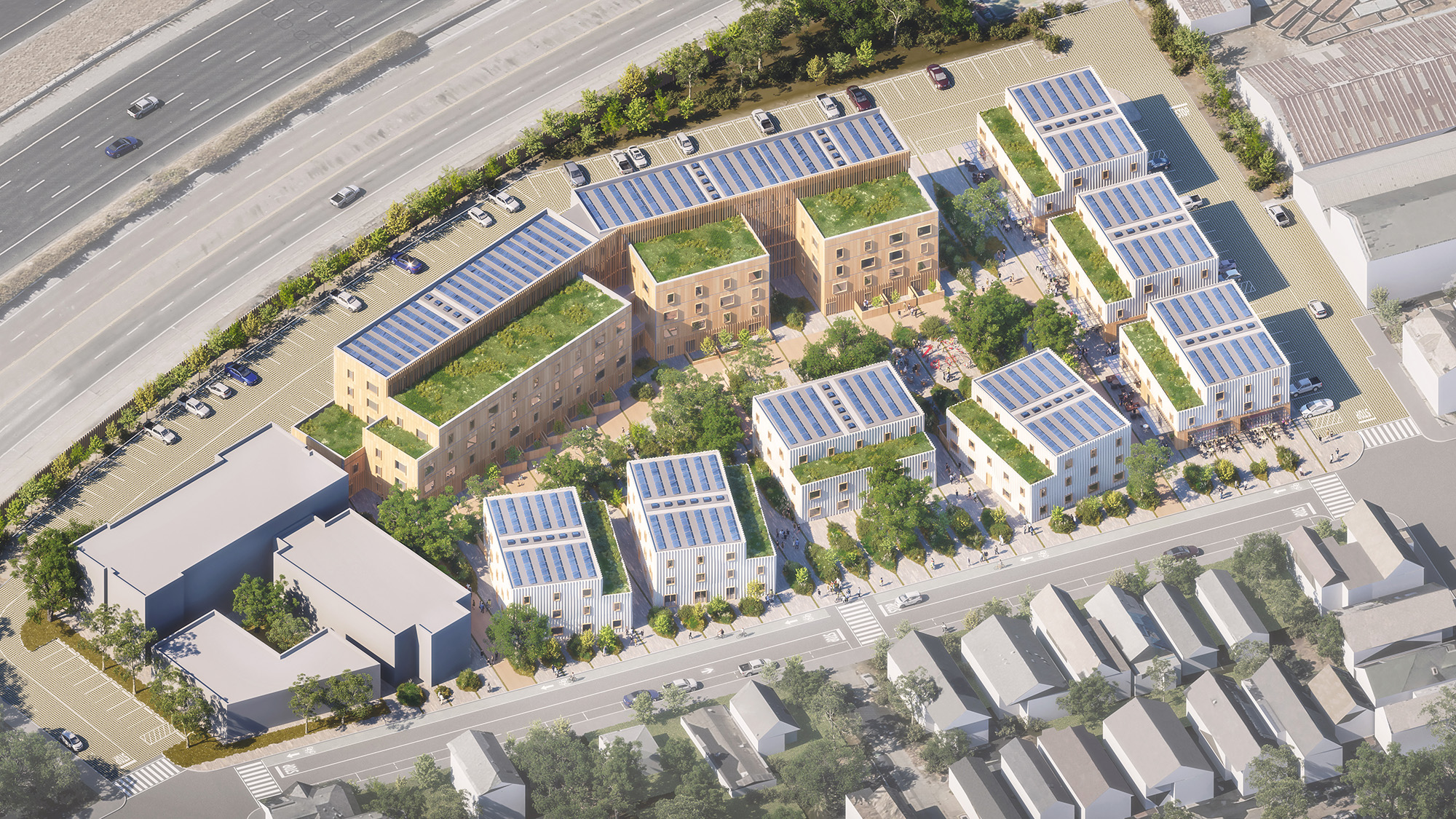
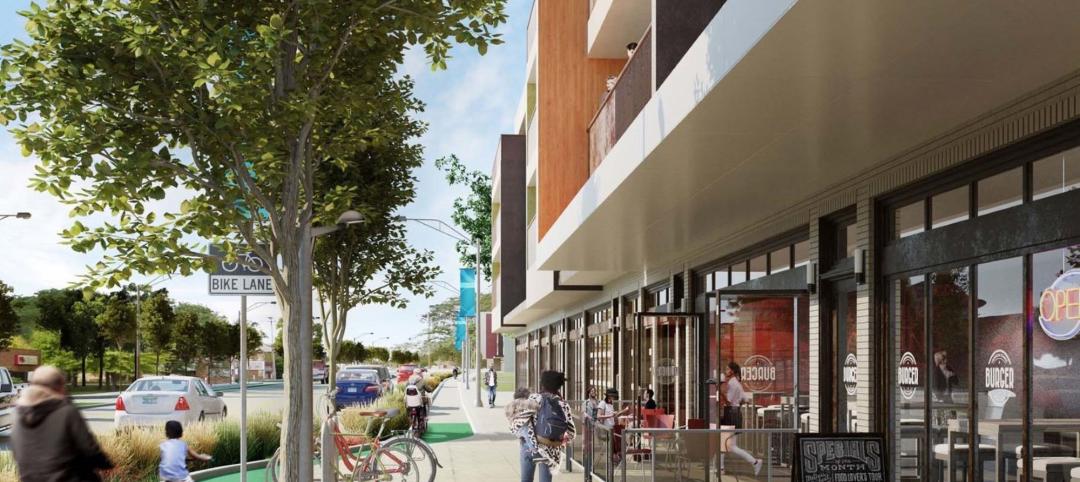
The phoenix: a mythological bird that symbolizes resurrection, rebirth, and life after death. Demolished in 1989, The Phoenix Ironworks Steel Factory left a five-acre hole in West Oakland, Calif. After sitting vacant for nearly three decades, the site will soon become utilized again as The Phoenix rises from the ashes—this time in the form of 316 affordable housing units.
In a collaboration between MBH Architects, modular construction company Factory_OS, technology provider Autodesk, bio-materials company Ecovative, building envelope consultant Heintges, and fabricator Kreysler & Associates, The Phoenix aims to be a revolutionary development made possible through groundbreaking biomaterials, innovative building methods, and Autodesk’s Design and Make Platform, which connected these teams and their data through cloud-based workflows and provided AI-powered insights.
AI Brings Affordable Housing Project to Life
In the case of The Phoenix, AI played a heavy role in optimizing the design of the affordable housing development.
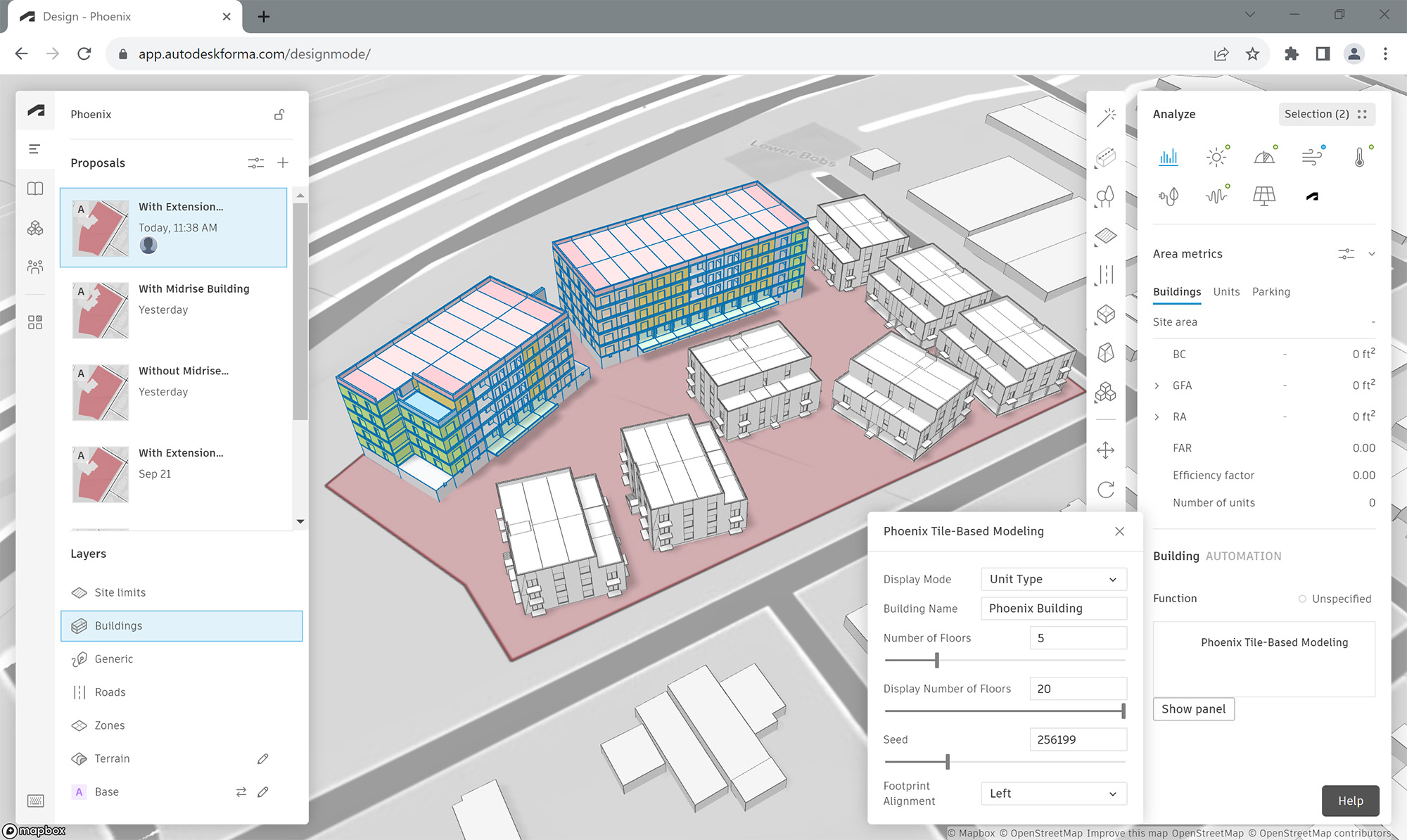
The team used Autodesk Forma in early-stage design to “rapidly explore a wide range of design options that would simultaneously meet the project’s goals for cost, carbon, and livability,” according to David Benjamin, Director, AEC Industry Futures at Autodesk.
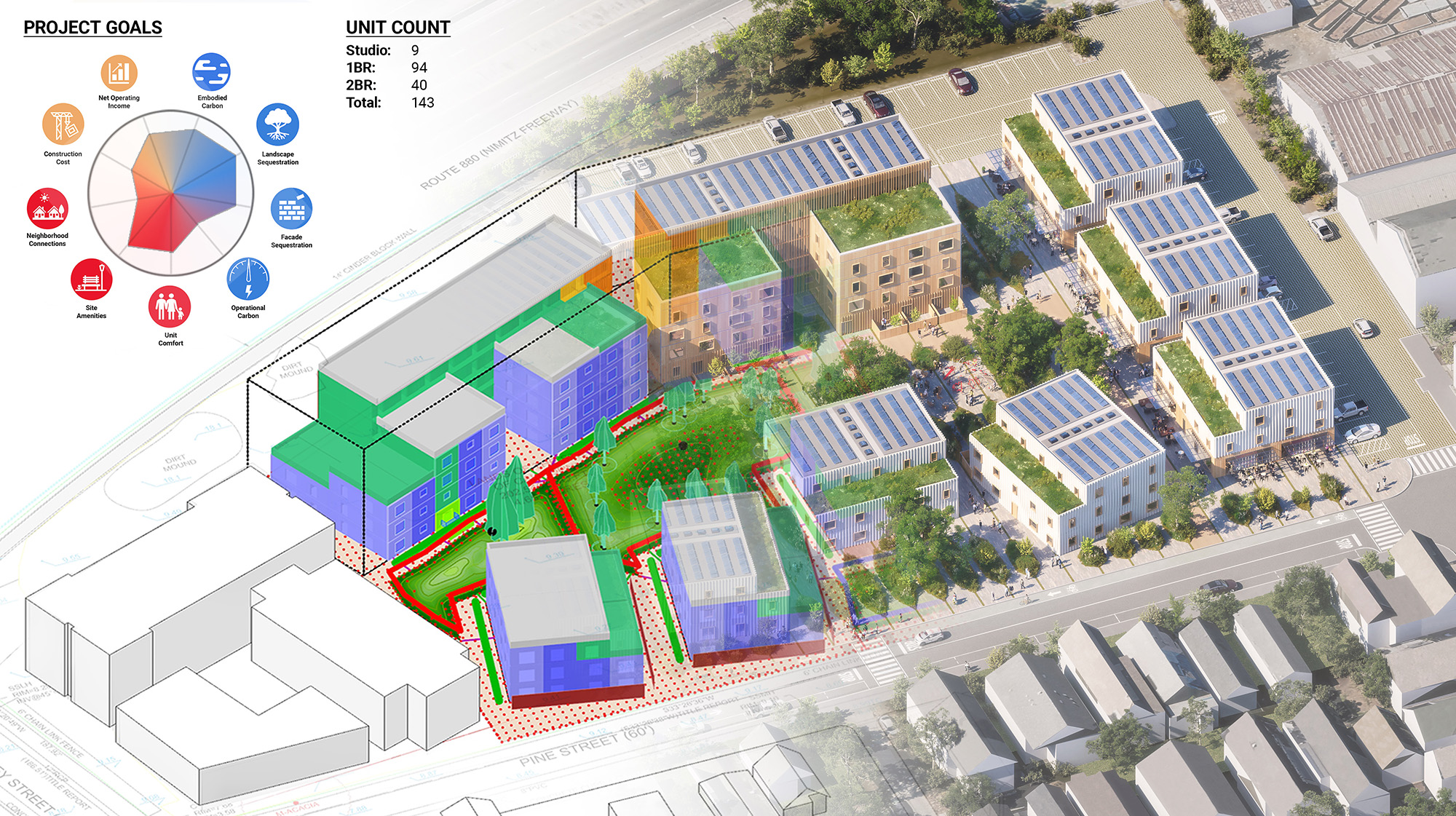
These capabilities allowed MBH to adjust and analyze different multifamily designs—such as adding buildings, or moving around structures and greenspaces—to find the most optimal layout.
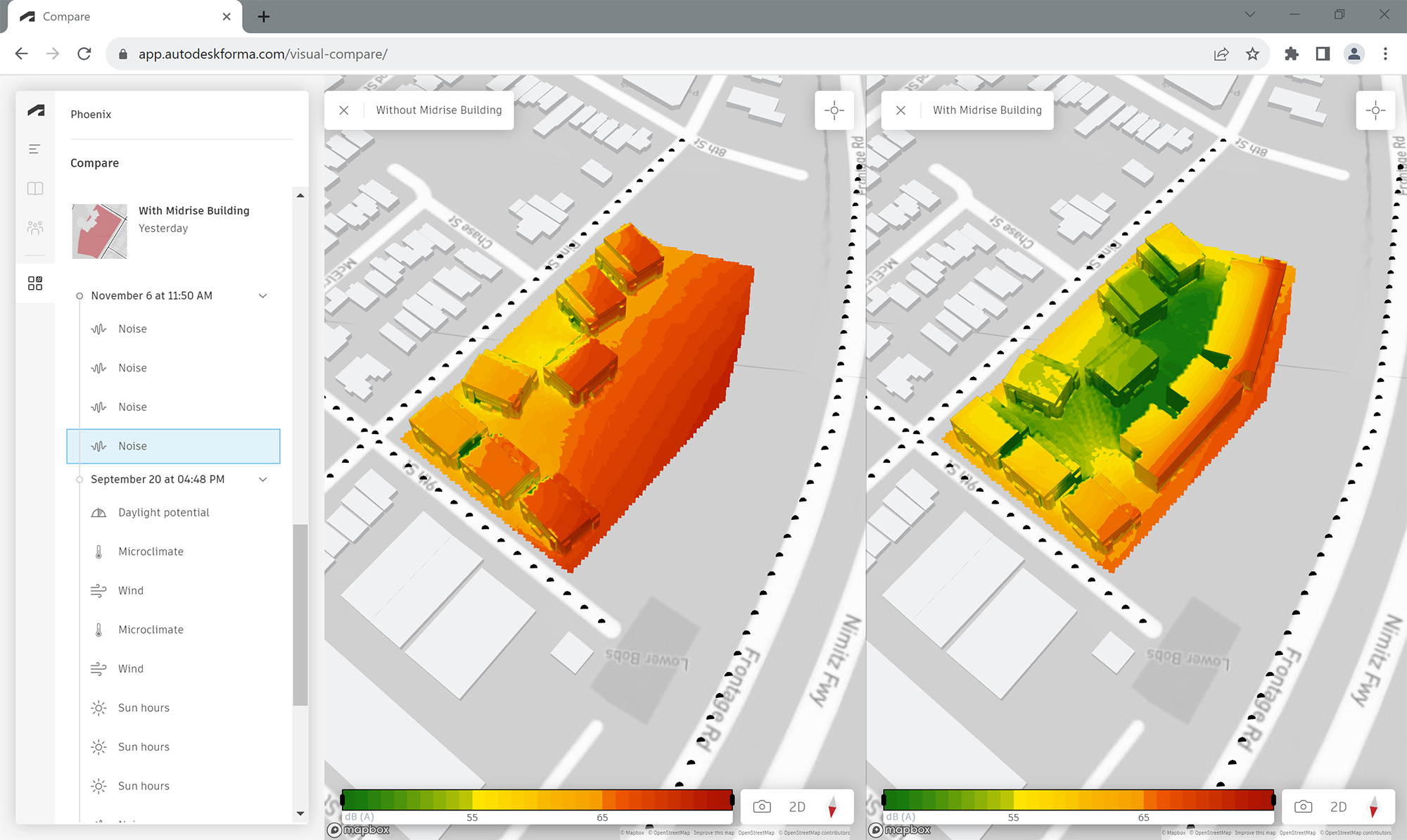
One analysis the project team did was to test how different building configurations were affected by noise from nearby highway traffic. With Autodesk Forma’s AI-powered tool, Rapid Noise Analysis, MBH Architects could optimize the final placement of structures on the building site to minimize noise. By using this technology MBH could explore the range of options and was able to complete an initial design package in just six hours—compared to the typical timeframe of two weeks.
“Time saving is probably the biggest benefit of [AI] tools, which enable us to ensure faster delivery of much-needed housing solutions,” says Ryan McNulty, Principal, Architect, MBH Architects.
Autodesk Forma was also used to measure goals for operational and embodied carbon, cost, and livability. The tool helped the team iterate on various designs like relocating playgrounds or shifting buildings to land on a final design that met the needs of the developer, the community, and stakeholders.
 |  |
Through this process, The Phoenix is projected to be completed in half the time, cost, and carbon footprint of a typical multifamily housing project in the Bay Area, which made the project eligible for state incentives, according to McNulty. While AI and cloud-based workflows supplied ample time-saving benefits on the front end, volumetric modular construction will present additional cost-effective opportunities once on-site construction begins.
Modular Construction with Innovative Biomaterials
Manufactured by Factory_OS, the modular units of The Phoenix can be assembled in just 10 days, according to MBH. Though this modular construction method speeds up project delivery, reduces waste, and removes the unpredictability of a traditional construction, it’s not without risk. Efficiently wrapping the modular units to ensure the building becomes weather-tight is “an ongoing design challenge,” says McNulty.
While standardizing window sizes has improved efficiency in building unit fabrication, incorporating prefabricated exterior panels introduces a new layer of complexity. The team is focused on systematizing various elements like windows and FRP panels to enable façade prefabrication.
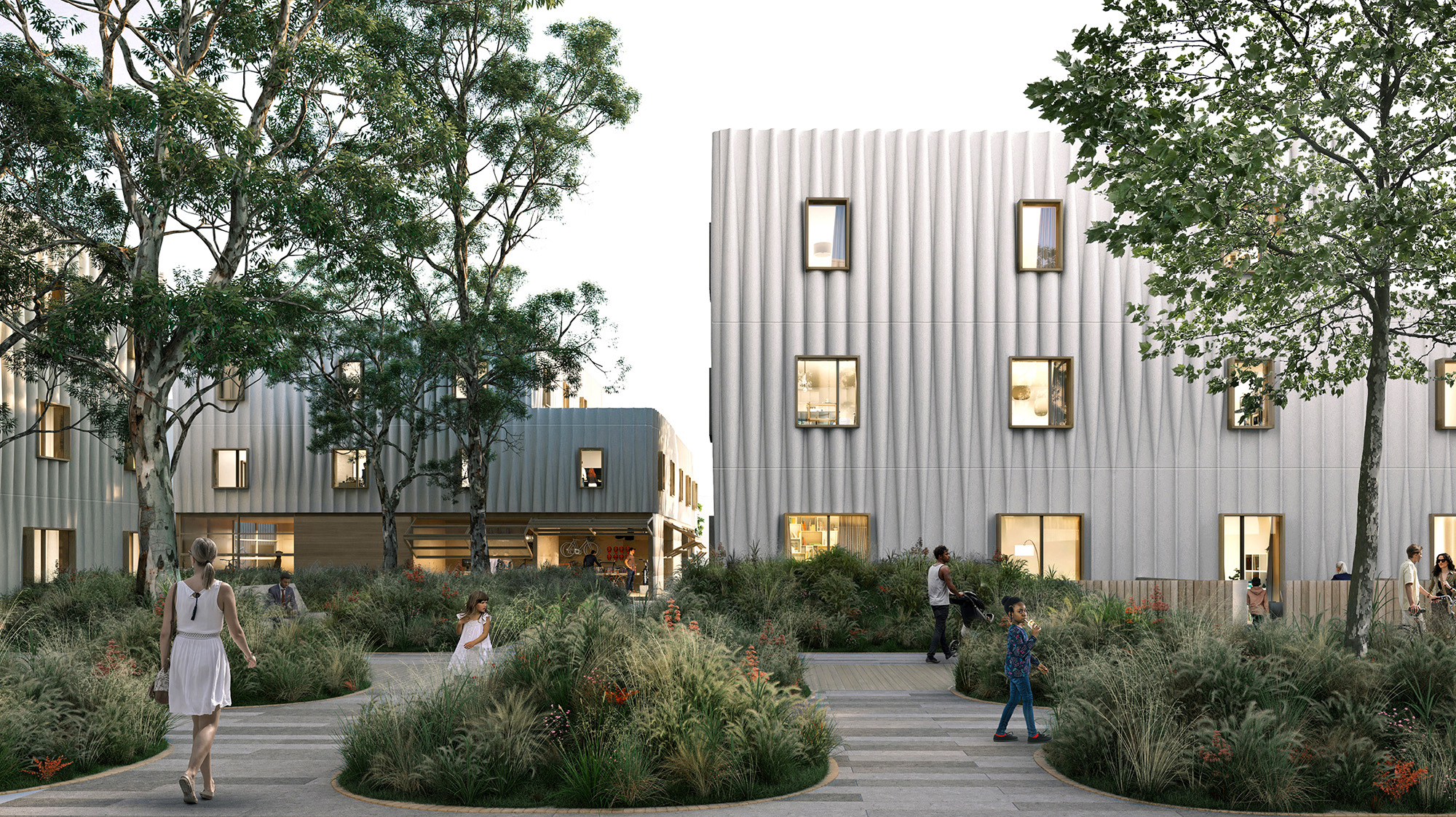

The façade presented an additional challenge for the team, as building façades often account for a significant portion of embodied carbon and can take months to install. Rather than take a traditional route, The Phoenix team turned to an innovative, sustainable biomaterial called MycoComposite to form the core of the façade.
Created by Ecovative, MycoComposite is a combination of mycelium—the living root structure of mushrooms—and shredded hemp stalks. Ecovative grows the material in just seven days, which absorbs more carbon than it emits, before forming the core to a fiber-reinforced-polymer shell. The Phoenix team used this to create 36-foot-long panels that act as the building’s carbon-negative façade.
These MycoComposite panels offer five performance benefits: structural, waterproofing, acoustic dampening, thermal insulation, and fire resistance. According to MBH, they can be used as-is with today’s building codes and construction methods.
The use of MycoComposite for The Phoenix marks the first use of the biomaterial in a commercial or residential building. Its use will shave another five months off the construction schedule as well, according to MBH.
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | Oct 28, 2024
A case for mid-rise: How multifamily housing can reshape our cities
Often referred to as “five-over-ones,” the mid-rise apartment type is typically comprised of five stories of apartments on top of a concrete “podium” of ground-floor retail. The main criticism of the “five-over-one” is that they are often too predictable.
Adaptive Reuse | Oct 22, 2024
Adaptive reuse project transforms 1840s-era mill building into rental housing
A recently opened multifamily property in Lawrence, Mass., is an adaptive reuse of an 1840s-era mill building. Stone Mill Lofts is one of the first all-electric mixed-income multifamily properties in Massachusetts. The all-electric building meets ambitious modern energy codes and stringent National Park Service historic preservation guidelines.
MFPRO+ News | Oct 22, 2024
Project financing tempers robust demand for multifamily housing
AEC Giants with multifamily practices report that the sector has been struggling over the past year, despite the high demand for housing, especially affordable products.
MFPRO+ Research | Oct 15, 2024
Multifamily rents drop in September 2024
The average multifamily rent fell by $3 in September to $1,750, while year-over-year growth was unchanged at 0.9 percent.
Affordable Housing | Oct 4, 2024
3 new affordable housing projects for October 2024
As affordable housing continues to grow, more projects are looking to diversify their footprint by adding mixed-use components, community areas, and more.
MFPRO+ News | Sep 24, 2024
Major Massachusetts housing law aims to build or save 65,000 multifamily and single-family homes
Massachusetts Gov. Maura Healey recently signed far-reaching legislation to boost housing production and address the high cost of housing in the Bay State. The Affordable Homes Act aims to build or save 65,000 homes through $5.1 billion in spending and 49 policy initiatives.
Adaptive Reuse | Sep 12, 2024
White paper on office-to-residential conversions released by IAPMO
IAPMO has published a new white paper titled “Adaptive Reuse: Converting Offices to Multi-Residential Family,” a comprehensive analysis of addressing housing shortages through the conversion of office spaces into residential units.
Legislation | Sep 9, 2024
Efforts to encourage more housing projects on California coast stall
A movement to encourage more housing projects along the California coast has stalled out in the California legislature. Earlier this year, lawmakers, with the backing of some housing activists, introduced a series of bills aimed at making it easier to build apartments and accessory dwelling units along California’s highly regulated coast.
Resiliency | Sep 3, 2024
Phius introduces retrofit standard for more resilient buildings
Phius recently released, REVIVE 2024, a retrofit standard for more resilient buildings. The standard focuses on resilience against grid outages by ensuring structures remain habitable for at least a week during extreme weather events.
Adaptive Reuse | Aug 29, 2024
More than 1.2 billion sf of office space have strong potential for residential conversion
More than 1.2 billion sf of U.S. office space—14.8% of the nation’s total—have strong potential for conversion to residential use, according to real estate software and services firm Yardi. Yardi’s new Conversion Feasibility Index scores office buildings on their suitability for multifamily conversion.


















