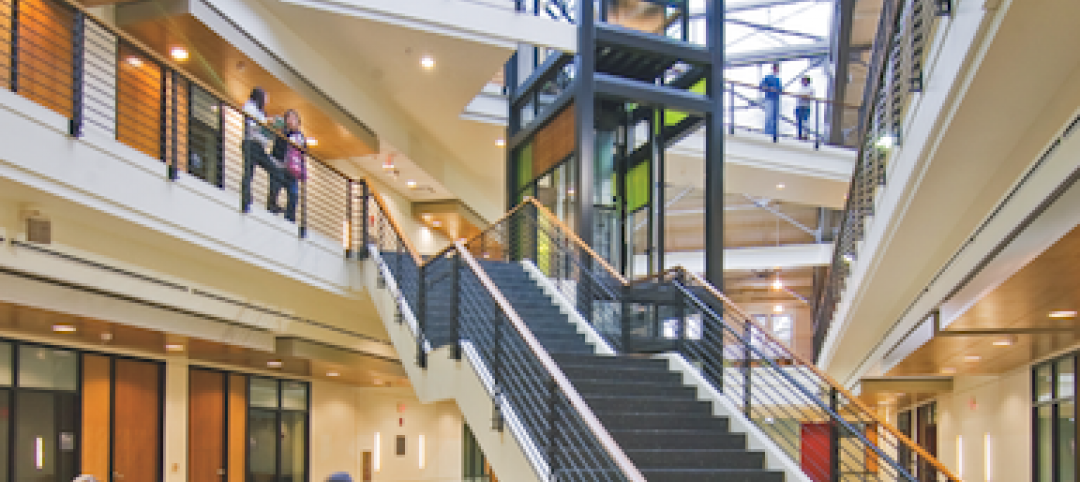
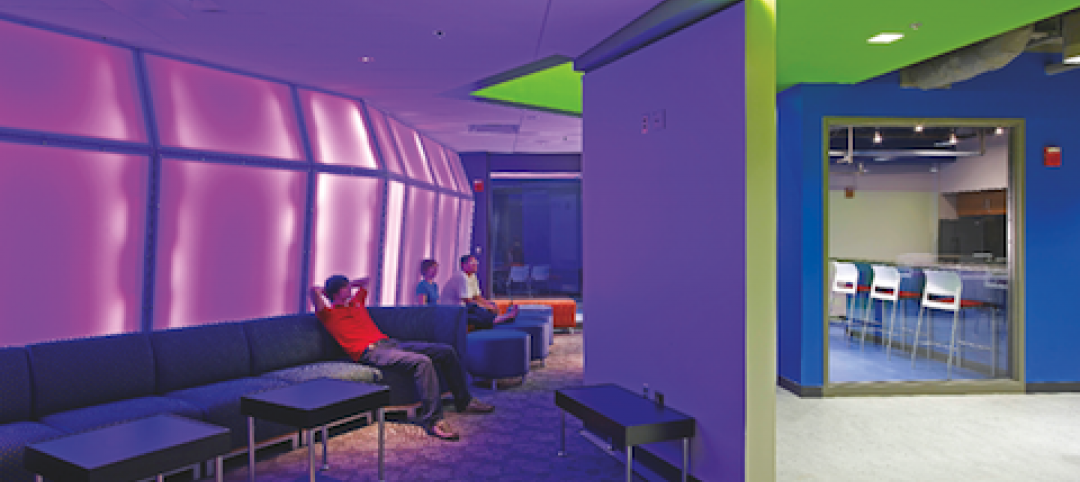
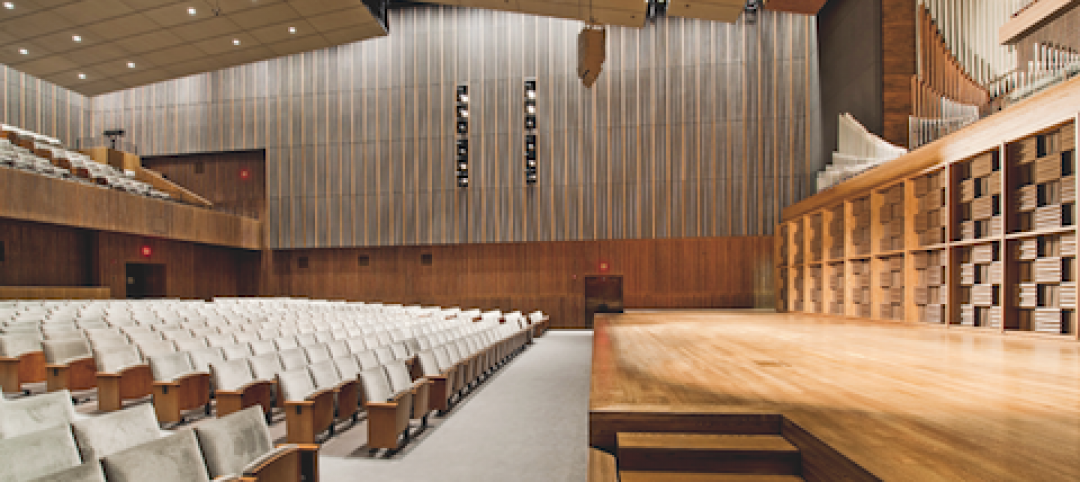
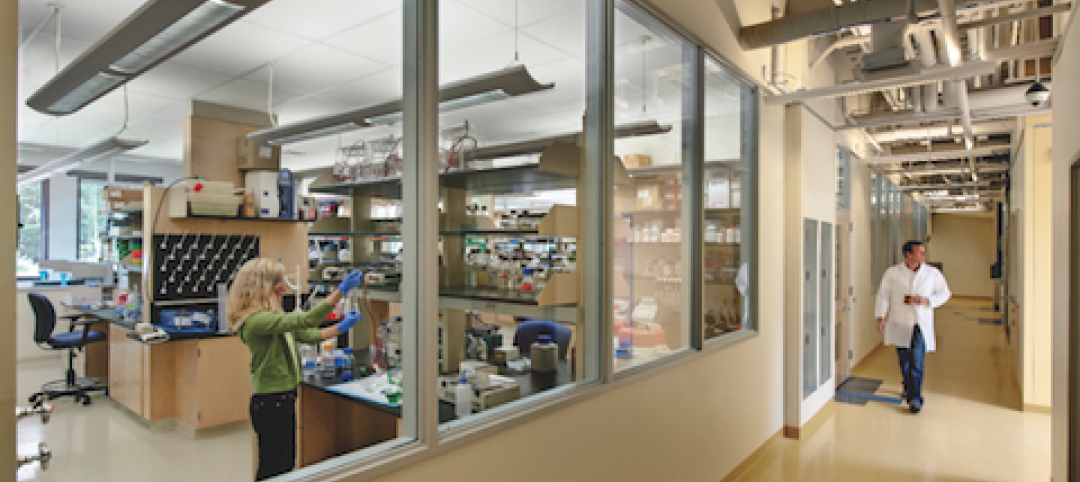
University officials and design firms are struggling to understand how rapidly changing student habits are altering how they use living spaces. To get a better feel for that phenomenon, Little Diversified Architectural Consulting earlier this year conducted a daylong student housing symposium at its Durham and Charlotte locations to pick the brains of 62 students from a dozen North Carolina institutions. The firm recapped the findings in a recent report, called "What Students Want."
“We were surprised at how much time students are spending in housing facilities,” says Thomas Carlson-Reddig, AIA, LEED AP, Global Practice Leader for Little's Community team. The discussion revealed that half the students surveyed studied in their rooms, while half “escaped” to other spaces to study, eat, and relax.
Here are highlights of the comments from 62 college students that participated in Little’s workshops:
What students want in their rooms:
• Ability to reconfigure the room
• Built-in furniture that defines the space (but is still reconfigurable)
• Mobile beds with a cushion seat that could rest below the desk
• “Work surface” desk space with a comfortable chair
• Ability to create a private zone in rooms with multiple students
• More storage, such as built-in closets (not wardrobes)
• A sink—accessible outside the bathroom—in the room
• No old-school “dorm furniture”
• Option to paint one wall in the room
• Rooms with some color and texture—not all gray, tan, or white walls
• Translucent divider wall along the bed
• “Murphy beds” or loft beds as options, but no bunk beds
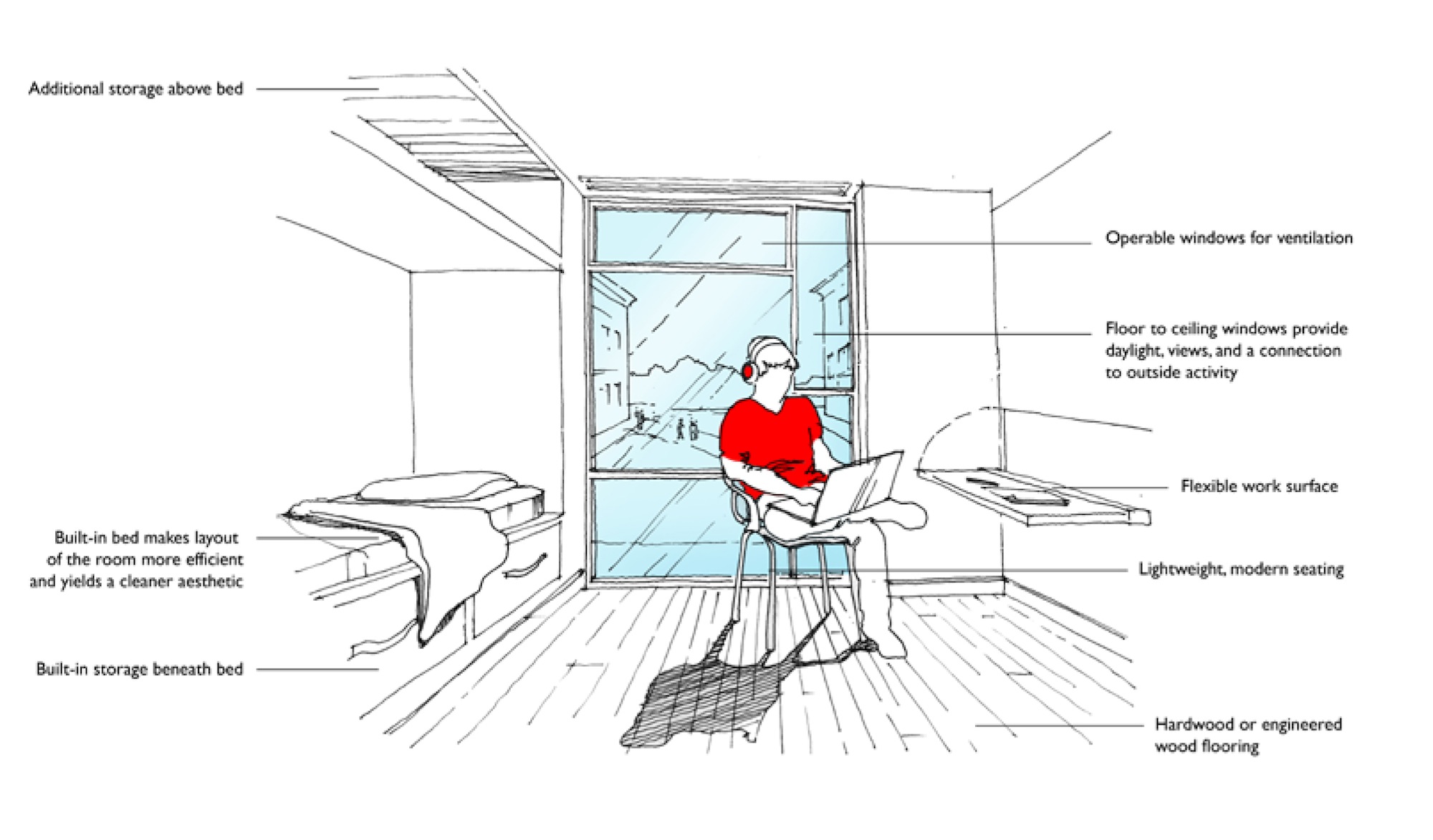
During the symposium, Little asked the students a variety of questions pertaining to their dorm room experiences. There was a broad consensus that traditional dorm furniture frequently impedes their optimal use of the space. Their responses generated ideas ranging from a multi-purpose wall where a bed, desk and storage can be easily reconfigured to moveable partitions that could help define living and sleeping spaces and provide privacy between roommates. What Little learned is that the efficiency of the room can be greatly improved without increasing floor area.
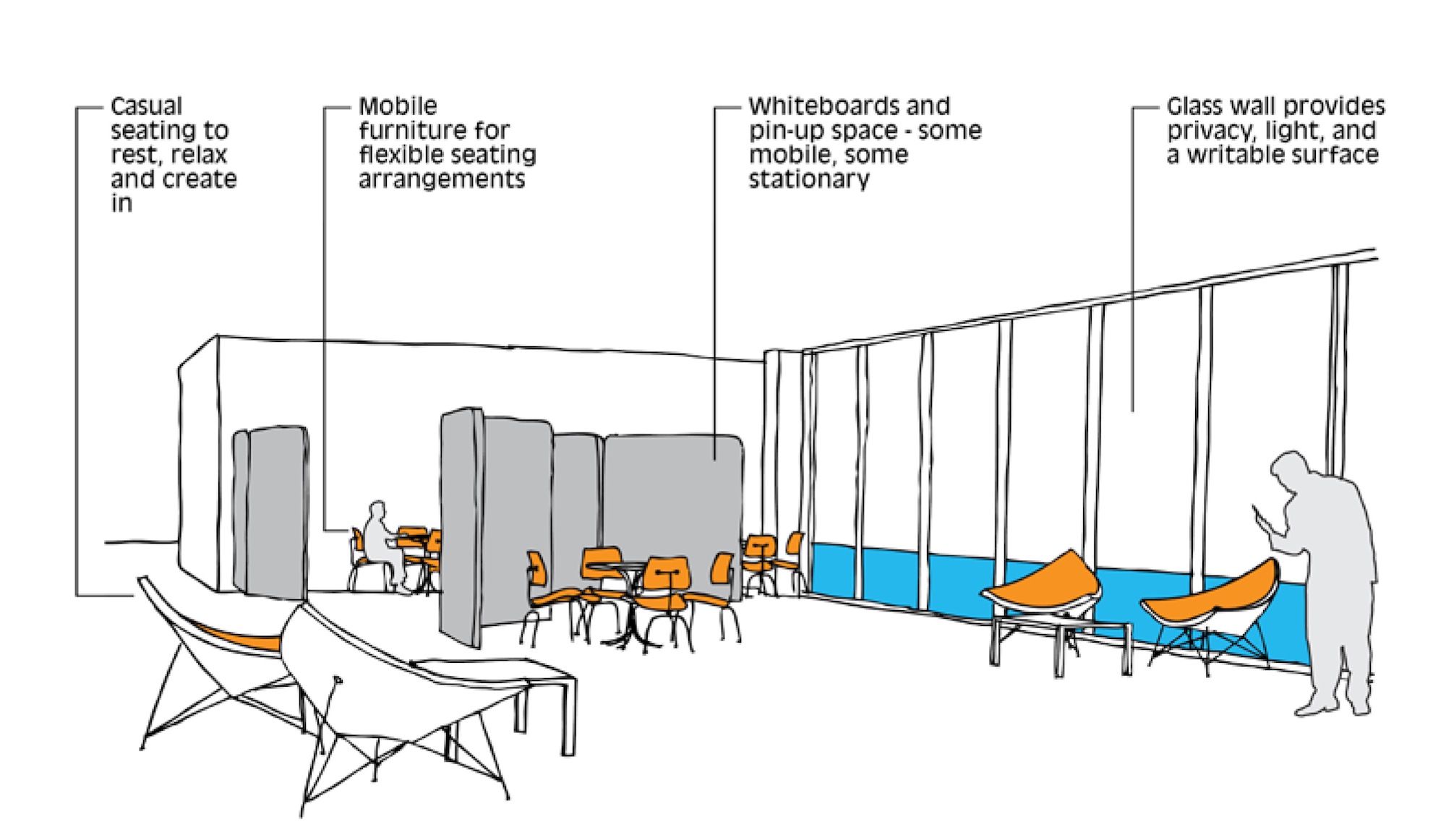
What students want in their study spaces:
• Small, individual study nooks scattered throughout the residence hall (and other buildings as well)
• Comfortable seating that is playful, whimsical, and relaxed
• Spaces that are full of light, with views of outdoors
• Quality of light is important, but avoid glare and heat gain
• Small study areas adjacent to stairs/elevators (to allow students to monitor activity, meet friends)
• Group study and collaboration areas
• Flexible furniture options, from small group tables to lounge seating
• Outdoor study space, where feasible
Over the course of a day, students find opportunities to study in various locations throughout campus. Little wanted to understand the characteristics of what makes a good study spot. The firm learned it should be bright and comfortable. It should be fairly quiet, yet visually connected to the more active spaces. Larger group study areas should be complemented by cozier individual study nooks. A student that chooses to study outside of his or her room doesn’t want to feel isolated.
What students want in their social lives:
• Learning spaces that can dovetail into “chill” spaces
• Laundry facilities that create an opportunity for social interaction
• Community lounges located in vertical circulation zones so that students can see others coming and going
• Kitchens that serve a smaller “community” are preferred over those that serve an entire building
• Chill spaces that provide as much variety as possible
• Active outdoor zones adjacent to housing for group-based casual fitness (e.g., Frisbee, volleyball)
• Rooftop gardens, green roofs, “working green spaces,” outdoor benches, and outdoor eating areas with picnic tables and barbecue grilles
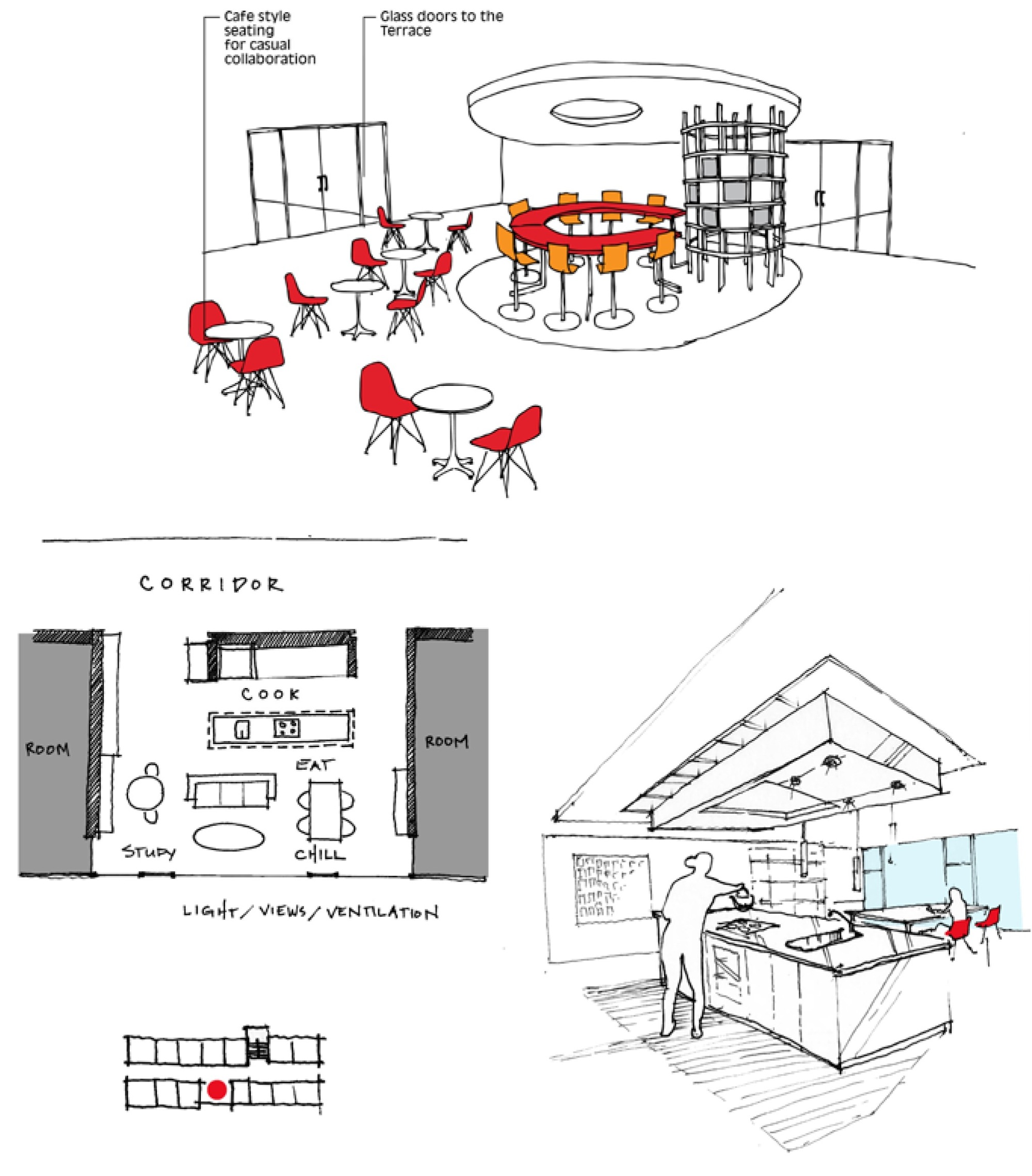
A sense of community is what students seek when they arrive on campus and it is what will keep them there for the course of their studies. Little defined the community as a relatively small group (16-32 students) that can take ownership of common areas, such as kitchens or lounges. In order to be activated, gathering areas should be located along the horizontal and vertical circulation paths, have access to light and views, and connect various communities to each other.
Download the complete "What Students Want" report from Little.
Related Stories
| Oct 13, 2010
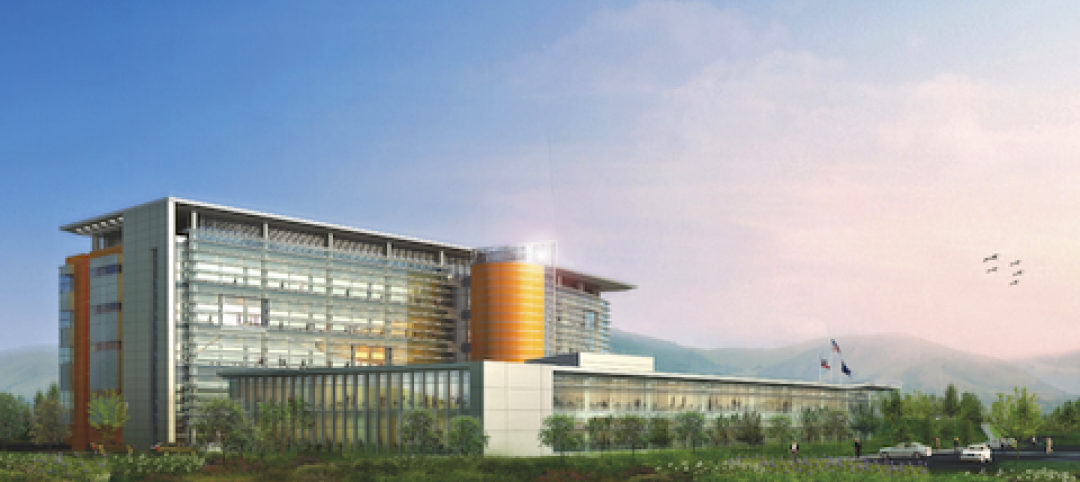
County building aims for the sun, shade
The 187,032-sf East County Hall of Justice in Dublin, Calif., will be oriented to take advantage of daylighting, with exterior sunshades preventing unwanted heat gain and glare. The building is targeting LEED Silver. Strong horizontal massing helps both buildings better match their low-rise and residential neighbors.
| Oct 12, 2010
Holton Career and Resource Center, Durham, N.C.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Special Recognition. Early in the current decade, violence within the community of Northeast Central Durham, N.C., escalated to the point where school safety officers at Holton Junior High School feared for their own safety. The school eventually closed and the property sat vacant for five years.
| Oct 12, 2010
Guardian Building, Detroit, Mich.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Special Recognition. The relocation and consolidation of hundreds of employees from seven departments of Wayne County, Mich., into the historic Guardian Building in downtown Detroit is a refreshing tale of smart government planning and clever financial management that will benefit taxpayers in the economically distressed region for years to come.
| Oct 12, 2010
Richmond CenterStage, Richmond, Va.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Bronze Award. The Richmond CenterStage opened in 1928 in the Virginia capital as a grand movie palace named Loew’s Theatre. It was reinvented in 1983 as a performing arts center known as Carpenter Theatre and hobbled along until 2004, when the crumbling venue was mercifully shuttered.
| Oct 12, 2010
University of Toledo, Memorial Field House
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Memorial Field House, once the lovely Collegiate Gothic (ca. 1933) centerpiece (along with neighboring University Hall) of the University of Toledo campus, took its share of abuse after a new athletic arena made it redundant, in 1976. The ultimate insult occurred when the ROTC used it as a paintball venue.
| Oct 12, 2010
Owen Hall, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Mich.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Officials at Michigan State University’s East Lansing Campus were concerned that Owen Hall, a mid-20th-century residence facility, was no longer attracting much interest from its target audience, graduate and international students.
| Oct 12, 2010
Gartner Auditorium, Cleveland Museum of Art
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Gartner Auditorium was originally designed by Marcel Breuer and completed, in 1971, as part of his Education Wing at the Cleveland Museum of Art. Despite that lofty provenance, the Gartner was never a perfect music venue.
| Oct 12, 2010
Cell and Genome Sciences Building, Farmington, Conn.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Administrators at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington didn’t think much of the 1970s building they planned to turn into the school’s Cell and Genome Sciences Building. It’s not that the former toxicology research facility was in such terrible shape, but the 117,800-sf structure had almost no windows and its interior was dark and chopped up.
| Oct 12, 2010
The Watch Factory, Waltham, Mass.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards — Gold Award. When the Boston Watch Company opened its factory in 1854 on the banks of the Charles River in Waltham, Mass., the area was far enough away from the dust, dirt, and grime of Boston to safely assemble delicate watch parts.
| Oct 12, 2010
Cuyahoga County Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Monument, Cleveland, Ohio
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Gold Award. The Cuyahoga County Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Monument was dedicated on the Fourth of July, 1894, to honor the memory of the more than 9,000 Cuyahoga County veterans of the Civil War.