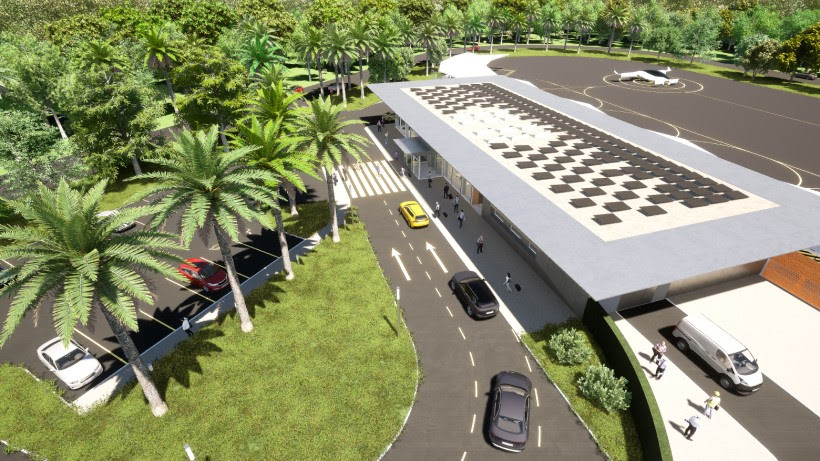
AECOM and Ferrovial have partnered to design a network of vertiports that will connect strategic locations in major Florida cities. Vertiports are a key component in enabling innovation in electric vertical take off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft by providing the necessary infrastructure for landing, recharging, and departure.
The vertiporm infrastructure emphasizes sustainability and efficiency by taking advantage of sunlight and natural elements. Noise abatement materials and surfaces are a key feature of the airfield design in order to further reduce the already ultra-low noise emissions from eVTOL jets. The veriport terminal buildings will provide a user-friendly passenger experience by enabling touches processes, quick journeys, and a comfortable environment.
"It is important for us that the design of the vertiport infrastructure reflects the innovative nature of the eVTOL crafts while creating a warm, welcoming environment,” said Elisabeth Bernitt, Senior Vice President and Managing Principal with AECOM’s Buildings + Places business, in a release. “By incorporating flexible and modular elements our partners will be able to scale the vertiports with growth, permitting an efficient space that allows for future innovation while emphasizing the passenger experience.”
The Ferrovial and AECOM-designed vertiporm infrastructure will help enable a high-speed, environmentally friendly, affordable alternative transport system that will connect Florida’s cities in new, sustainable, and more convenient ways.
Related Stories
| Jun 30, 2014
Research finds continued growth of design-build throughout United States
New research findings indicate that for the first time more than half of projects above $10 million are being completed through design-build project delivery.
| Jun 30, 2014
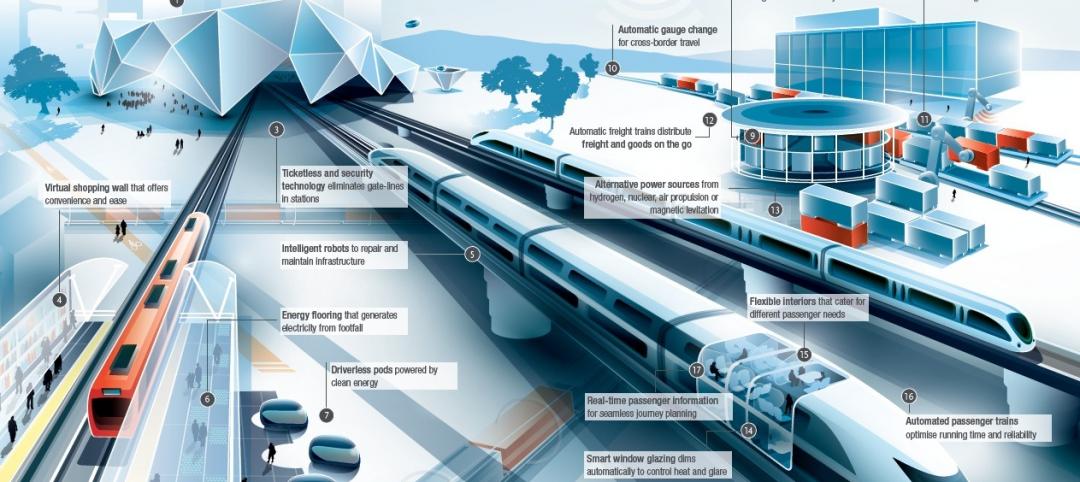
Arup's vision of the future of rail: driverless trains, maintenance drones, and automatic freight delivery
In its Future of Rail 2050 report, Arup reveals a vision of the future of rail travel in light of trends such as urban population growth, climate change, and emerging technologies.
| Jun 18, 2014
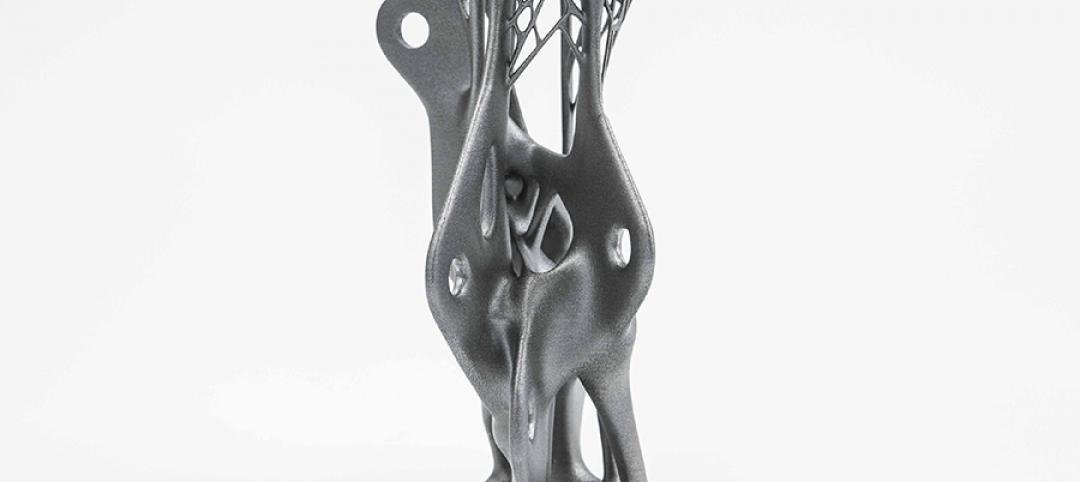
Arup uses 3D printing to fabricate one-of-a-kind structural steel components
The firm's research shows that 3D printing has the potential to reduce costs, cut waste, and slash the carbon footprint of the construction sector.
| Jun 12, 2014
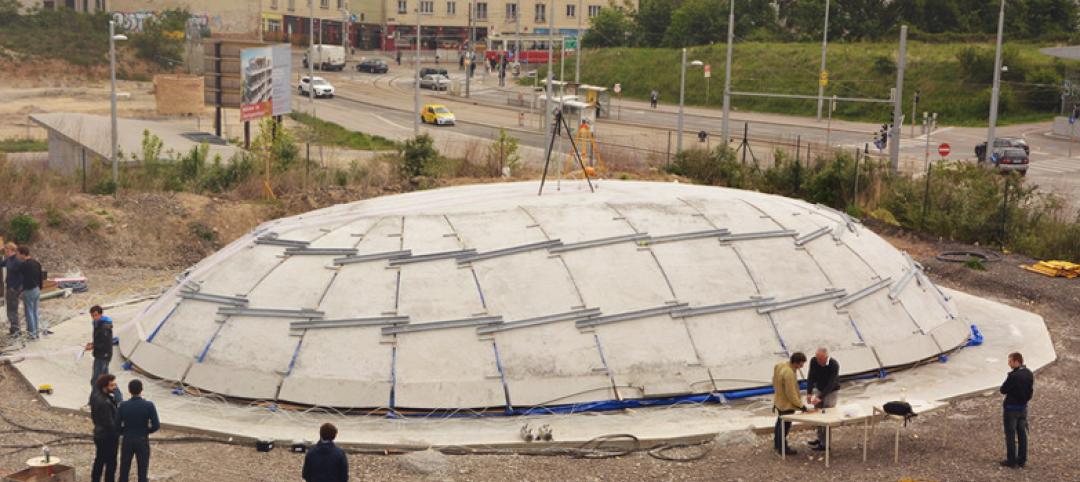
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 6, 2014
Shipping container ship terminal completed in Spain
In Seville, Spain, architectural firms Hombre de Piedra and Buró4 have designed and completed a cruise ship terminal out of used shipping containers.
| Jun 2, 2014
Parking structures group launches LEED-type program for parking garages
The Green Parking Council, an affiliate of the International Parking Institute, has launched the Green Garage Certification program, the parking industry equivalent of LEED certification.
| Jun 2, 2014
SOM unveils plans for Miami transit hub
The elevated station will be a key portal within All Aboard Florida’s rail system, the nation's only privately owned, operated, and financed rail network.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.