Last month, one of the world's most well-known retailers filed for bankruptcy. Barneys is almost 100 years old and will close 15 of its 22 stores as part of a major restructure, and they aren’t alone. Barneys is among dozens of other retailers filing for bankruptcy this year. The question is, how do landlords transform this valuable empty space? The solution lies in repurposing existing square footage.
Brick-and-mortar environments can no longer offer consumers a singular purpose. Developments must be multi-functional destinations, hybrid facilities that support retail’s changing landscape and benefit the consumer, retailer, and the developer. The goal is to create physical environments that offer both a differentiated customer experience but also one that allows for faster product access.
With a national vacancy rate over 10% and a market that’s inundated with empty anchor space, the challenge will be to repurpose these once thriving mall beacons to become multi-purpose destinations that are both functional and still aesthetically pleasing for developers and remaining anchor tenants. The solution for dark anchors should not be to simply "plug the hole" with traditional solutions, but to look toward "out-of-the-box" concepts. A more innovative distribution center concept can offer a longer-lasting, versatile solution focusing on engagement, helping with supply chain, and better addressing today’s speed of transaction. The ideal repurposed distribution center offers three distinct uses.
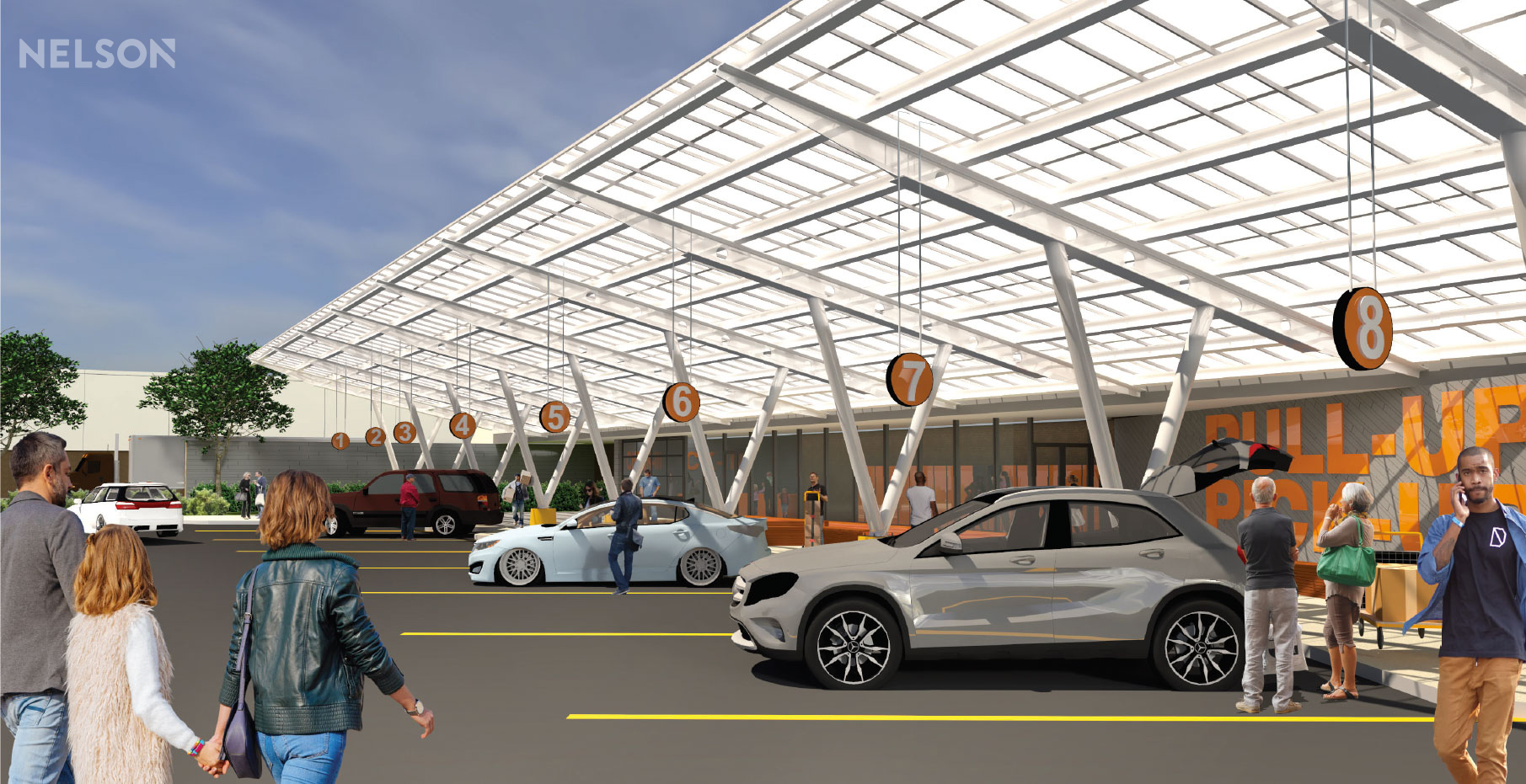
First, is a warehouse “lite” facility offering last-mile delivery services – a smaller format transportation hub focusing on last-mile logistics to deliver items to the end user as fast as possible. The repurposed distribution center could leverage key elements from previous anchors, like the loading dock, receiving area and freight elevators. And keeping truck traffic to the backside of the development, ideally with a separate entrance, prevents a disruption to guest traffic flow.
Next, a robust click-and-collect facility, from parcel lockers to drive-through pick-ups, it will allow customers, as well as third-party delivery vendors, faster access to merchandise. This could also support newer concepts like cloud kitchens that rely on multiple delivery providers and a seamless pick-up process. Supporting new business-models from BOPIS to ridesharing, will keep the concept fresh and flexible, to support the growing ecommerce market.
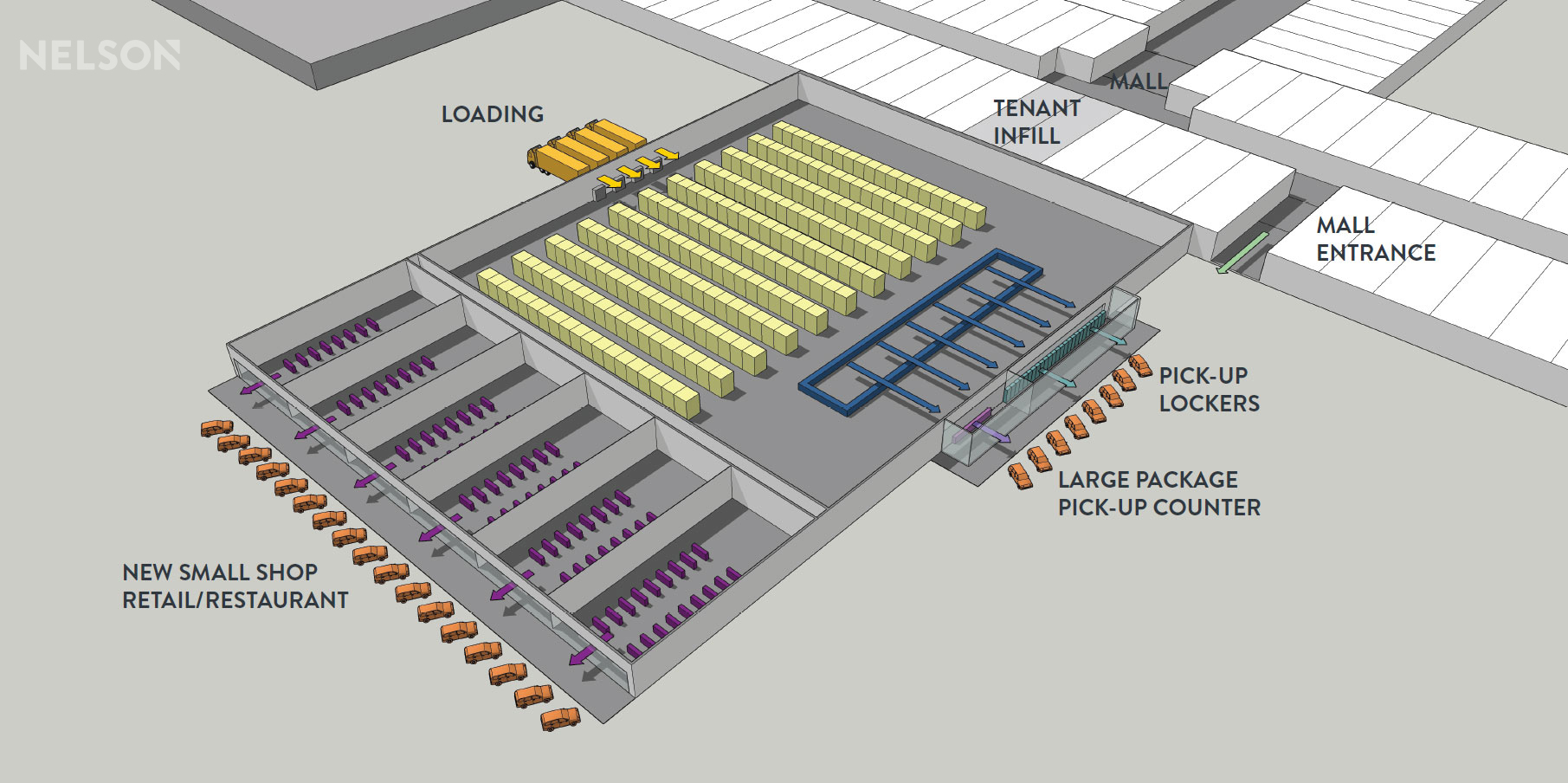 One solution for dark anchors is to convert them to warehouse “lite” facilities, which offer last-mile delivery services. The repurposed distribution center could leverage key elements from previous anchors, like the loading dock, receiving area and freight elevators. Rendering: NELSON
One solution for dark anchors is to convert them to warehouse “lite” facilities, which offer last-mile delivery services. The repurposed distribution center could leverage key elements from previous anchors, like the loading dock, receiving area and freight elevators. Rendering: NELSON
The third and final usage will be to leverage the street-facing facade for new, small format retail and restaurants. Providing unique localized offerings and a varied tenant mix will keep the development feeling current. These new consumer-facing environments should offer plenty of opportunities for consumer engagement and provide a new draw for legacy tenants within the development.
The refreshed exterior will help increase street traffic while creating an aesthetically pleasing façade to the much-needed back-of-house functions within the warehouse and click-and-collect environments. The small-format footprint could entice new offerings from start-ups to online-first retailers, providing developers and guests an elevated and differentiated experience.
This multi-faceted concept could support various industries beyond just traditional retail, such as breweries, beer distributers, and a consumer-facing beer garden or tasting room. With the rise of farm-to-table dining, it could be home to a grow house, farmers market, and signature-chef restaurant. Or even provide a footprint for cloud kitchens, a food truck park, and designated pick-up for food delivery apps. The options are endless when the concept supports consumers, ecommerce and supply chain.
Related content: In the age of Amazon there's nowhere to go but up
Moreover, many of today’s anchor spaces are large, unarticulated boxes that do not address today’s consumer needs and wants. The architecture is often forgettable and many of the exteriors haven’t been renovated since the original tenant opened their doors. This strategy may have been appropriate when most shopping centers were inward facing, enclosed malls, but today’s shoppers are looking for differentiated environments that not only speak to their unique communities, but also support their online habits to offer a more seamless, convenient experience.
So, while shopping centers have been turning inside out, replacing long stretches of back of house exterior walls with engaging outward facing tenant facades, the market has now created an opportunity for anchors to participate in this transformation.
This revolution starts with converting these unarticulated boxes into vibrant offerings that are approachable and engaging. Implementing a hybrid anchor solution provides a win for consumers, retailers, and developers, and will keep the space flexible for innovative new business models and functional for last-mile delivery opportunities. A new concept that merges experience with instant gratification to bring malls into the 21st century.
About the Author
Eric Arter leads the Mixed-Use studio at NELSON where he oversees a multi-disciplinary team serving both domestic and international clients including Simon, Brookfield, Unibail-Rodamco-Westfield, Macerich, Washington Prime Group, Cordish, Lotte and Hyundai Development Company. Eric has over 20 years of experience in mixed-use, retail, office, multifamily, hospitality, restaurant and entertainment projects as well as a background in institutional and industrial projects. Eric’s comprehensive experience and well-rounded skill set provides a unique understanding in support of a collaborative project approach. Projects in which he has played a key role have been the recipient of many awards throughout his career including: AIA Design & Honor Awards, NAIOP Awards and design competitions. Eric earned his Bachelor of Architecture degree from the University of Cincinnati. He is a registered architect, a member of the AIA, ICSC and he is a LEED accredited professional.
Related Stories
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
BIG’s One High Line finally reaches completion in New York City’s West Chelsea neighborhood
One High Line, a luxury residential project spanning a full city block in New York’s West Chelsea neighborhood, reached completion this summer following years of delays related to investor lawsuits.
Urban Planning | Oct 30, 2024
Bridging the gap: How early architect involvement can revolutionize a city’s capital improvement plans
Capital Improvement Plans (CIPs) typically span three to five years and outline future city projects and their costs. While they set the stage, the design and construction of these projects often extend beyond the CIP window, leading to a disconnect between the initial budget and evolving project scope. This can result in financial shortfalls, forcing cities to cut back on critical project features.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
Luxury waterfront tower in Brooklyn features East River and Manhattan skyline views
Leasing recently began for The Dupont, a 41-story luxury rental property along the Brooklyn, N.Y., waterfront. Located within the 22-acre Greenpoint Landing, where it overlooks the newly constructed Newtown Barge Park, the high-rise features East River and Manhattan skyline views along with 20,000 sf of indoor and outdoor communal space.
Libraries | Oct 30, 2024
Reasons to reinvent the Midcentury academic library
DLR Group's Interior Design Leader Gretchen Holy, Assoc. IIDA, shares the idea that a designer's responsibility to embrace a library’s history, respect its past, and create an environment that will serve student populations for the next 100 years.
Resiliency | Oct 29, 2024
Climate change degrades buildings slowly but steadily
While natural disasters such as hurricanes and wildfires can destroy buildings in minutes, other factors exacerbated by climate change degrade buildings more slowly but still cause costly damage.
Office Buildings | Oct 29, 2024
Editorial call for Office Building project case studies
BD+C editors are looking to feature a roundup of office building projects for 2024, including office-to-residential conversions. Deadline for submission: December 6, 2024.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 28, 2024
New surgical tower is largest addition to UNC Health campus in Chapel Hill
Construction on UNC Health’s North Carolina Surgical Hospital, the largest addition to the Chapel Hill campus since it was built in 1952, was recently completed. The seven-story, 375,000-sf structure houses 26 operating rooms, four of which are hybrid size to accommodate additional equipment and technology for newly developed procedures.
Multifamily Housing | Oct 28, 2024
A case for mid-rise: How multifamily housing can reshape our cities
Often referred to as “five-over-ones,” the mid-rise apartment type is typically comprised of five stories of apartments on top of a concrete “podium” of ground-floor retail. The main criticism of the “five-over-one” is that they are often too predictable.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Oct 24, 2024
Stadium renovation plans unveiled for Boston’s National Women’s Soccer League
A city-owned 75-year-old stadium in Boston’s historic Franklin Park will be renovated for a new National Women’s Soccer League team. The park, designed by Fredrick Law Olmsted in the 1880s, is the home of White Stadium, which was built in 1949 and has since fallen into disrepair.
Laboratories | Oct 23, 2024
From sterile to stimulating: The rise of community-centric life sciences campuses
To distinguish their life sciences campuses, developers are partnering with architectural and design firms to reimagine life sciences facilities as vibrant, welcoming destinations. By emphasizing four key elements—wellness, collaboration, biophilic design, and community integration—they are setting their properties apart.

















