Hospital noise can be an insidious seed planted in a patient’s memory.
“They will recall extraordinary acts of kindness and consideration. However, they will also remember the agony of not being able to sleep, and hearing the nurses and others laughing just beyond their door,” says Chris Kay, ACHE, Managing Principal–National Healthcare & Science Buildings Practice at engineering giant Jacobs.
Some patients are bothered by noise that others shrug off. Volume isn’t necessarily the key factor. That’s the “noise conundrum,” says Kay. Every hospital has its own “culture” of loudness and quiet.
Kay says noise can impact patients through sleep deprivation, greater anxiety, and heightened blood pressure, respiration, and heart rates. It can also affect hospital workers, adding to their stress, lowering their ability to concentrate, and possibly leading to medical and nursing errors.
Kay offers steps to a therapeutic auditory environment:
1. Keep assessing your facility’s noise status. Hospital administrators and clinical staffs can become oblivious to daily noise patterns. They need to stop and listen to determine how loud is loud from the standpoint of patients, families, and visitors.
2. Establish relevant sound standards. EPA noise standards from the 1970s are out of date, says Kay. Any current sound standard needs to reflect the normal functioning of the facility and the needs of patients. That means going beyond decibel measurements and getting personnel involved in monitoring and modeling behavior that results in a healing environment.
3. Set noise impact standards for equipment purchases. For example, if a hospital plans to purchase a portable MRI, it should know beforehand where it’s going to be used, who will actually use it, and its impact on hospital noise.
4. Place nonclinical equipment in appropriate locations. In addition to the beep-beep of clinical and monitoring equipment, patients are bombarded with noise from vacuum cleaners, TVs, ice-making machines, and so on. Decide where and when such devices can be used around patients. “Housekeeping and nursing must bond to care for patients,” Kay notes.
5. Design spaces for sound control. Kay recommends that hospitals retain a noise control engineer to help find and mitigate “erratic” sounds. Spaces should also be retrofitted with acoustic materials that have high sound transmission ratings.
6. Engage and educate staff. Don’t blame the staff for being noisy; instead, make it a matter of patient care and professionalism. Emphasize that excessive noise shows a lack of respect for patients and their families. Whether it’s a door that slams or a cell phone that rings when it shouldn’t, hospitals need to “reclaim the sacred relationship and sacred space for healing,” says Kay.
7. Measure results. Collect data on how such metrics as patients’ complaints, calls for assistance at night, and request for pain medication correlate with noise levels on patient floors.
Related Stories
| Jun 6, 2012
KLMK Group awarded contract with Parkland Health & Hospital System in Texas
KLMK will also provide planning guidance in all aspects of the project related to facility activation.
| Jun 1, 2012
New BD+C University Course on Insulated Metal Panels available
By completing this course, you earn 1.0 HSW/SD AIA Learning Units.
| Jun 1, 2012
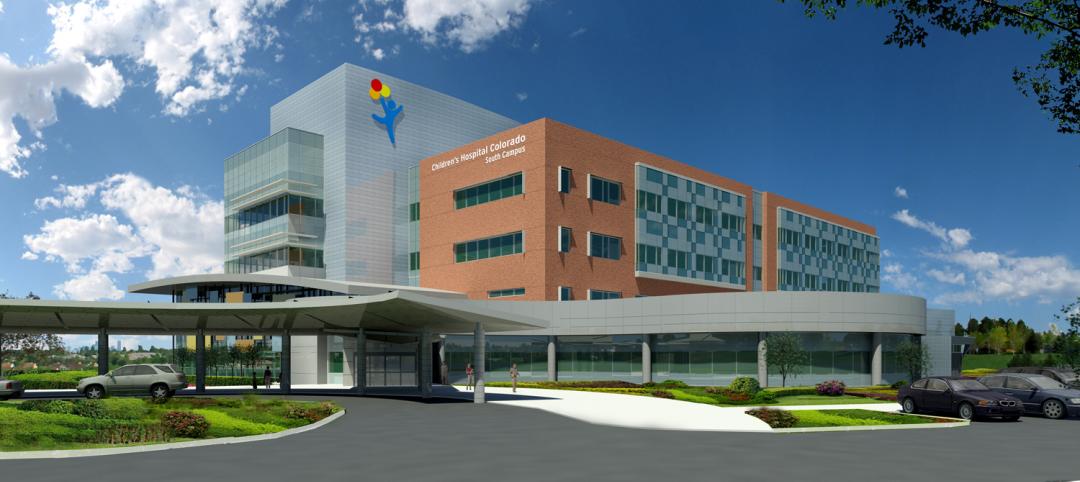
Ground broken for Children’s Hospital Colorado South Campus
Children’s Hospital Colorado expects to host nearly 80,000 patient visits at the South Campus during its first year.
| Jun 1, 2012
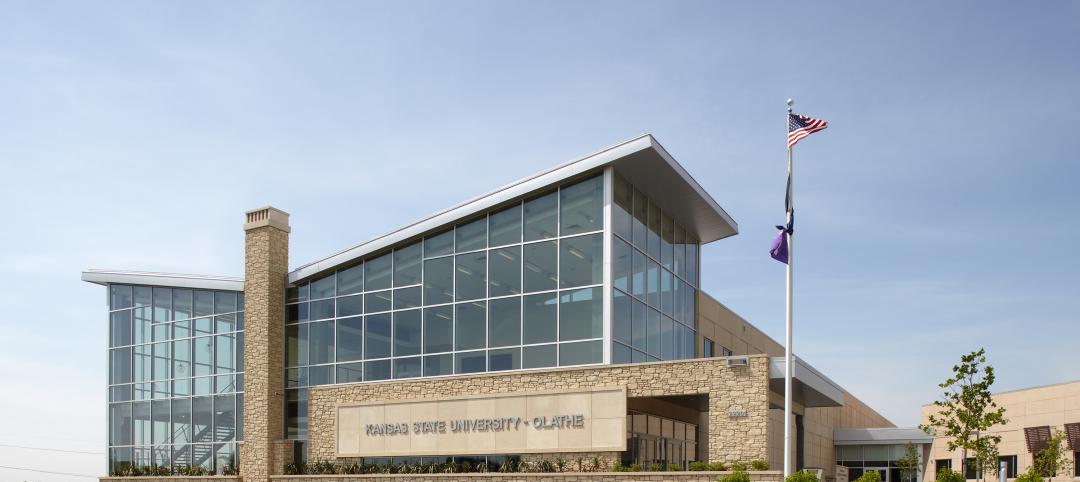
K-State Olathe Innovation Campus receives LEED Silver
Aspects of the design included a curtain wall and punched openings allowing natural light deep into the building, regional materials were used, which minimized the need for heavy hauling, and much of the final material included pre and post-consumer recycled content.
| May 31, 2012
5 military construction trends
Defense spending may be down somewhat, but there’s still plenty of project dollars out there if you know where to look.
| May 29, 2012
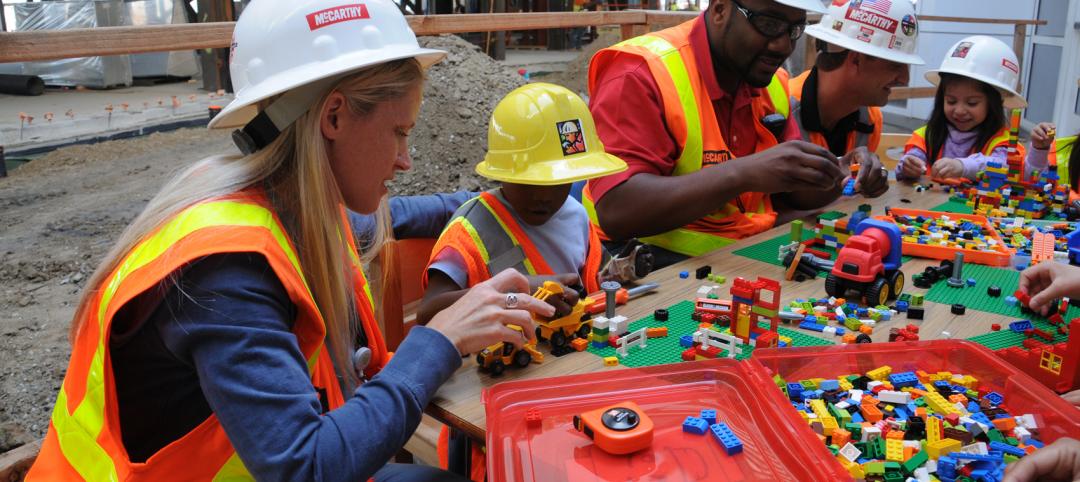
Torrance Memorial Medical Center’s pediatric burn patients create their version of new Patient Tower using Legos
McCarthy workers joined the patients, donning construction gear and hard hats, to help with their building efforts.
| May 29, 2012
Reconstruction Awards Entry Information
Download a PDF of the Entry Information at the bottom of this page.
| May 24, 2012
2012 Reconstruction Awards Entry Form
Download a PDF of the Entry Form at the bottom of this page.
| May 23, 2012
New hospitals invest in data centers to manage growth in patient info
Silver Cross became one of the first hospitals to install patient tracking software so families know where a patient is at all times. New communication equipment supports wireless voice and data networks throughout the hospital, providing access to patients and their families while freeing clinicians to use phones and computers where needed instead of based on location.
| May 22, 2012
Batson-Cook names Partin VP of Business Development
Partin joins general contractor from Georgia Hospital Association.