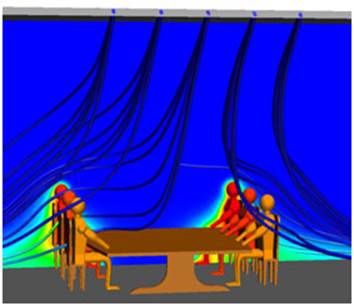
A misperception about computational fluid dynamics is that it is only effective when designing a jet plane, a formula one car, or an outer space rocket. Today, building designers can apply the same basic principles in fluid dynamics tested on these exotic high-flyers to common building airflows.
Here are three reasons why you might consider CFD for your next building project.
1. Best guess approach — Although guided by ASHRAE standards, current HVAC specs are usually “best guesses” based on experience with various equipment and designs. Most engineers oversize HVAC units because they just don’t “know” exactly where thermal differentials including cyclic variations, radiant temperature asymmetries, and drafts will happen in an operating building. Using CFD insight, you can right-size HVAC solutions to eliminate redundant equipment and save costs.
2. BIM modeling is standard — The widespread adoption of BIM has led to an unprecedented ability to model new designs. Now, engineers and designers routinely run time and light studies, finite element analyses and energy efficiency studies working with the BIM model. The extension of a building model to CFD analysis is not the leap it may have been ten years ago. Now, airflow designers can run through a number of scenarios for ventilation and heating using different strategies inside the actual building model.
5 benefits of CFD analysis
1. Assess ventilation effectiveness before construction
2. Eliminate equipment redundancy
3. Weigh equipment costs against performance and environmental requirements
4. Substantiate performance claims
5. Locate supply/return for optimal airflow
3. Seeing is believing — CFD analyses produce easy to understand visuals that show the impact of design alternatives, allowing architects to move walls, alter service conduit pathways and change glazing effects—among other things—to improve energy efficiency and occupant comfort. These visuals are crucial in explaining to owners the impact of design changes, airflow strategies and or equipment purchases. When everyone can easily grasp the results of the sophisticated math behind CFD, you can reach agreement more quickly and with a higher level of confidence.
Typically, designers do not have the time, knowledge or technology to perform a CFD analysis. The alternative is to work with outsourced CFD experts to generate the best airflow strategy for your project. The key here is to find the right fit. Make sure your CFD supplier has a demonstrated range of experience with the kind of building you are designing.
Your CFD partners should recognize precisely how to properly model an environment to reveal key performance insights—thermal stratification and restricted flows, for example. In addition, your CFD consultant should be collaborative—working with the design team to explore options for improvement.
No matter what kind of project you are designing—a new manufacturing plant, a new residential building or healthcare institution, or a retrofit of a landmark office complex—a proper CFD analysis will save money in initial capital costs and far more over time in building operating and energy costs. As a designer, you can provide your client with a better, less expensive solution.
About the Author
Jason Pfeiffer is Director CFD Analysis Consulting with IMAGINiT Technologies. He can be reached at jpfeiffer@rand.com.
Related Stories
| Nov 22, 2011
New Green Matters Conference examines emerging issues in concrete and sustainability
High-interest topics will be covered in technical seminars, including infrared reflective coatings for heat island mitigation, innovative uses of concrete to provide cooling and stormwater management, environmental benefits of polished concrete, and advancements in functional resilience of architectural concrete.
| Nov 22, 2011
Suffolk Construction selected as contractor for Boston luxury residential tower
Project team breaks ground on 488,000-sf building that will feature world-class amenities.
| Nov 22, 2011
Jones Lang LaSalle completes construction of two new stores in Manhattan
Firm creates new global design standard serving as project manager for Uniglo’s 89,000-sf flagship location and, 64,000-sf store.
| Nov 21, 2011
Mortenson and enXco partnership to build its 19th wind project
The 8,500 acres project will generate140 megawatts of wind power – enough energy to power approximately 39,000 homes.
| Nov 21, 2011
FDH Engineering acquires Energy Solutions
All ESI employees have been merged into FDH’s staff at its St. Louis office.
| Nov 18, 2011
Centre for Interactive Research on Sustainability opens
Designed to exceed LEED Platinum, the Centre for Interactive Research on Sustainability (CIRS) is one of the most innovative and high performance buildings in North America today, demonstrating leading-edge green building design products, technologies, and systems.
| Nov 17, 2011
SmithGroup changes name to SmithGroupJJR
SmithGroup and JJR join brands to become a single, multi-disciplinary company.
| Nov 17, 2011
Campus-wide energy-efficiency program aims to deliver $3.5 million in energy and operational savings
Merced College and Honeywell will use the school’s energy usage statistics to develop a course curriculum on sustainability, and raise awareness among students of the positive impact conservation practices contribute to the community.