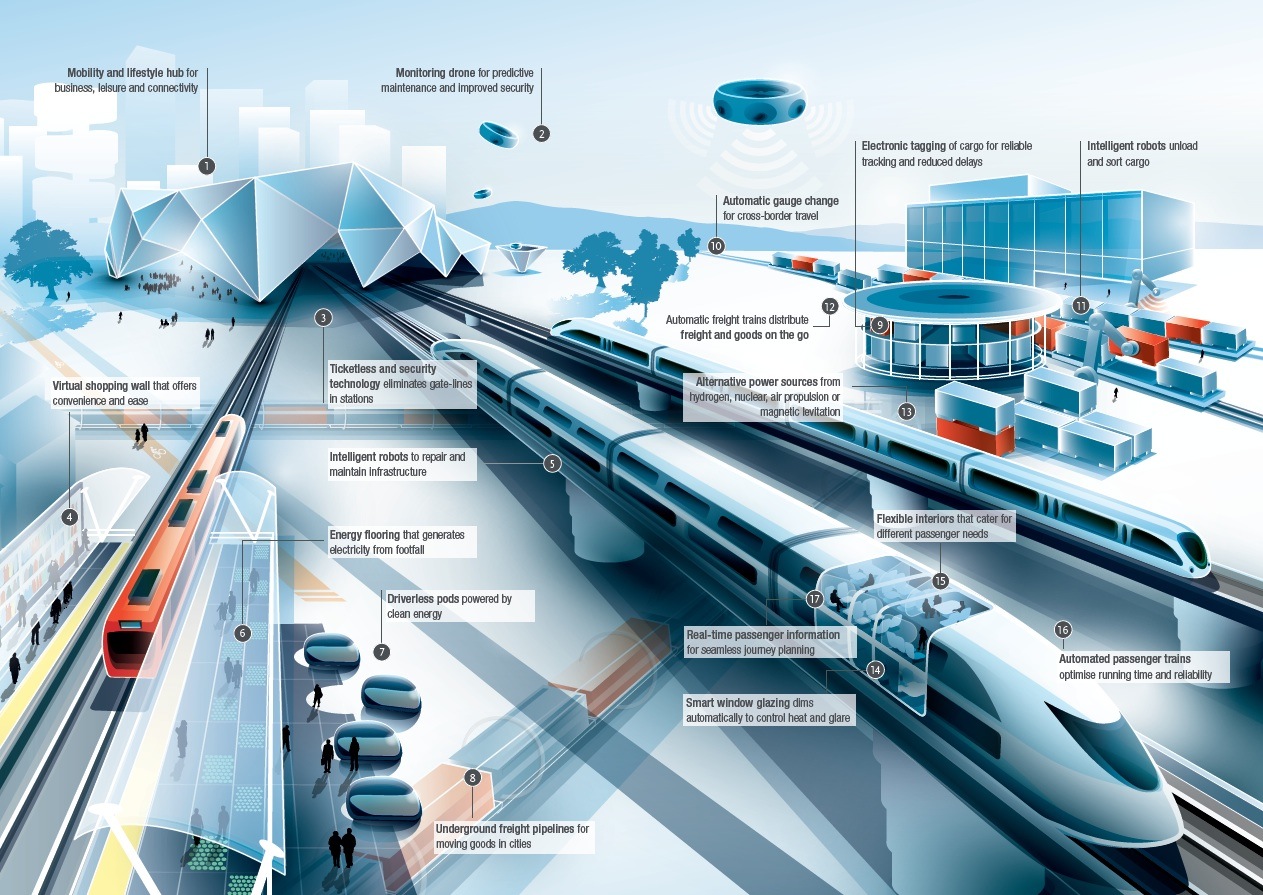
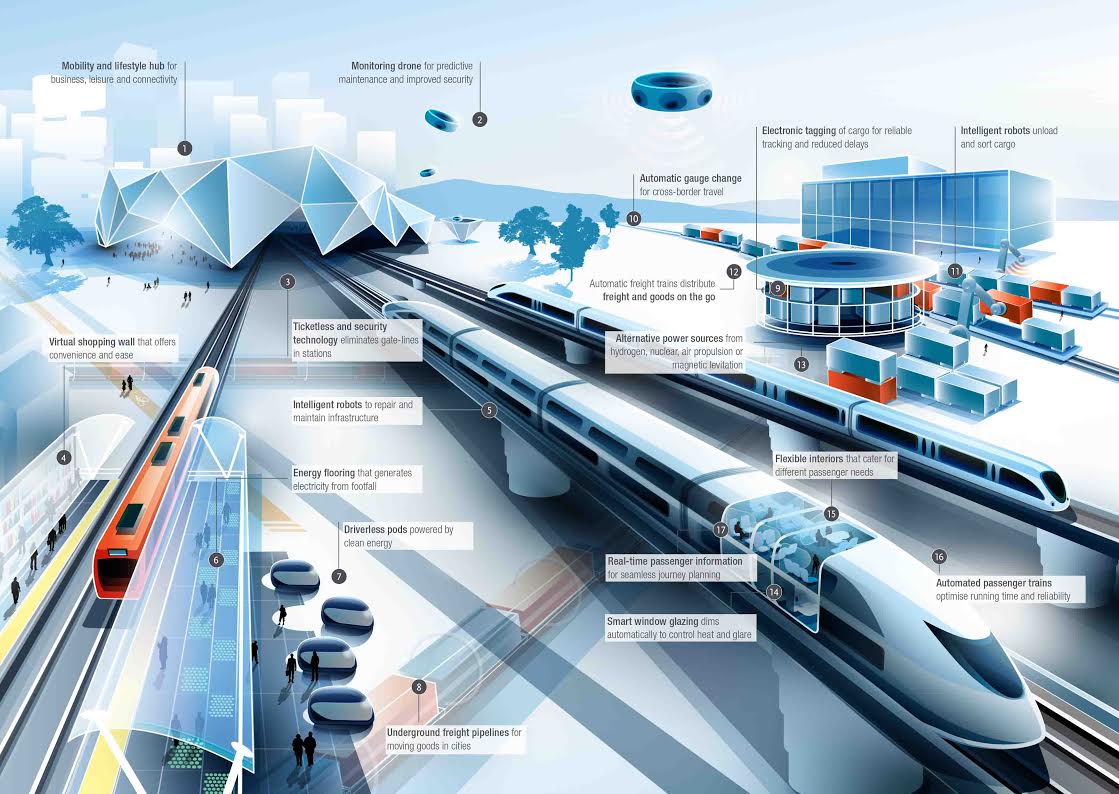
A new report by Arup reveals a vision of the future of rail travel in light of trends such as urban population growth, climate change and emerging technologies. Future of Rail 2050 foresees predictive maintenance of rail lines by robot drones, driverless trains travelling safely at high speed, freight delivered automatically to its destination, and smart technology able to interface with mobile and wearable devices to improve passenger experience and enable ticketless travel.
Arup has been involved in many of the world’s high speed rail, metro and driverless train projects including HS1 and Heathrow PRT in the UK and Cityringen Metro in Copenhagen, as well as the creation of Beijing South Railway Station and the redevelopment of St. Pancras International Station. The report is based on developments from current Arup rail projects, as well as insight from Arup’s Foresight + Research + Innovation team and global contributors.
Convenience: a reliable network
With the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, the report looks at future construction and maintenance techniques to reduce travel delays and shape railway resilience. It predicts intelligent robots building new, and retrofitting old rail infrastructure.
Swarm robotics, a theory based on swarm behavior amongst ant and bee colonies, could see small robots working collaboratively on major railway repair and structural testing. Monitoring drones would enable rail operators to perform advanced maintenance on tracks, eradicating lengthy journey delays and line closures.
To further increase efficiency and speed of travel, Future of Rail 2050 suggests that automated systems will optimise the running time of passenger trains and increase the reliability and safety of the network. Driverless trains, for example, would be in constant communication with one another with the sensors embedded in rail infrastructure, travelling in close succession and responding in real time to their location on a given track.
Freight activity, meanwhile, is due to increase globally by up to 250% by 2050, so improved transit times and reliability are key to increase efficiency and minimize congestion. The report foresees dedicated elevated platforms and underground pipelines to transport goods, freeing up rail and highway infrastructure for passenger travel.
Freight pipelines would use intelligent, aerodynamic pods and embedded sensors, to provide an energy efficient and low maintenance method of delivering goods in heavily populated urban areas.
Supporting the above are ongoing developments in nanotechnology, biotechnology, information technology and cognitive sciences, which will see new materials that are lighter, stronger, smarter and greener. Graphene, for example, is revolutionary in its flexibility, strength and conductivity and brings the potential for completely new, reliable rail structures and design.
Conurbations: integrated transport systems
To truly deliver a smooth, convenient passenger experience, rail needs to be fully integrated with other modes of transport – a possibility enabled, in part, by big data and the Internet of Things.
Greater internet connectivity will provide passengers with accurate, real-time updates on train times and connections to other transport modes, complete with optimum pricing.
Ticketless technology will remove gate-lines in stations. Authorisation to travel will be universal and payment processed automatically when the journey is taken, allowing a seamless connection between various modes of transport. This could be through interoperable electronic passes (valid for trains, businesses, car sharing schemes and bicycles) or through personal accounts which would authorise travel and automatically process payment – removing congestion at ticket barriers and eliminating unauthorised travel.
Personal rapid transport systems, powered by clean energy, could also provide the crucial last mile link in urban areas. These systems could, for example, use magnetic levitation to connect vehicles to a high-speed guideway, eliminating vibration, pollution, noise and the usual wear caused by moving parts. These automated systems would allow passengers to check emails or read the news while travelling to their final destination.
Connectivity: plugging into journeys
The convergence of mobile devices, big data, and wearable and location-aware technology are at the heart of improving passenger experience. As well as providing accurate, real-time travel information, high-performance networks will grant uninterrupted access to work and entertainment systems on the move.
The report imagines a future where train passengers can contact friends, family and colleagues via ‘HoloCalls’ (holographic image displays) and train windows will adjust automatically to prevent external glare. Virtual shopping walls will be located in train stations and even carriages themselves, enabling products from the wall displays to be purchased via mobile devices.
“The global urban population is growing rapidly and by 2050, around 75% of the world’s population will live in cities,” said Colin Stewart, Global Rail Leader, Arup. “This places huge pressure on transport infrastructure and resources, but also creates a significant opportunity for rail, which relies on passenger density to function most effectively. The challenge will lie in juggling the responsibility of providing reliable travel for millions while simultaneously tailoring each journey for the individual.
“However, by rapidly developing technology and taking bold steps to overcome capacity and cost challenges through maximising efficiencies , the rail renaissance can deliver a future where rail is the backbone of our travel system, linking major urban hubs and feeding into multi-modal transport networks for the benefit of the passenger.”
Check out the full report here, and a demonstrative infographic below:
Related Stories
| Jan 11, 2014
Getting to net-zero energy with brick masonry construction [AIA course]
When targeting net-zero energy performance, AEC professionals are advised to tackle energy demand first. This AIA course covers brick masonry's role in reducing energy consumption in buildings.
| Dec 13, 2013
Safe and sound: 10 solutions for fire and life safety
From a dual fire-CO detector to an aspiration-sensing fire alarm, BD+C editors present a roundup of new fire and life safety products and technologies.
| Dec 10, 2013
16 great solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
From a crowd-funded smart shovel to a why-didn’t-someone-do-this-sooner scheme for managing traffic in public restrooms, these ideas are noteworthy for creative problem-solving. Here are some of the most intriguing innovations the BD+C community has brought to our attention this year.
| Nov 27, 2013
Wonder walls: 13 choices for the building envelope
BD+C editors present a roundup of the latest technologies and applications in exterior wall systems, from a tapered metal wall installation in Oklahoma to a textured precast concrete solution in North Carolina.
| Nov 26, 2013
Construction costs rise for 22nd straight month in November
Construction costs in North America rose for the 22nd consecutive month in November as labor costs continued to increase, amid growing industry concern over the tight availability of skilled workers.
| Nov 25, 2013
Building Teams need to help owners avoid 'operational stray'
"Operational stray" occurs when a building’s MEP systems don’t work the way they should. Even the most well-designed and constructed building can stray from perfection—and that can cost the owner a ton in unnecessary utility costs. But help is on the way.
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 15, 2013
Metal makes its mark on interior spaces
Beyond its long-standing role as a preferred material for a building’s structure and roof, metal is making its mark on interior spaces as well.
| Nov 13, 2013
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Oct 30, 2013
11 hot BIM/VDC topics for 2013
If you like to geek out on building information modeling and virtual design and construction, you should enjoy this overview of the top BIM/VDC topics.