Thermal bridging has a huge effect on energy efficiency in windows. Designers typically try to specify thermally broken or thermally improved window frames, only to be forced by budget constraints to settle for standard frames.
The determination of the age and make of a window should provide some idea as to whether the frame has a thermal break, says George M. Blackburn III, AIA, NCARB, who chairs the Dallas Building Enclosure Council and serves on the national board of the Building Enclosure Technology & Environment Council.
A visual inspection of the window is often sufficient to determine the condition and degree of any deterioration, defects, or damage, and whether the glass is single pane or insulated, he says.
Many existing steel and aluminum sashes were not originally configured with a thermal break. Furthermore, says Jonathan A. Morris, AIA, of Carmine Wood Morris. It’s “nearly impossible” to add thermal breaks into an existing framing system, as the area of cold aluminum is so small in relation to the glass area. When full replacement is not an option, you’ll have to settle for insulating the glass.
In the case of fixed-glass commercial windows, there are companies that can custom manufacture a retrofit glazing insert over the existing window that will provide a thermal break and insulating air space between the existing glass, says Blackburn. This can be installed on either the interior or exterior and is less expensive than a complete replacement of the existing window.
Kevin Kalata, with Wiss, Janney, Elstner Associates, offers these tips to control thermal bridging:
1. Align the thermal breaks in the frames with the insulating glass unit.
2. For storefronts, use thermally broken subsill members. Subsills are required at the base of storefront systems for drainage of water that penetrates into the system. Thermally improved subsills may use vinyl or other low-conductive materials for subsill end dams when thermally broken dams are not available.
3. For curtain walls, maximize the thermal separation distance between the aluminum pressure plate and structural mullion. Where higher thermal performance is needed, consider using fiberglass or vinyl pressure plates and spacers in lieu of aluminum plates.
4. Use insulated glass units for both vision and spandrel areas. Stainless steel or thermally broken “warm-edge” spacers are often used as a means of reducing thermal bridging effects between the glass lites. Other options for improved thermal performance include triple-glazed window units or vacuum-insulated glass. Spandrel glazing options for higher thermal performance also include the use of vacuum-insulated panels that are sandwiched between the exterior glass lite and the interior metal facer.
5. Align the thermal break in the window system as closely as possible with the insulation in the surrounding wall assembly. Offsets between insulation layers and thermal breaks in windows can provide a heat flow path or thermal bridge. Give careful consideration to the placement of the window within the opening in order to minimize thermal bridging effects.
6. Provide adequate separation between perimeter claddings and the window system to minimize direct heat loss. Attachment clips or angles should be located on the inboard side of the thermal break as well as the inboard side of the perimeter wall construction insulating layer, where possible. Never extend clip supports across the thermal break.
7. Provide thermal breaks in all perimeter flashings or trim that surround the window. Flashings and trim should not extend beyond the thermal break in the window system. Flashing extensions are often created by preformed silicone sheets or membrane flashings.
8. Apply an air barrier at the perimeter of the window system that is integrated with the surrounding wall system. Air flow around the frames from the exterior or from cavities within the wall system that are vented to the exterior can reduce the performance benefit of thermal breaks.
Related Stories
| Sep 22, 2014
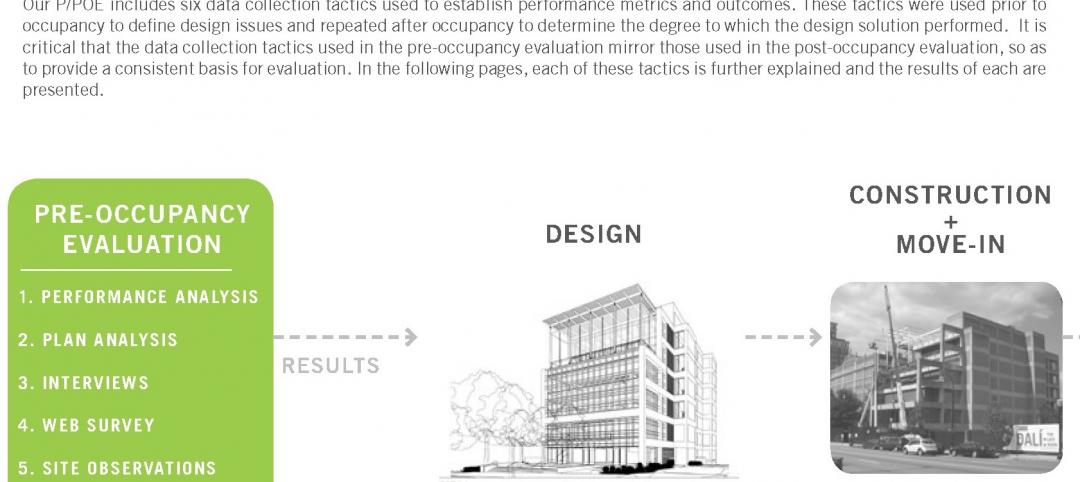
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 15, 2014
Ranked: Top international AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Parsons Brinckerhoff, Gensler, and Jacobs top BD+C's rankings of U.S.-based design and construction firms with the most revenue from international projects, as reported in the 2014 Giants 300 Report.
| Sep 9, 2014
Using Facebook to transform workplace design
As part of our ongoing studies of how building design influences human behavior in today’s social media-driven world, HOK’s workplace strategists had an idea: Leverage the power of social media to collect data about how people feel about their workplaces and the type of spaces they need to succeed.
| Sep 8, 2014
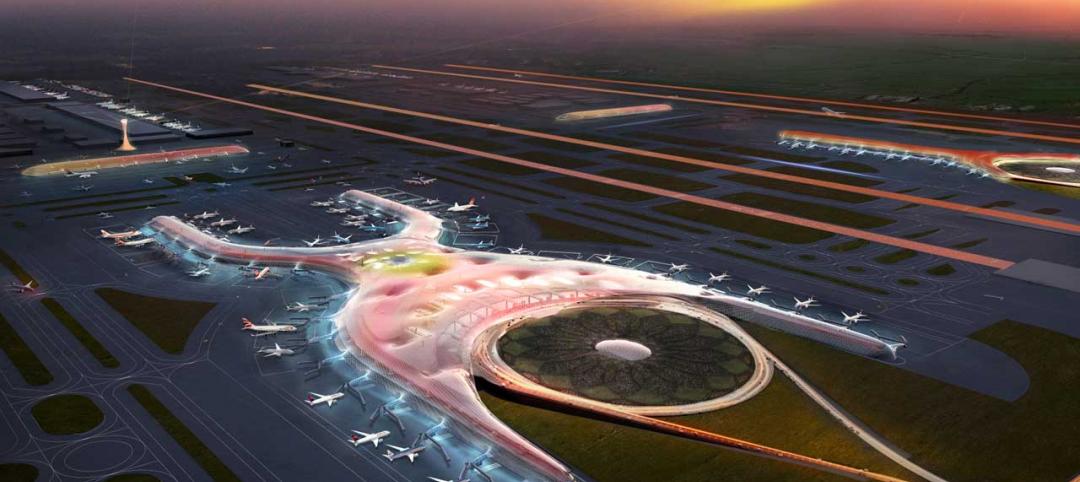
First Look: Foster + Partners, Fernando Romero win competition for Mexico City's newest international airport
Designed to be the world’s most sustainable airport, the plan uses a single, compact terminal scheme in lieu of a cluster of buildings, offering shorter walking distances and fewer level changes, and eliminating the need for trains and tunnels.
| Sep 3, 2014
New designation launched to streamline LEED review process
The LEED Proven Provider designation is designed to minimize the need for additional work during the project review process.
| Sep 2, 2014
Ranked: Top green building sector AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
AECOM, Gensler, and Turner top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest green design and construction firms.
| Sep 1, 2014
Ranked: Top federal government sector AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Clark Group, Fluor, and HOK top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest federal government design and construction firms, as reported in the 2014 Giants 300 Report.
| Aug 19, 2014
HOK to acquire 360 Architecture
Expected to be finalized by the end of October, the acquisition of 360 Architecture will provide immediate benefits to both firms’ clients worldwide as HOK re-enters the sports and entertainment market.
| Aug 11, 2014
Air Terminal Sector Giants: Morphing TSA procedures shape terminal design [2014 Giants 300 Report]
The recent evolution of airport terminals has been prompted largely by different patterns of passenger behavior in a post-9/11 world, according to BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 Report.