A single mobile phone uses more energy per unit than a refrigerator, not so much in terms of recharging but in the data traffic and other actions the phone creates.
The Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector consumes as much as 10% of the world’s electricity, a sizable portion of which goes toward operating data centers that are the spine of the Internet and the cloud.
Large data centers can use more electricity than a midsize town. However, much of that energy ends up being released as heat into the atmosphere, to the point where carbon emissions from data centers could exceed what the entire airline industry spews annually within the next five years.
Consequently, as data centers expand, greater emphasis is being placed on controlling their impact on the environment. Apple claims that all of its data centers are powered by 100% renewable energy, including new data centers in Denmark and Ireland that will be completed in 2017. Apple has also made an $850 million investment in a solar farm in California to power its new campus in Silicon Valley, all its California offices and data centers, and its data center in Newark, Calif.
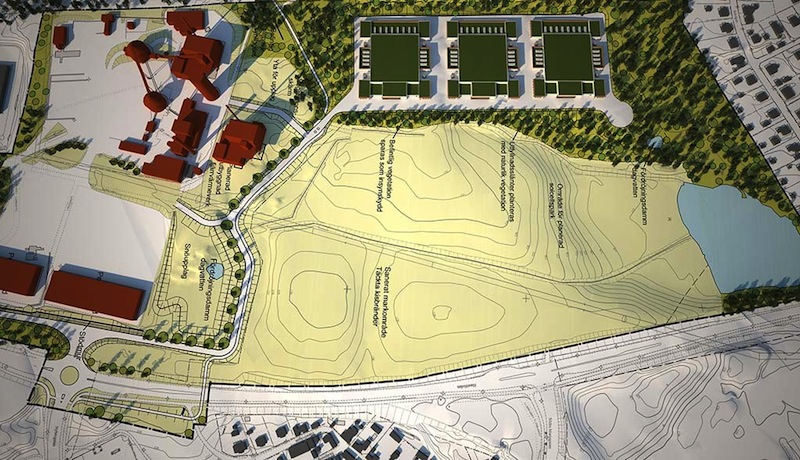
In Falun, Sweden, the municipality owned Falu Energi & Vatten is collaborating with Schneider Electric and EcoDC AB, which specializes in designing and building climate-smart data centers, to build what this team is calling the world’s first climate-positive data center.
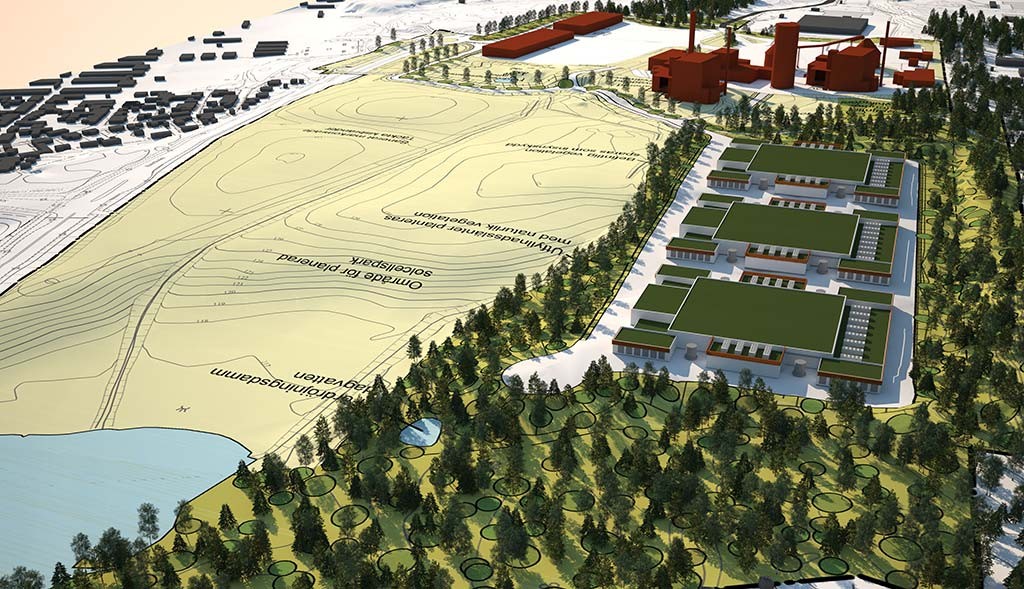
The location of this three-building, 250,000-sf EcoDataCenter is relevant. Falun is one of the greenest towns on the planet. Ninety-five percent of houses with district heat in Falun (about half of all homes in the municipality) are provided with heat from a cogeneration plant that recycles forestry waste to produce electricity and warm water.
The town also has one of Sweden’s largest solar panel arrays. More than half of Falun’s energy needs are provided by hydro, wind, and cogeneration plants, with the rest coming from renewable sources such as solar and secondary biofuels.
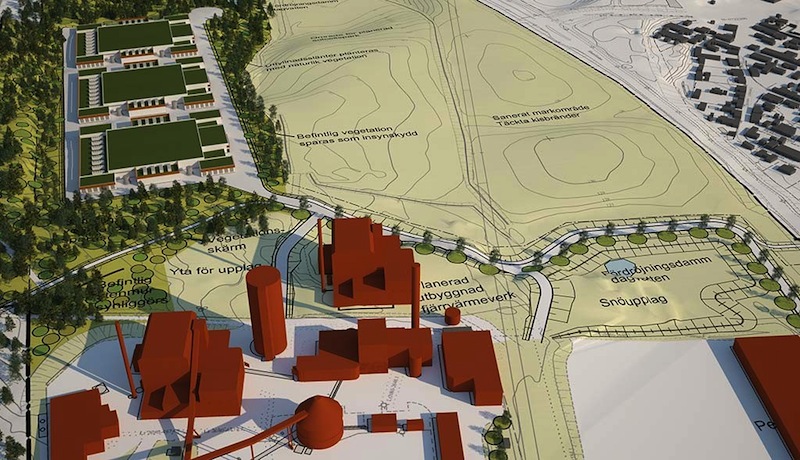
Consequently, 100% of the energy that the EcoDataCenter would use will come from renewable sources. The 18-megawatt data center will be connected to Falun’s energy grid, and excess heat from its servers and equipment will warm buildings in the town’s district heating system. During the summer, excess steam from a local electricity plant will run machines that cool the data center.
No electricity will be required to increase the return water temperature from the data center. Heat from the data center replaces existing marginal heat production with high CO2 emissions. This CO2 replacement will exceed total CO2 emissions from the data center during a year.
EcoDataCenter’s first building should be completed in the first quarter of 2016. When fully operational, EcoDataCenter should attain the highest levels of availability and security classification. (It is expected to be Sweden’s first to achieve a Tier IV certification from Uptime Institute.)
The data center is projected to operate with a power usage effectiveness (PUE)—useful IT kilowatts divided by totally used kilowatts—of less than 1.15.

Related Stories
Giants 400 | Aug 19, 2022
2022 Giants 400 Report: Tracking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms
Now 46 years running, Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report rankings the largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. This year a record 519 AEC firms participated in BD+C's Giants 400 report. The final report includes more than 130 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
Industrial Facilities | Jul 26, 2022
As industrial sector sizzles, investors watch impact of inflation and interest rates
Demand continues to top supply, especially on the coasts, according to latest CommercialEdge report.
Urban Planning | Jul 19, 2022
The EV charger station market is appealing to investors and developers, large and small
The latest entry, The StackCharge, is designed to make recharging time seem shorter.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 21, 2022
Two birds, one solution: Can we solve urban last-mile distribution and housing challenges at the same time?
When it comes to the development of both multifamily housing and last-mile distribution centers, particularly in metropolitan environments, each presents its own series of challenges and hurdles. One solution: single-use structures.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 17, 2022
A new Innovation Center in Wyoming focuses on finding sustainable ways to use coal
The 10-acre site is part of the area’s R&D push.
Self-Storage Facilities | May 19, 2022
A steady increase in new self-storage space is meeting growing need in large metros and their suburbs
Rent Café’s study projects a 9 percent bump in the nation’s existing inventory.
Adaptive Reuse | May 18, 2022
An auto plant in Detroit to get a retread as mixed-use housing
Fisher 21 Lofts could be the largest minority-led redevelopment in the city’s history.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 30, 2022
CapRock Partners taps into industrial space demand
The investment firm is committed to building 15 million sf of warehouses.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 14, 2022
JLL's take on the race for industrial space
In the previous decade, the inventory of industrial space couldn’t keep up with demand that was driven by the dual surges of the coronavirus and online shopping. Vacancies declined and rents rose. JLL has just published a research report on this sector called “The Race for Industrial Space.” Mehtab Randhawa, JLL’s Americas Head of Industrial Research, shares the highlights of a new report on the industrial sector's growth.
Industrial Facilities | Apr 6, 2022
Development underway for Missouri’s largest logistics park
Hunt Midwest envisions 27 buildings will be completed over the next 10 years.