In a world of advancing technology, virtual design is meant to look as real as a photograph but have the potential to tell a deeper, more meaningful story.
When well executed, renderings can be a powerful marketing tool. Increasingly, retailers such as IKEA, as well as real estate developers and architectural firms, are using photorealistic renderings—in lieu of photography—to market their products and services online.
The most important rule to follow when creating a rendering is to tell the right story. Who is your audience? What are you marketing? How can you best reach the audience through a rendering or computer-generated film? These questions need to be addressed before any computer wireframe or designs are put together.
What’s the real test of a great rendering? It’s photorealistic. It needs to look so similar to a photograph that it’s hard to tell what is real and what was designed on a computer.
5 tips for creating photorealistic renderings
1. Know the story you need to tell. Storytelling fundamentals—whether for books, movies, or branding—have not changed. The goal is to engage the audience and make them care about what you are saying. Understanding the client’s goals and expectations is the first step, and getting involved in planning meetings to understand the narrative is critical. The audience and the ideal tenant need to be established in order to frame the rendering.
Not everything can be accomplished in a conference room. Visit the project site to see what views the building will have (or has, if it is already built). Consider using a drone to capture aerial views and landscapes. Make sure to take into account the culture of the neighborhood. Site exploration will help the story resonate through the rendering.
2. Avoid a cookie-cutter approach. Having a process in place for rendering creation is important, but every project needs a clean slate to tell a specific story. Some firms make the mistake of having a template for what a condo tower or mixed-use development should look like. No design should be repeated. That’s when creativity, innovation, and the project’s unique story are lost.
3. Make it about more than digital design. A great rendering cannot be created from the mind of the digital artist alone. Consult with the architects, developers, and marketers to be a part of the strategy development and story creation processes. Architects understand that a rendering will sell their design. They can advise the digital artist on the building’s design and scale of the space. Developers understand how renderings tie into the overall brand strategy, and can help incorporate key points into the final artwork.
 Rendering creation involves multiple steps: wire framing to help develop a good composition that tells an engaging story (far left); 3D render passes like Z depth (middle left) and reflection (middle right) to adjust the volume, hue, lighting, and reflectivity of elements; addition of details (people, sky) and color correction (far right).
Rendering creation involves multiple steps: wire framing to help develop a good composition that tells an engaging story (far left); 3D render passes like Z depth (middle left) and reflection (middle right) to adjust the volume, hue, lighting, and reflectivity of elements; addition of details (people, sky) and color correction (far right).
4. Add custom details. Composition, lighting, texture, color, time of day, angle of the sun or moon, even the choice of the lens for films, can make all the difference between a quality rendering and one that is truly lifelike.
Ask questions like, Will the building look better if presented in daylight, at dusk, or nighttime? Should the rendering incorporate people? If yes, what’s the demographic breakdown? For example, if you’re working on a rendering for an office building targeted at startup companies, the people in the rendering should not be wearing suits, and the workspaces should not include cubicles, but rather open, collaborative areas.
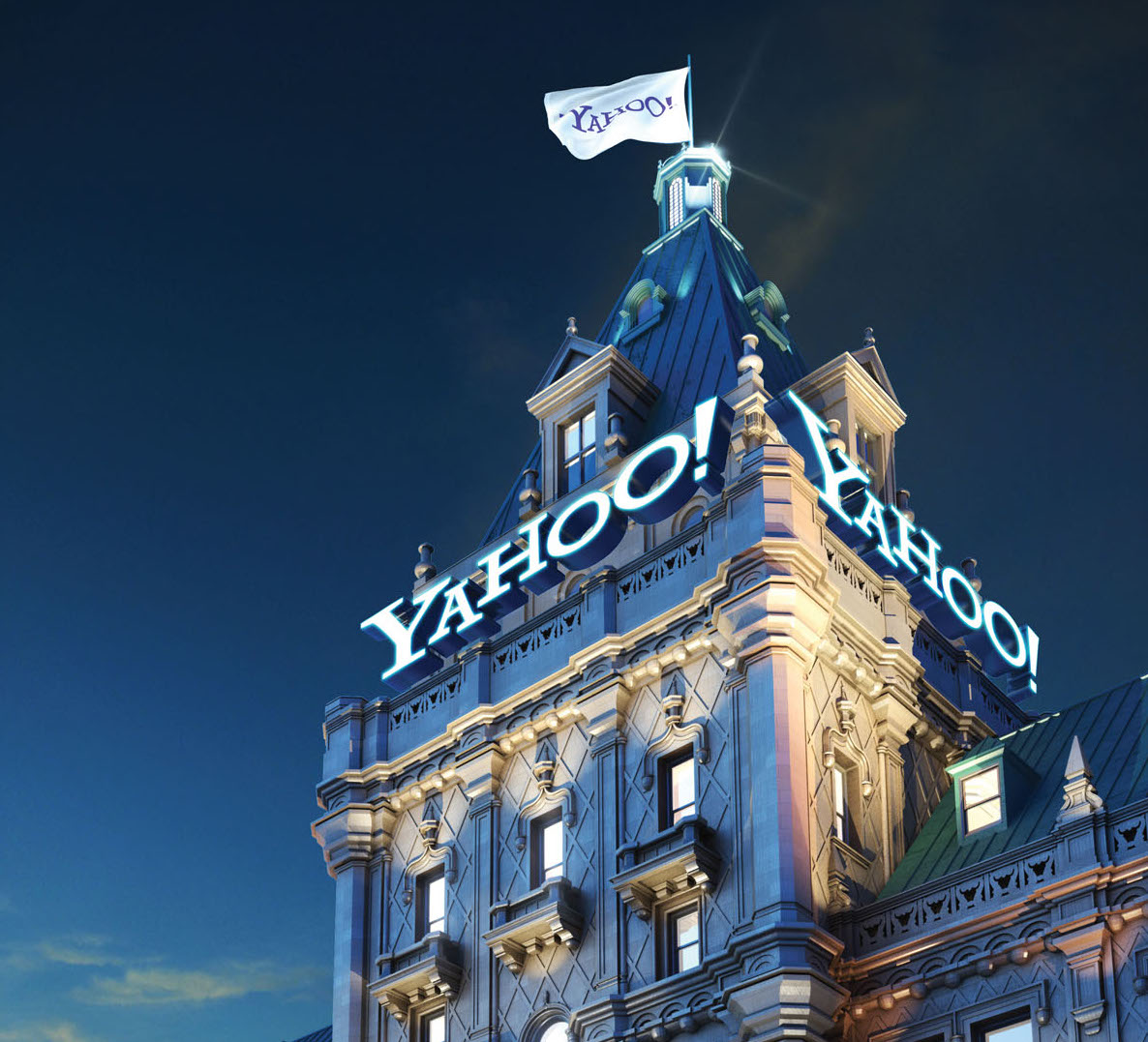
Going bold and adding the desired tenant’s name to the top of the building in a rendering can be the final piece to getting the company to sign the lease—as was the case with Yahoo at the 229 West 43rd Street project in Manhattan.
5. Experiment with new technology. As technology advances—especially real-time tools—people want new ways to tell their stories, or enhance a traditional experience. This is where virtual reality and augmented reality come into play.
In architecture and real estate development, virtual reality can provide depth and scale to renderings. Through the use of simple VR tools, such as Google Cardboard, a rendering can come to life. People can move through the space, under the impression that they have control. The rendering tells the story that the designer wants to tell and only allows certain views and spaces for exploration, but the user can decide where to turn and what to look at next. They make their own journey through the curated space.
The success or failure of project artwork doesn’t necessarily hinge on how photorealistic it is. Rather, it works best when the creator develops an effective, cohesive story that ties into the overall marketing strategy and delivers the brand’s narrative. That’s when the rendering comes to life in the viewer’s mind.
About the Author: Matthew Clarey is the New York office Art Director at Neoscape, a 20-year-old creative studio that specializes in artwork for the built environment. Clarey has worked as a 3D artist for more than a decade.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Dec 14, 2017
Top 150 BIM design firms
Jacobs, Gensler, and WSP top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest BIM design firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
BIM and Information Technology | Dec 12, 2017
Reflecting on the future of work
'I believe in the potential for new technology to positively impact the quality of the built environment with immense speed and great efficiency,' writes Proving Ground's Nathan Miller.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Nov 30, 2017
A million small connections: Designing the new NY bridge
New York’s Tappan Zee Bridge first opened to traffic in 1955.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Nov 8, 2017
3 ways to protect your firm from cyber threats
While AEC firms may not have the vast quantity of financial information that certain other types of businesses do, the confidential and sensitive information your firm has can be just as damaging to your clients if it gets into the wrong hands.
Augmented Reality | Nov 6, 2017
Three VR + AR innovations to watch
From heat mapping to VR-based meetings, check out this trio of virtual and augmented reality applications for AEC teams.
Sponsored | Building Team | Nov 3, 2017
4 strategies for marketing your AEC firm
Having a clearly defined competitive brand and a fine-tuned marketing approach can give your firm a significant competitive advantage.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 18, 2017
Project Frog announces Autodesk investment
Autodesk’s investment in Project Frog creates a common data environment, streamlines design and engineering processes, and optimizes architectural design for manufacturing.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 12, 2017
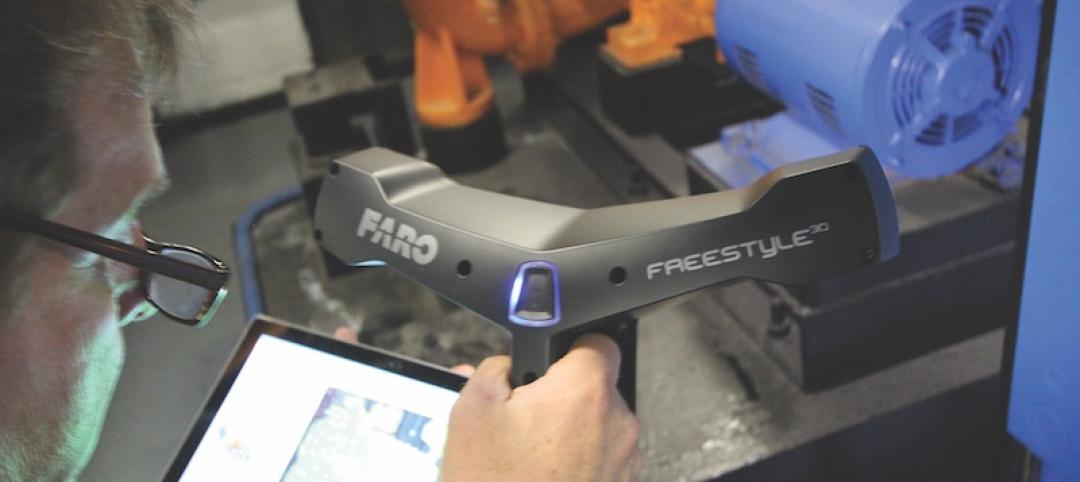
Laser scanners go handheld
The emergence of handheld 3D laser scanners has been a boon for firms looking to lower costs and speed up turnaround time.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Oct 10, 2017
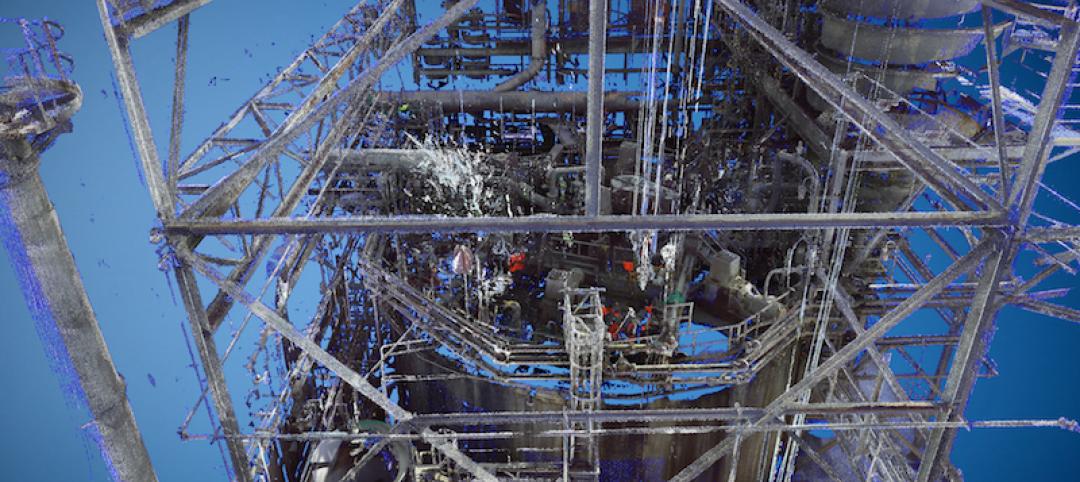
Moody Engineering, Inc. utilizes 3D scanner to meet challenges of phosphoric acid tank remodel
By integrating creativity and ingenuity with practicality, the Moody team was able to address the project’s specific requirements in order to save the customer time and money on this challenging project.
AEC Tech | Oct 6, 2017
How professional bias can sabotage industry transformation
Professional bias can take the form of change-resistant thinking that can keep transformational or innovative ambitions at bay. Tech consultant Nate Miller presents three kinds of bias that often emerge when a professional is confronted with new technology.