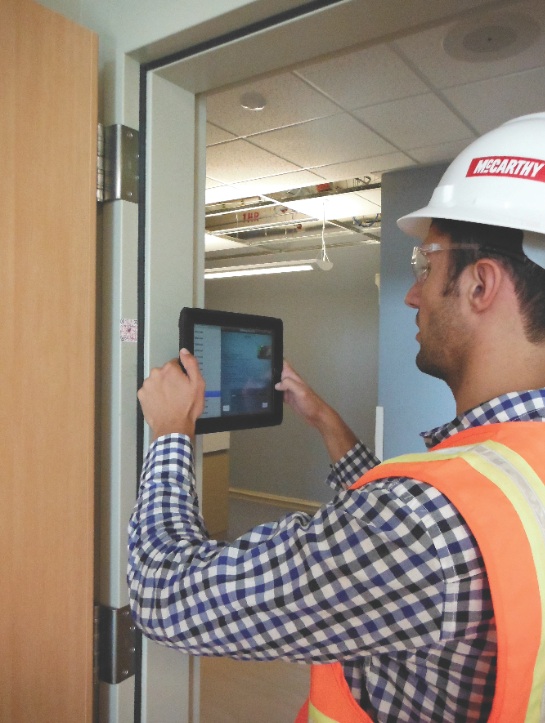
When Kaiser Permanente opens its massive, one-million-sf Oakland Medical Center Replacement Project early next year, staff, patients, and families may notice something peculiar about the place. Open almost any door in the complex and they’ll find a stamp-size, red-and-white emblem affixed to the hinge side of the doorjamb. A closer look will reveal the logo of McCarthy Building Companies at the center of the label.
No, this isn’t a sly branding scheme by the project’s general contractor. It’s a quick response (QR) code created for that specific location in the building—for use by both the Building Team during construction and Kaiser Permanente’s facilities team throughout the life of the buildings.
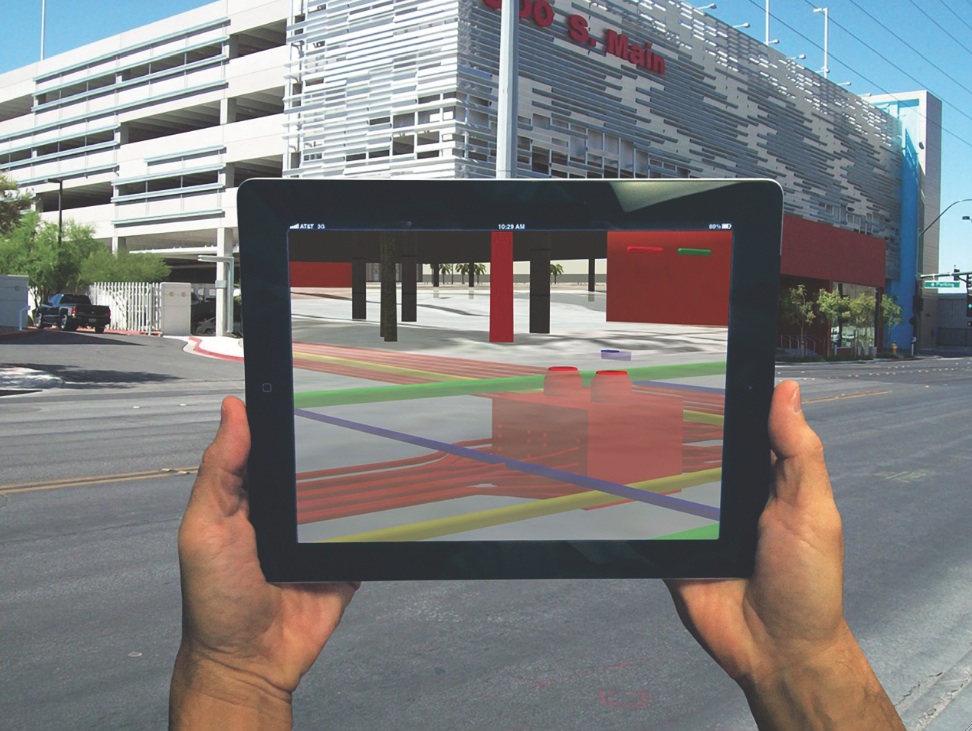
The QR codes are a vital component of one the largest implementations to date of augmented reality (AR) technology in the U.S. construction industry. At any given time, a project superintendent, subcontractor, architect, facilities team member, or other field personnel can scan one of the QR codes throughout the campus with a smartphone or tablet computer and instantly immerse themselves in the up-to-date, as-built 3D BIM model or 3D laser scan of that space.
Augmented reality: 12 applications for design and construction professionals
Building Design+Construction reached out to AEC professionals who have studied and applied augmented reality and asked them to pinpoint applications that are ripe for the technology. Here’s what they had to offer. Read article.
Want to see what’s behind a wall? Simply scan the QR code on the doorjamb in the room, point the mobile device’s camera lens toward the wall, and voilà!, you have an x-ray view of the wall assembly. From that point in the model, you can navigate to other spaces in the facility while maintaining the AR session. You could, for instance, compare the behind-wall infrastructure of the room you’re in to that of the adjacent room. The QR codes serve as a marker to help team members quickly place themselves at a specific point in the model or 3D laser scan.
“The intent was to keep it as simple and easy as possible for the end users in field,” says Chris Pechacek, McCarthy’s Virtual Design and Construction Director (www.mccarthy.com). “They don’t have to be software gurus and know how navigate through the model, or start their AR session on the outside of the building and have to make their way into the building. It enables all users to instantly access the information they need, saving precious time and avoiding frustrations with traditional systems.”
The QR codes also provide the team with one-click access to important project documentation, including RFIs, change orders, warranties, 2D plans, submittals, equipment manuals, and markups. To deliver this information to the field, McCarthy’s IT team built a custom digital document dashboard, which connects all relevant project information using a 2D interface. The setup incorporates a collection of software apps, including Bluebeam Vu, BIMAnywhere, BIM 360 Glue, and Faro Webshare, to allow a range of document types to be quickly accessed and viewed on tablets and smart phones in the field.
To help field personnel quickly access 3D BIM models and other project documents for the Oakland Medical Center Replacement Project, general contractor McCarthy Building Companies placed hundreds of QR codes throughout the complex. Users simply scan one of the QR codes with a smartphone or tablet computer and instantly immerse themselves in the up-to-date, as-built 3D BIM model or 3D laser scan of that space. Photo: McCarthy Building Companies
Pechacek says there are huge advantages to implementing AR on the job site, especially for complex, legacy buildings like hospitals. Take change orders, for example. In long-running hospital construction projects, where technologies and processes may change multiple times during a three- to five-year project span, change orders can have a significant impact on the project schedule and budget.
“Say the client wants to change out a piece of equipment in a patient room,” says Pechacek. “Traditionally, the subs would have to open up the entire wall, clean it out, locate the hookups for the equipment, wait for inspection approval, and close and patch up the wall—a process that can take more than a day.”
Using AR, the team would be able to cut that timeframe down to hours, says Pechacek. “The laser scanning shows exact, as-built information, so you know precisely where the wall backing, pipes, boxes for the connections, med gas, etc., are located behind the wall or above the ceiling,” he says. “So instead of opening the entire wall, they can hole saw to the exact location of the pipe, connect it, and do a quick patch in about an hour.”
The same goes for operations and maintenance applications. Not having to take a patient room out of commission to perform maintenance, repairs, or upgrades offers substantial savings for the healthcare system client. Also, all major building systems will have their own QR code, for instant access to manuals, warranties, preventive maintenance schedules, and work histories.
“For them to be able to walk into a room with a tablet and see exactly where everything is or access information on a piece of equipment without having to run back to their computer, that’s a huge benefit,” says Pechacek.
The key to McCarthy’s AR implementation is capturing the as-built environment at several stages during construction using 3D laser scanning. The McCarthy team conducted comprehensive scanning sessions during the final-inspection stage, when all building systems and infrastructure were installed and the team was waiting for final signoff to close up the walls and ceilings.
“Most AEC firms will laser scan existing conditions for use for design development on a renovation project,” he says. “We’re doing it during the course of construction, creating as-builts as we go, and using that as a component within our change-management process. This has allowed us to mitigate the impacts of changes, and has helped to keep us on schedule and within budget. For such a large project, it’s a substantial feat to be able to pull this off.”
Eventually, several hundred QR codes will be placed throughout the complex, on the doorjambs of most rooms, as well as on key building and medical equipment and systems.
AR comes to the AEC sector
Since the mid-1960s, computer scientists and inventors have tested the concept of overlaying digital information onto the real world, first with bulky, head-mounted displays and later with sleek, portable monitors. But it wasn’t until Apple popularized the iPad in early 2010 that AR would become financially feasible for general construction applications. With the meteoric rise of tablet computing came the boom in tablet apps—the combination of which provided AEC professionals with a relatively low-cost, consumer-level hardware/software solution for bringing AR to the field. Almost overnight, any design or construction professional with $500 and basic knowledge of AR had a method for bringing his or her 3D models to life on the job site.
Today, there are nearly a dozen AR-related apps available on iTunes or Google Play, and more are in the works, according to Dace Campbell, AIA, LEED AP, Customer Success Manager with Autodesk, who has been developing, applying, and promoting AR in the AEC industry for years (Campbell authored an article on the topic for BD+C in February 2012).
“Products like Google Glass have made augmented reality more of a household term,” says Campbell, who was named a BD+C “40 Under 40” honoree in 2011. While real-world AR applications are still rare in the construction industry, Campbell sees the adoption rate growing as the next generation of tools is developed and AEC professionals become more familiar with the technology.
Campbell says the next iteration of AR software apps will offer better integration with existing BIM workflows, allowing field users to access, review, and update the model in real time.
“The current state of apps requires you to divorce away from your standard tools, do a one-off exploration with consumer-level AR tools, and then you’re left with a branch in the workflow that’s a dead end,” says Campbell. “If you don’t have software that works with your everyday tools, AR becomes an expensive, specialized case. AR shouldn’t be a standalone app. Soon, the best BIM apps will likely have an AR mode.”
Another obstacle is the sheer amount of data in models. Many consumer-level AR apps and tablet computers have a difficult time handling rich data sets, especially for large projects like stadiums and hospitals. Some teams have had to simplify their data sets in order to implement AR, which goes back to the BIM-workflow disconnect problem.
Campbell also sees accuracy problems related to AR hardware and software. “AR is all about the co-location of virtual and physical space, or virtual data onto physical space, no matter what the display device is,” he says. “Through that you have to co-locate that data correctly in the space, which comes down to position tracking, orientation tracking, and scale. AEC models are built full-scale, and orientation tracking is relatively easy, especially with a tablet’s gyroscope. Position tracking is the real challenge—there’s no consumer-level, out-of-the box solution for accurate position tracking today. We have GPS, which works with line-of-sight applications outdoors, but that’s only accurate to the nearest meter.”
Finally, in the not-too-distant future, teams won’t have to use QR codes or markers on the job site, because the AR application will recognize precisely where the mobile device is located on the site and will automatically orient and match the model view.
“That’s the Holy Grail, and I think we’re getting there,” says Campbell. “In the meantime we have to work with markers to get reasonably accurate tracking.
“A number of software companies have been hard at work to come up with the next generation of tools that address the problems that people have encountered,” he says. “I’m optimistic that we’re less than 18 months away from some big developments.”
Related Stories
Building Technology | Jun 18, 2024
Could ‘smart’ building facades heat and cool buildings?
A promising research project looks at the possibilities for thermoelectric systems to thermally condition buildings, writes Mahsa Farid Mohajer, Sustainable Building Analyst with Stantec.
University Buildings | Jun 18, 2024
UC Riverside’s new School of Medicine building supports team-based learning, showcases passive design strategies
The University of California, Riverside, School of Medicine has opened the 94,576-sf, five-floor Education Building II (EDII). Created by the design-build team of CO Architects and Hensel Phelps, the medical school’s new home supports team-based student learning, offers social spaces, and provides departmental offices for faculty and staff.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Mass Timber | Jun 17, 2024
British Columbia hospital features mass timber community hall
The Cowichan District Hospital Replacement Project in Duncan, British Columbia, features an expansive community hall featuring mass timber construction. The hall, designed to promote social interaction and connection to give patients, families, and staff a warm and welcoming environment, connects a Diagnostic and Treatment (“D&T”) Block and Inpatient Tower.
Concrete Technology | Jun 17, 2024
MIT researchers are working on a way to use concrete as an electric battery
Researchers at MIT have developed a concrete mixture that can store electrical energy. The researchers say the mixture of water, cement, and carbon black could be used for building foundations and street paving.
Codes and Standards | Jun 17, 2024
Federal government releases national definition of a zero emissions building
The U.S. Department of Energy has released a new national definition of a zero emissions building. The definition is intended to provide industry guidance to support new and existing commercial and residential buildings to move towards zero emissions across the entire building sector, DOE says.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 14, 2024
AEC inspections are the key to financially viable office to residential adaptive reuse projects
About a year ago our industry was abuzz with an idea that seemed like a one-shot miracle cure for both the shockingly high rate of office vacancies and the worsening housing shortage. The seemingly simple idea of converting empty office buildings to multifamily residential seemed like an easy and elegant solution. However, in the intervening months we’ve seen only a handful of these conversions, despite near universal enthusiasm for the concept.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 13, 2024
Top 10 trends in the hospital facilities market
BD+C evaluated more than a dozen of the nation's most prominent hospital construction projects to identify trends that are driving hospital design and construction in the $67 billion healthcare sector. Here’s what we found.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 13, 2024
4 ways to transform old buildings into modern assets
As cities grow, their office inventories remain largely stagnant. Yet despite changes to the market—including the impact of hybrid work—opportunities still exist. Enter: “Midlife Metamorphosis.”
Affordable Housing | Jun 12, 2024
Studio Libeskind designs 190 affordable housing apartments for seniors
In Brooklyn, New York, the recently opened Atrium at Sumner offers 132,418 sf of affordable housing for seniors. The $132 million project includes 190 apartments—132 of them available to senior households earning below or at 50% of the area median income and 57 units available to formerly homeless seniors.