Since April, Arup, the global built environment consultant, has been gathering data on an undisclosed number of buildings it has worked as a prelude to its commitment, which commenced this month, to conduct whole lifecycle carbon assessments for all of its construction and renovation projects going forward.
Those assessments will attempt to estimate a building’s carbon emissions from pre- and post construction, and encompass such variables as manufacturing, transportation, materials selection, operations, and maintenance. Arup estimates that as much as half of a building’s lifecycle CO2 emissions is attributable to embodied carbon before the building is operational.
Arup’s goal through its commitment is to confidently advise its developer-owner clients, within budgetary and quality parameters, on what products for each of a building’s systems and subsystems will produce the least amount of carbon emissions during a building’s duration. “We’re attempting to build our insights so that CO2 becomes a performance metric,” explains Erin McConahey, PE, FASHRAE, Principal and Arup Fellow. What’s been lacking—and what Arup is trying to address with its assessments—has been a critical mass of data.
ASSESSMENTS REQUIRED MORE DATA
When it announced its commitment last November, Arup stated that fewer than 1 percent of building projects was evaluated to quantify carbon emissions over their lifecycles.
Adopting whole lifecycle carbon assessments is essential to Arup’s and the building sector’s shared ambition to reduce projects’ carbon emissions 50 percent by 2030. The insights gained from conducting thousands of whole lifecycle carbon assessments each year “will help the built environment sector advance toward net zero,” stated the firm, which is developing similar methodology to extend its assessments to its infrastructure work.
Using a digital platform it devised, hundreds of project teams at Arup have been collecting carbon data on several of its 1,300 projects that met certain dollar thresholds of activity within the last fiscal year, and on whose design Arup was directly involved, says McConahey. That platform leverages materials information from measuring tools such as the Embodied Carbon in Construction Calculator (EC3), whose database allows users to compare materials for their embodied carbon impact; and Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs), through which manufacturers present objective, third-party verified data to report on the impact of their products and services.
McConahey says that, at present, manufacturers “are the only source of truth” when it comes to lifecycle carbon assessments of their own products. She adds that more contractors are asking for EPDs as part of their bidding and estimating.
DESIGNING FOR CARBON REDUCTION
The data that Arup has been assembling will allow the firm to review and adjust its design practices “using carbon rules of thumb,” says McConahey. Early next year, Arup intends to share some of its top-line insights with the industry, with an aspiration of providing a blueprint for the built environment’s path toward net zero.
Arup’s commitment is part of an ever-growing focus on environmental, social, and governance topics and reporting for construction and engineering firms. “Health, safety and labor; contracts and competitive bidding; and carbon emissions from buildings and construction form the backbone of their ESG agendas,” wrote the accounting and management consultant EY in a paper it posted last November about the state of ESG in the engineering and construction industry.
That paper found that among the 24 engineering and construction companies reviewed, leaders were making disclosures against at least 20 of 24 metrics covering ESG issues. This level of transparency is being driven by investors that evaluate ESG performance on corporate disclosures; and by Millennial workers who are three times more likely to seek employment with a company because of its stances on environmental and/or social issues.
Related Stories
Green | Apr 27, 2016
Top 10 green building projects for 2016
The Exploratorium at Pier 15 in San Francisco and the West Branch of the Berkeley Public Library are two of the projects recognized by AIA COTE as the top green buildings of 2016.
Sponsored | Energy-Efficient Design | Mar 29, 2016
How long-term O&M combats complex climates
With the full O&M package, solar adopters are able to maximize return on investment, optimize system performance and minimize operating costs while controlling long-term costs.
Green | Feb 18, 2016
Best laid plans: Masdar City’s dreams of being the first net-zero city may have disappeared
The $22 billion experiment, to this point, has produced less than stellar results.
Energy-Efficient Design | Feb 18, 2016
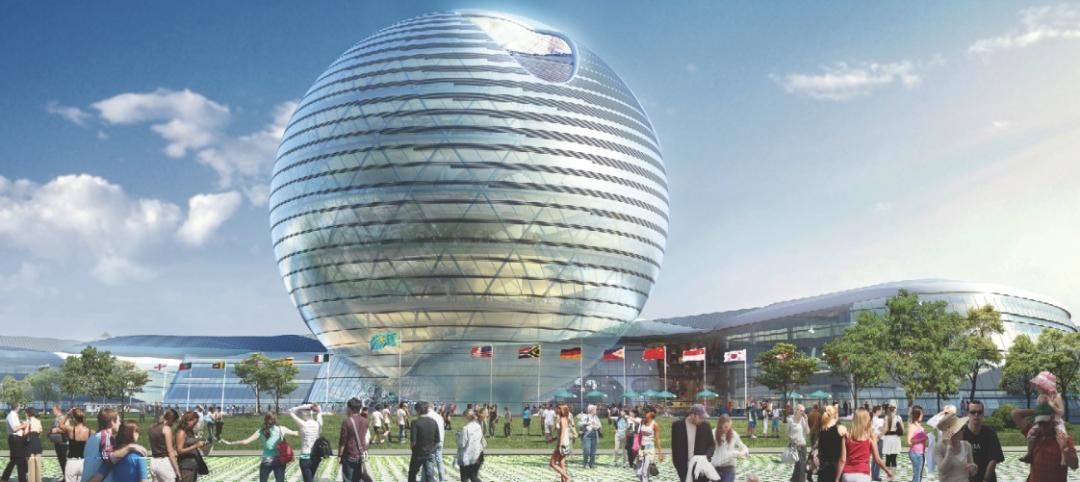
How to make a ‘pure’ glass sphere
Creating a 25-story energy-generating globe for Expo 2017 in Kazakhstan put Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture to the test.
Codes and Standards | Jan 22, 2016
State Savings Calculator analyzes savings associated with energy codes
The calculator breaks down the cost-effectiveness of energy codes on a state-by-state basis.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Jan 6, 2016
A solar canopy makes Miami’s arena more functional
NRG Energy teams with Miami Heat to transform an underused open-air plaza and reinforce the facility’s green reputation
BIM and Information Technology | Nov 18, 2015
AIA: Energy modeling key to reaching carbon neutrality in buildings
Energy modeling allows architects to be more ambitious with energy-saving in their design projects.
Energy-Efficient Design | Nov 2, 2015
Energy Department’s Building Technology Office seeks public input
Draft Multi-Year Program Plan available for review.
Energy-Efficient Design | Aug 31, 2015
South Carolina business school on track to be region’s first net-zero energy commercial building
The project is part of a large DOE initiative to develop more buildings that can generate as much energy as they consume.
Green | Jul 16, 2015
7 parking facilities first to earn Green Garage Certification
The new program rates parking structures based on 48 elements of operation, from water reuse to bicycle parking to car sharing options.