Jim Wilson thinks that, in their haste to make their schools modern and efficient, some school districts are installing energy management systems that are overtaxing the ability of their maintenance staffs.
Wilson owns JFW Inc., a 25-year-old project management company in Gaithersburg, Md. Most of the K-12 work he does is with private schools like Sidwell Friends, the Quaker school that President Obama’s daughters attend. Wilson says that Sidwell’s middle school has 3,000 contact points that have to be monitored, which puts a significant burden on the facility’s maintenance staff.
He says energy codes keep raising the complexity level of what’s being installed. Maintenance crews are having trouble keeping up with EMS technology that has jumped by leaps and bounds over the past 10 years. “We didn’t have all of these [air exchange] requirements that we do now,” he says.
Wilson recounts one school’s head of maintenance who was so flummoxed by the facility’s systems that he operated the building as if it were occupied 24/7 so he didn’t have to deal with the controls. “I got a call from the school asking why its electric bills were running sky high,” says Wilson.
Jim Deluge, a Project Executive with Turner Construction, believes that maintenance staffs have a responsibility to “catch up” to the sophistication level of these new EMS systems. On the flip side, HMC Architects’ Sandy Kate thinks problems could be reduced if maintenance staff were included in early planning meetings before construction begins.
School district officials who recognize this potential problem but still want state-of-the-art operating systems will sometimes outsource the monitoring. DRL Group’s Jim French says his firm’s engineers have the ability to remotely monitor a client’s systems and let that school know almost immediately if anything’s askew.
“You have to be careful not to get too exotic,” says Fanning Howey’s Chuck Tyler. The design firm recently worked with a school district in Belleville, Mich., that demanded the systems for a 320,000-sf high school be simple enough for the district’s current maintenance personnel to manage.
Wilson contends that some schools simply don’t need the high-octane systems they specify. One project he worked on called for a $180,000 EMS. What ultimately got installed, he says, was a $40,000 system “that can do pretty much what’s needed in the building” and matches the skill set of the maintenance team.
When school districts demand the latest and greatest, they need to think about how those choices will impact the district’s facilities employees. On one recent project in Connecticut, Wilson had the contractor conduct six months of training sessions for the maintenance staff. “You can’t learn this stuff in two days of classes.”
Related Stories
| Jun 12, 2014
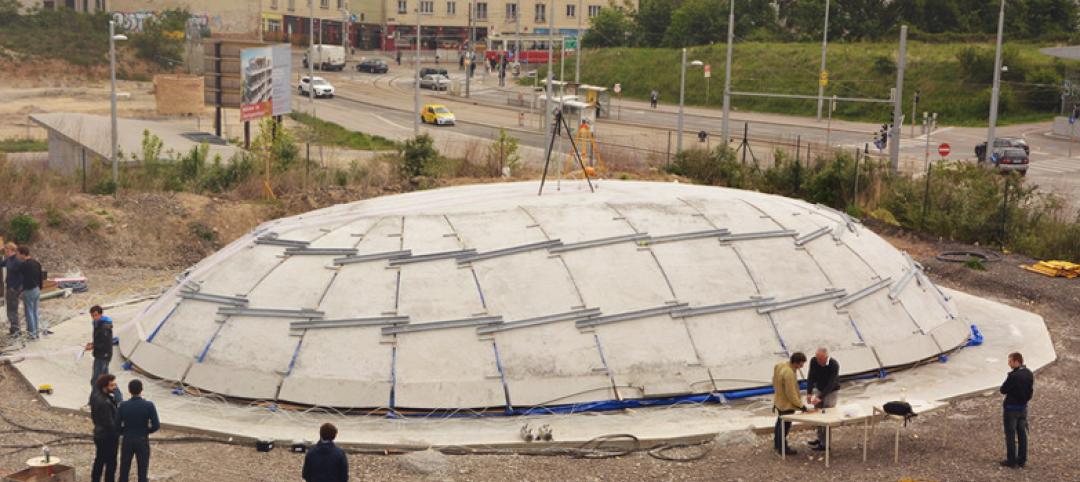
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 9, 2014
Green Building Initiative launches Green Globes for Sustainable Interiors program
The new program focuses exclusively on the sustainable design and construction of interior spaces in nonresidential buildings and can be pursued by both building owners and individual lessees of commercial spaces.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 23, 2014
Top interior design trends: Gensler, HOK, FXFOWLE, Mancini Duffy weigh in
Tech-friendly furniture, “live walls,” sit-stand desks, and circadian lighting are among the emerging trends identified by leading interior designers.
| May 22, 2014
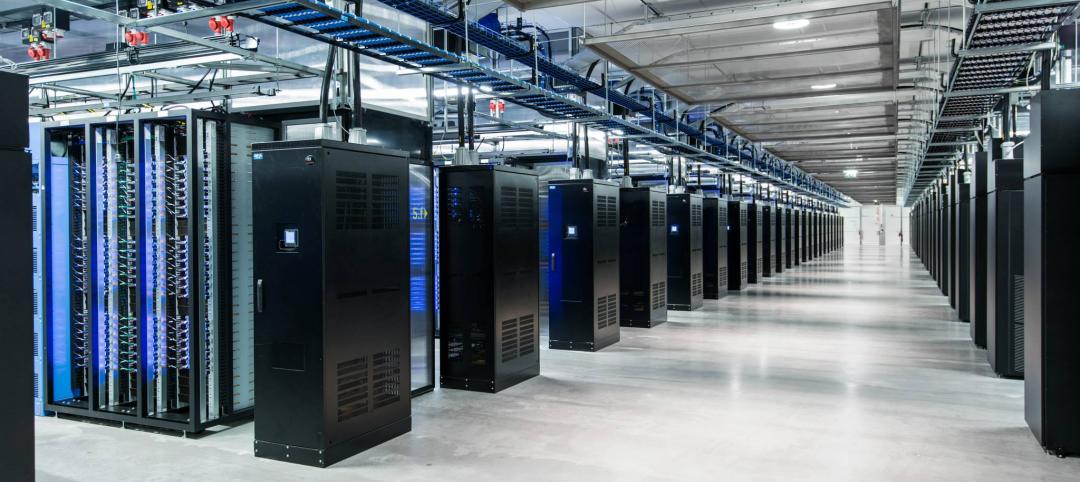
Big Data meets data centers – What the coming DCIM boom means to owners and Building Teams
The demand for sophisticated facility monitoring solutions has spurred a new market segment—data center infrastructure management (DCIM)—that is likely to impact the way data center projects are planned, designed, built, and operated.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 15, 2014
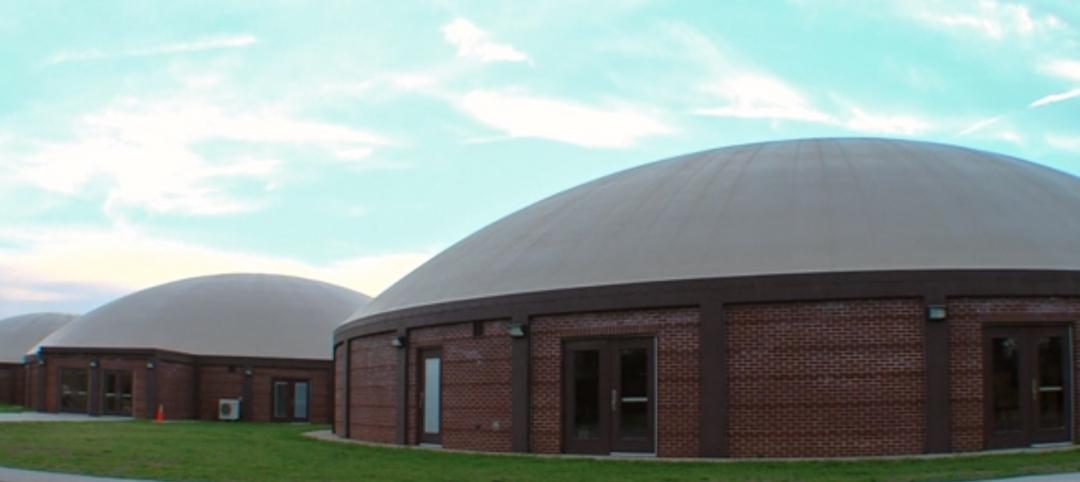
'Virtually indestructible': Utah architect applies thin-shell dome concept for safer schools
At $94 a square foot and "virtually indestructible," some school districts in Utah are opting to build concrete dome schools in lieu of traditional structures.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.