Can the use of wood in school construction create healthier, safer, more productive learning environments?
In Japan, there's an ongoing effort by government officials to construct school buildings with wood materials and finishes—everything from floors and ceilings to furniture and structural elements—in the belief that wood environments have a positive impact on students.
Officials with Japan's Ministry of Education believe wood has numerous endemic qualities that promote the learning process. Visually, they say, wood evokes feelings of warmth, softness, and "positive sensations" among students and teachers. Wood's natural insulating properties help control temperature and humidity swings and sound reverberation, and its shock absorbency reduces the risk of injury. And a three-year study of 700 schools by the Japanese Wood Academic Society reports some data to indicate reduced incidence of influenza outbreaks in wooden schools compared to flu outbreaks in reinforced concrete facilities.
While the research on the benefits of wood in schools is largely anecdotal, the Ministry of Education is fully committed to promoting the social and cultural aspects of this traditional Japanese construction material. Since 1985, the ministry has subsidized school construction projects that incorporate wood with between $19,000 and $190,000, depending on the size and scale of the facility. This effort has resulted in a new breed of timber-framed schools and an even greater number of schools incorporating wood-based interior finishes, such as floors, walls, and ceilings. The ministry has committed subsidies through 2007.
At the 8,530-sm Gumma International Academy in Ota, scheduled for completion next month, exposed Southern yellow pine and Douglas fir glulam timbers form the structural post and beam elements for the roof of the K-9 school. Inside, local architect Ceolacanth and Associates specified wood flooring and ceiling panels.
However, the ministry has a long way to go in its mission to infuse Japan's school system with wood. Timber-framed schools make up just 2% of the country's 44,500 schools. Japan is one of the world's largest wood importers, but wood is generally more costly than concrete, and procuring materials can be a challenge for Building Teams, depending on the capacity of the local mills. There are also limitations to the size and scale of timber-frame structures, and they must meet strict fire and seismic safety standards.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2022
Top 200 Contractors for 2022
Turner Construction, STO Building Group, Whiting-Turner, and DPR Construction top the ranking of the nation's largest general contractors, CM at risk firms, and design-builders for nonresidential buildings and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2022
Top 45 Engineering Architecture Firms for 2022
Jacobs, AECOM, WSP, and Burns & McDonnell top the rankings of the nation's largest engineering architecture (EA) firms for nonresidential buildings and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2022
Top 80 Engineering Firms for 2022
Kimley-Horn, Tetra Tech, Langan, and NV5 head the rankings of the nation's largest engineering firms for nonresidential buildings and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 21, 2022
Top 110 Architecture/Engineering Firms for 2022
Stantec, HDR, HOK, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture engineering (AE) firms for nonresidential and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 20, 2022
Top 180 Architecture Firms for 2022
Gensler, Perkins and Will, HKS, and Perkins Eastman top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture firms for nonresidential and multifamily buildings work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 19, 2022
2022 Giants 400 Report: Tracking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms
Now 46 years running, Building Design+Construction's 2022 Giants 400 Report rankings the largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. This year a record 519 AEC firms participated in BD+C's Giants 400 report. The final report includes more than 130 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
Daylighting | Aug 18, 2022
Lisa Heschong on 'Thermal and Visual Delight in Architecture'
Lisa Heschong, FIES, discusses her books, "Thermal Delight in Architecture" and "Visual Delight in Architecture," with BD+C's Rob Cassidy.
| Aug 9, 2022
Designing healthy learning environments
Studies confirm healthy environments can improve learning outcomes and student success.
K-12 Schools | Aug 1, 2022
Achieving a net-zero K-12 facility is a team effort
Designing a net-zero energy building is always a challenge, but renovating an existing school and applying for grants to make the project happen is another challenge entirely.
Education Facilities | Jul 26, 2022
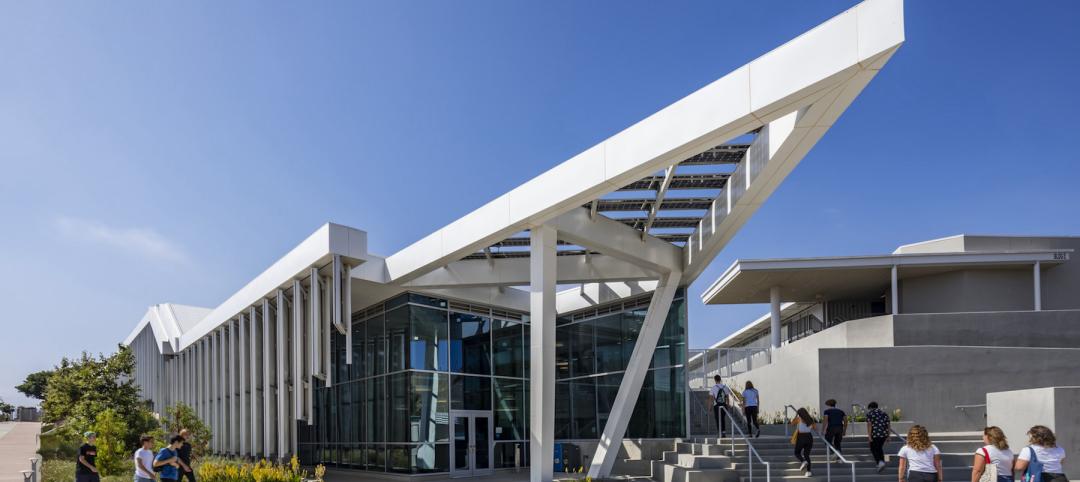
Malibu High School gets a new building that balances environment with education
In Malibu, Calif., a city known for beaches, surf, and sun, HMC Architects wanted to give Malibu High School a new building that harmonizes environment and education.