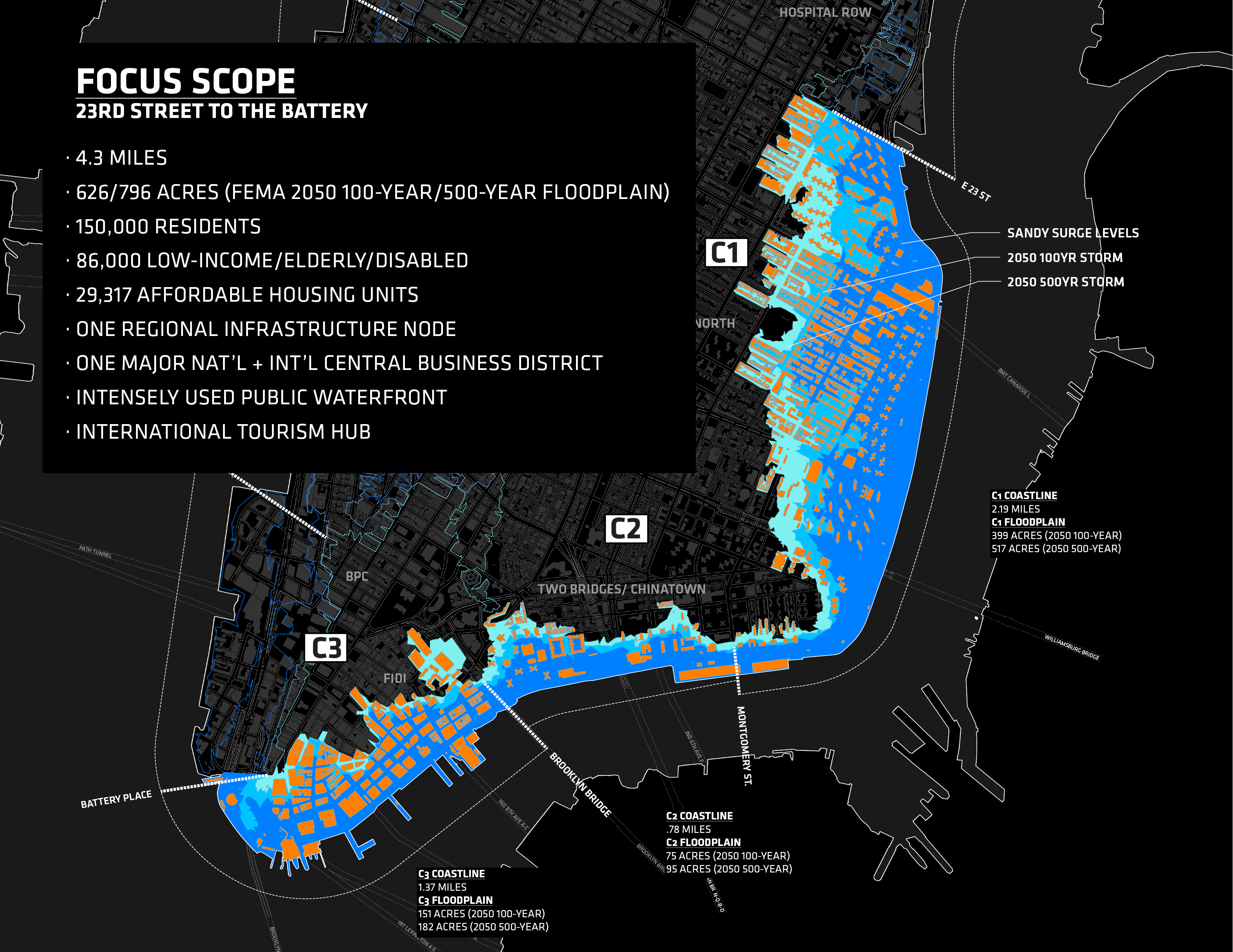
Once upon a time, New York City only had to worry about 100-year storm surges. But as sea levels rise, new research shows that the city may need to worry about these high-intensity weather events as often as every three years.
To protect the Big Apple from flooding, a new design by Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) is under consideration: the Big U. It's one of 10 entries in the Rebuild by Design competition, held by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development.
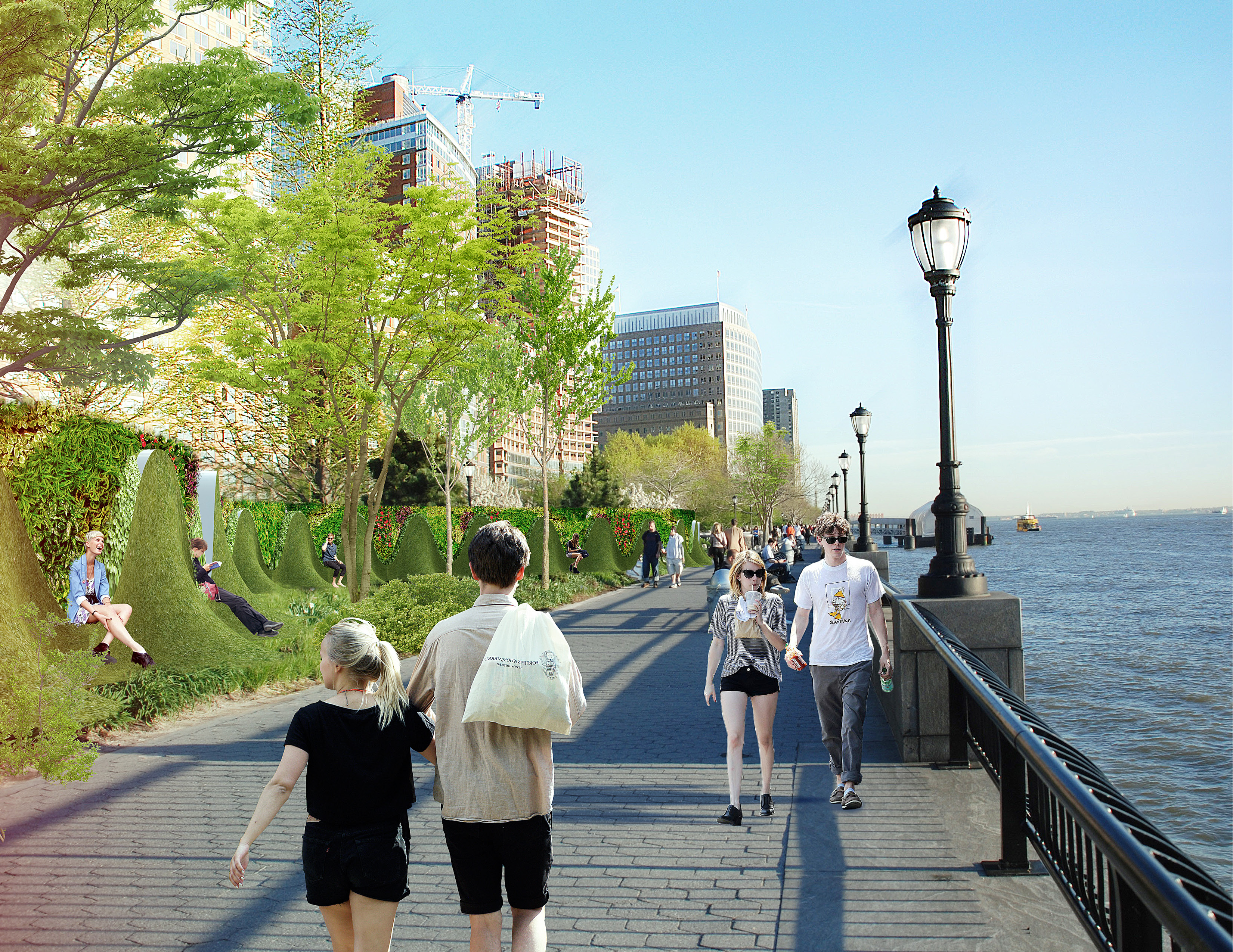
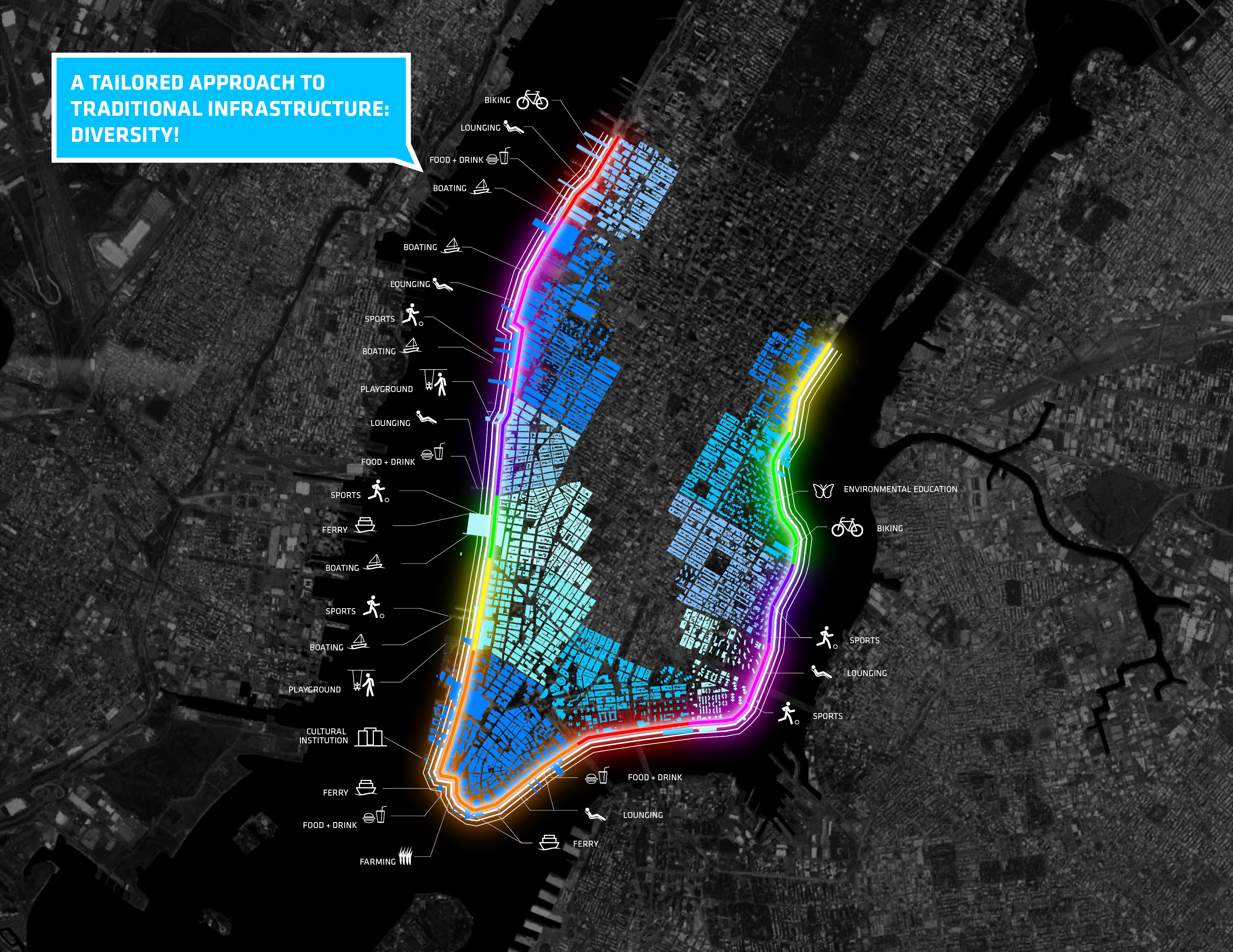
The design of the Big U doesn't just address the concerns of engineers, it is built with community needs in mind.
“In the history of New York with the legacy of Robert Moses, most of the infrastructure—whether that’s highways or parks—have generally been imposed without a lot of regard for existing community fabric,” Jeremy Siegel, the project leader, told FastCompany. “If you’re going to be investing so much money into an infrastructure for resiliency—that’s going to be sitting along one of the most spectacular coastlines in the world—there’s a huge opportunity there to also improve civic infrastructure, so it can protect the city, but also become a platform for civic life."
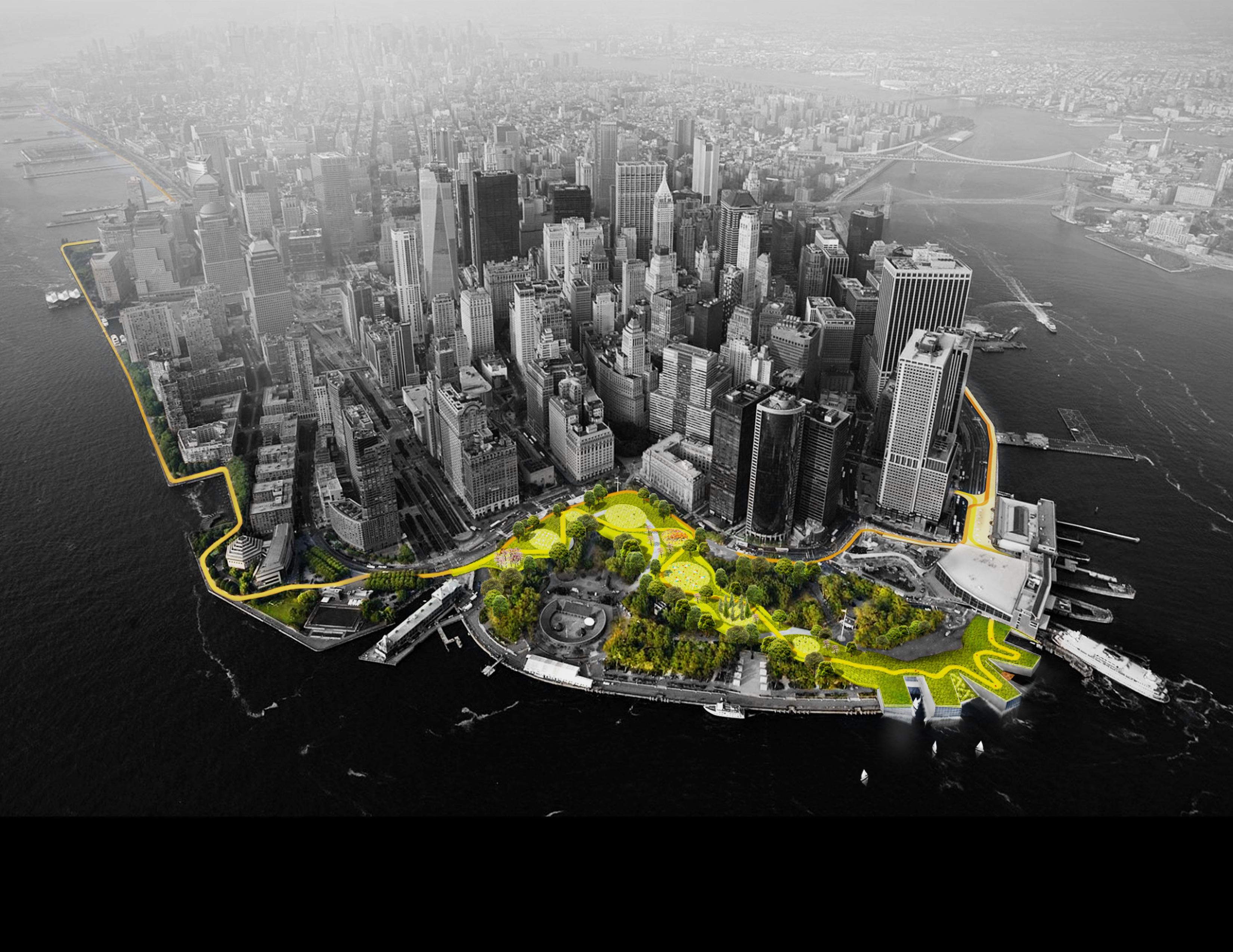
The design extends from West 57th Street to the tip of the Battery, then up to East 42nd Street—but within that range, the coast is divided into completely separate flood protection zones. Essentially, this is the same design principle used in ship-building. If one part of the ship is breached by water, that water is contained in one area, rather than being free to spread throughout the hull. In the same way, the Big U flood protection zones are all completely autonomous. If one fails, that doesn't men the whole system fails.
This also means that as funding comes in, each section could be built on its own. In its competition entry, BIG focused on sections of the city that might benefit a bit more than others in the event of flooding—two of the three sections in the original design are located in the Lower East Side, which sustained serious damage during Hurricane Sandy.
“When it floods, it’s a population that doesn’t necessarily have the means to head out of town or take a hotel somewhere else,” Siegel says. “It’s a place that makes a lot of sense to start.”
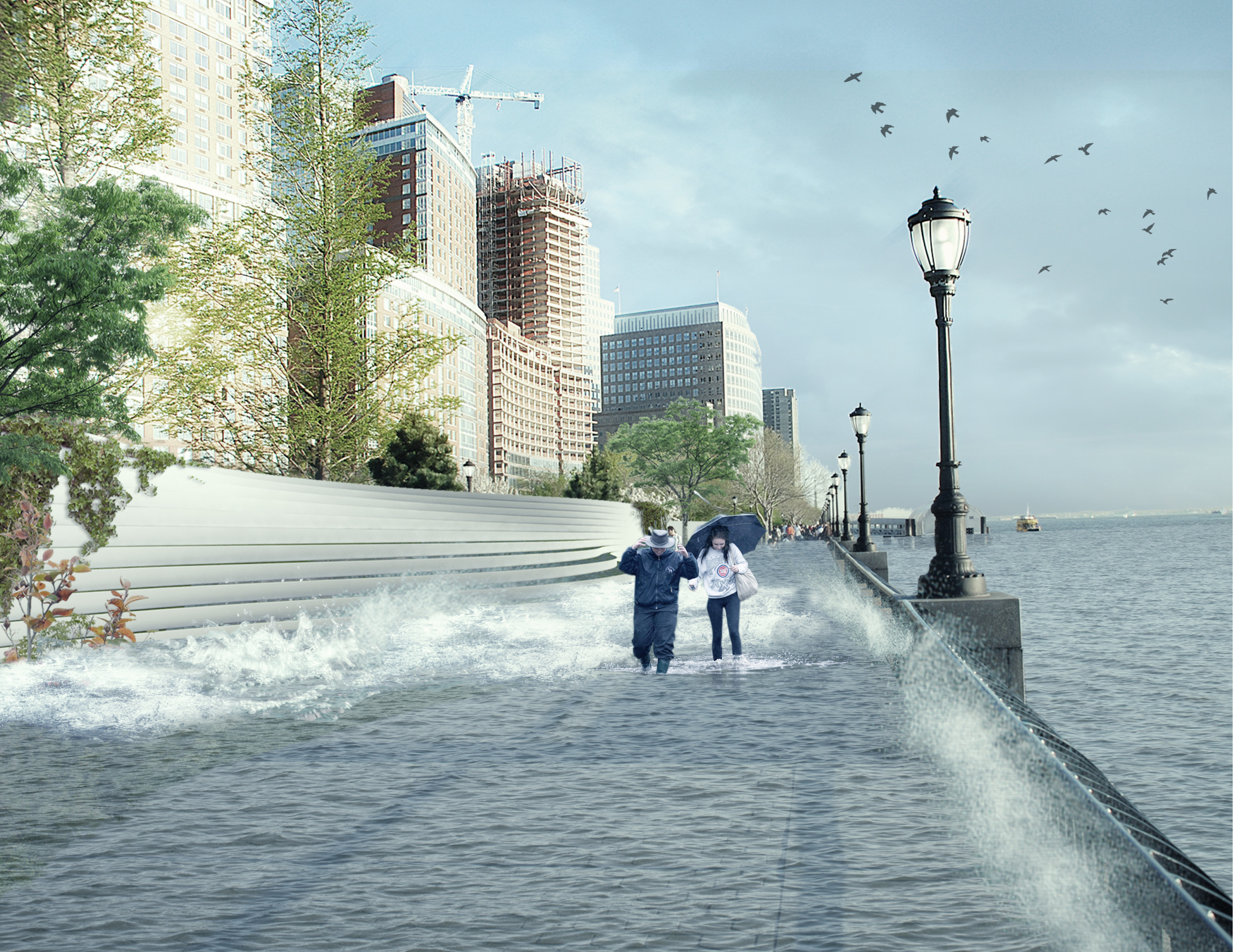
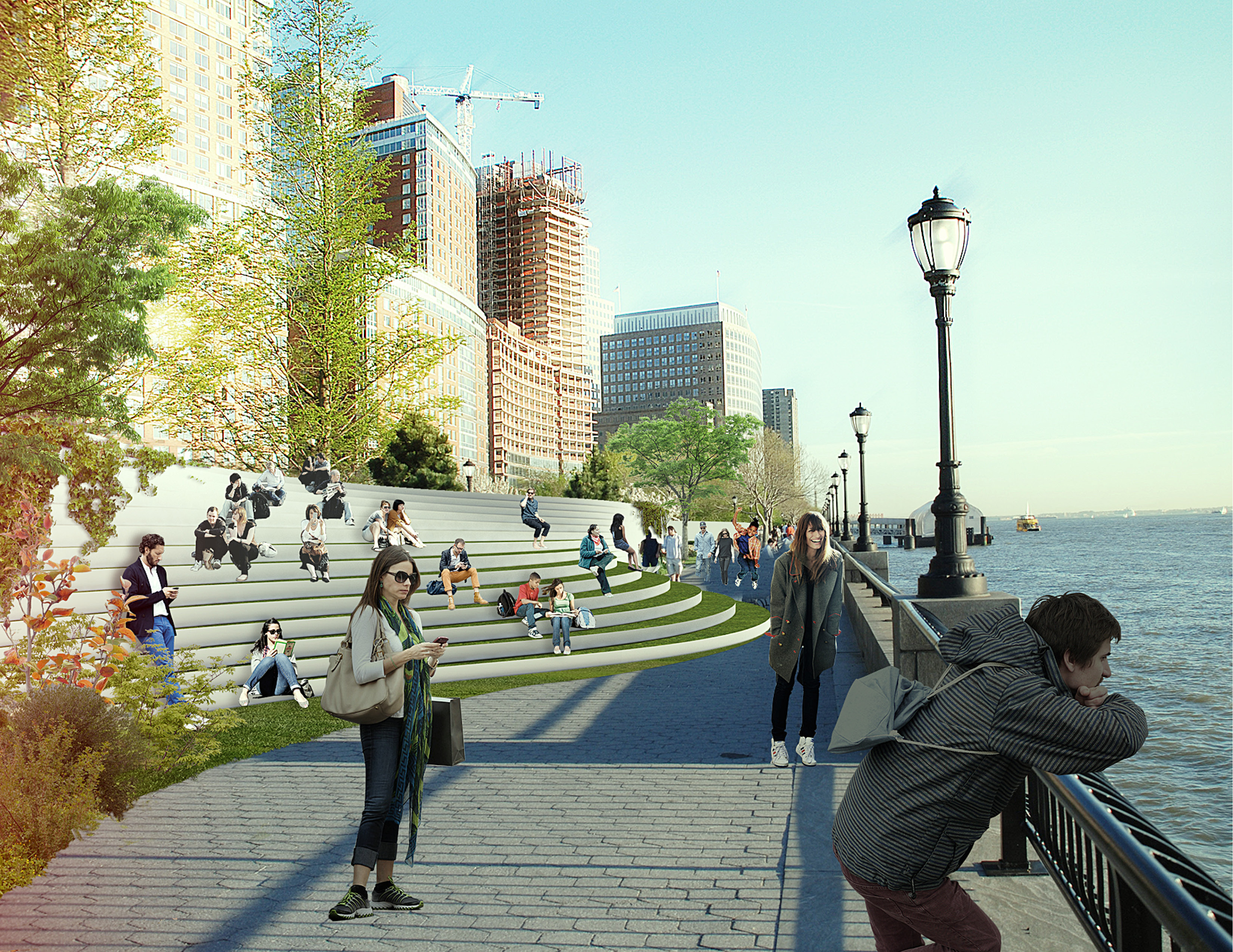
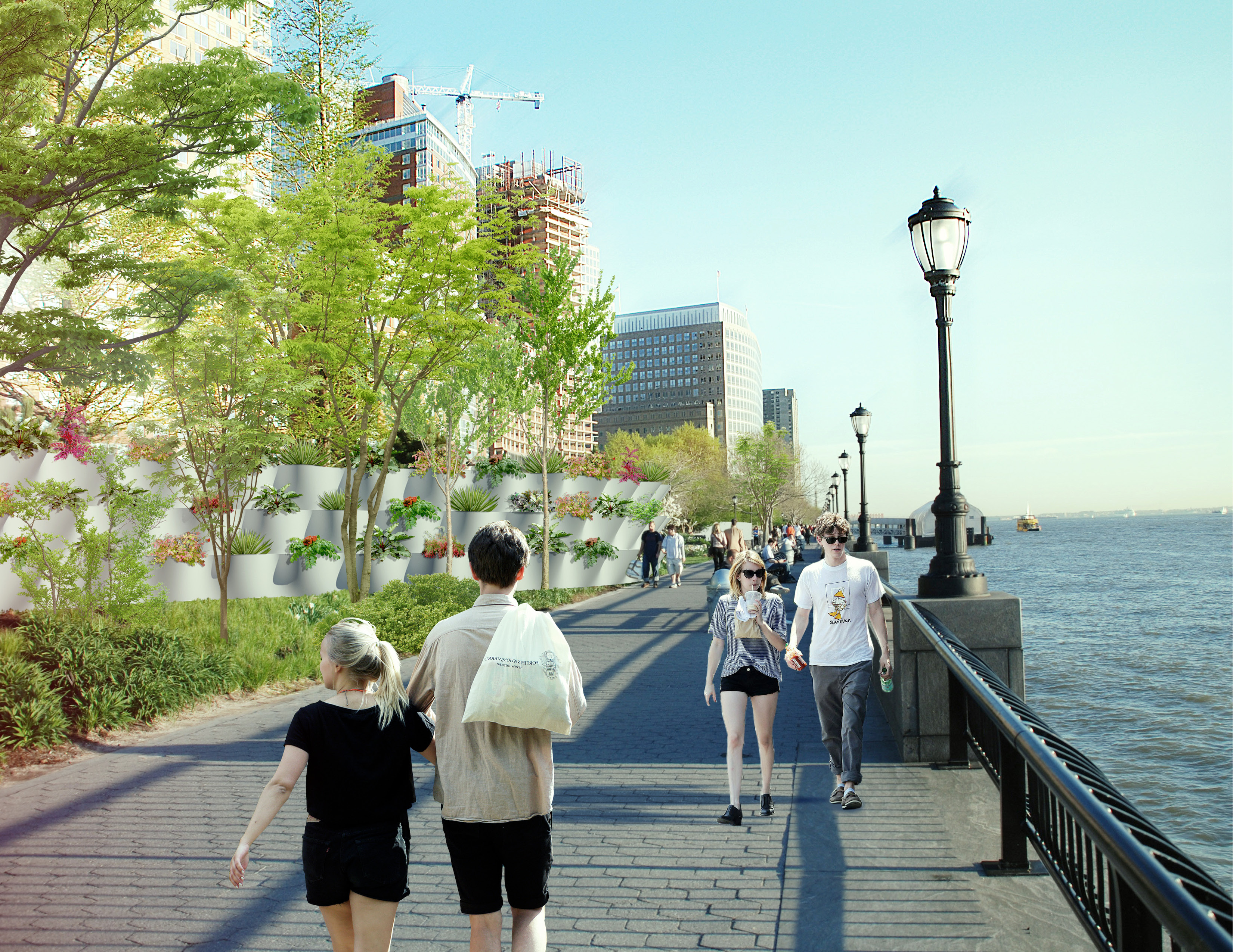
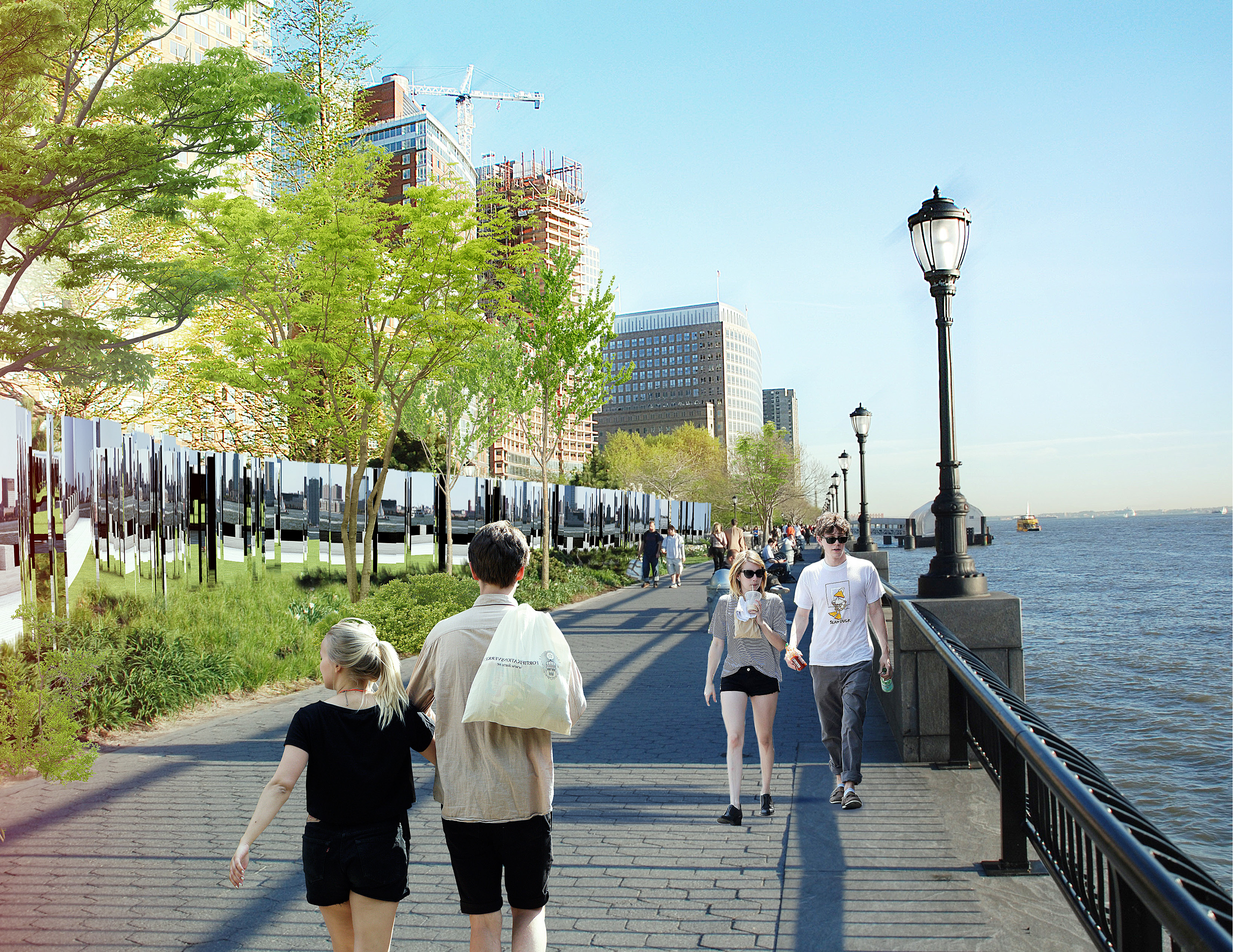
The third section BIG focused on was the southern end of Manhattan, in order to protect vital financial institutions and create more effective public spaces. The design includes raised portions of land, both to prevent flooding and provide new park space. Beneath FDR drive, flood walls can be flipped up at will—either to stop incoming water, or to create a sheltered public space.
Check out the initial renderings of the Big U below. Renderings courtesy of BIG.
Related Stories
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
BIG’s One High Line finally reaches completion in New York City’s West Chelsea neighborhood
One High Line, a luxury residential project spanning a full city block in New York’s West Chelsea neighborhood, reached completion this summer following years of delays related to investor lawsuits.
Urban Planning | Oct 30, 2024
Bridging the gap: How early architect involvement can revolutionize a city’s capital improvement plans
Capital Improvement Plans (CIPs) typically span three to five years and outline future city projects and their costs. While they set the stage, the design and construction of these projects often extend beyond the CIP window, leading to a disconnect between the initial budget and evolving project scope. This can result in financial shortfalls, forcing cities to cut back on critical project features.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Oct 30, 2024
Luxury waterfront tower in Brooklyn features East River and Manhattan skyline views
Leasing recently began for The Dupont, a 41-story luxury rental property along the Brooklyn, N.Y., waterfront. Located within the 22-acre Greenpoint Landing, where it overlooks the newly constructed Newtown Barge Park, the high-rise features East River and Manhattan skyline views along with 20,000 sf of indoor and outdoor communal space.
Libraries | Oct 30, 2024
Reasons to reinvent the Midcentury academic library
DLR Group's Interior Design Leader Gretchen Holy, Assoc. IIDA, shares the idea that a designer's responsibility to embrace a library’s history, respect its past, and create an environment that will serve student populations for the next 100 years.
Resiliency | Oct 29, 2024
Climate change degrades buildings slowly but steadily
While natural disasters such as hurricanes and wildfires can destroy buildings in minutes, other factors exacerbated by climate change degrade buildings more slowly but still cause costly damage.
Office Buildings | Oct 29, 2024
Editorial call for Office Building project case studies
BD+C editors are looking to feature a roundup of office building projects for 2024, including office-to-residential conversions. Deadline for submission: December 6, 2024.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 28, 2024
New surgical tower is largest addition to UNC Health campus in Chapel Hill
Construction on UNC Health’s North Carolina Surgical Hospital, the largest addition to the Chapel Hill campus since it was built in 1952, was recently completed. The seven-story, 375,000-sf structure houses 26 operating rooms, four of which are hybrid size to accommodate additional equipment and technology for newly developed procedures.
Multifamily Housing | Oct 28, 2024
A case for mid-rise: How multifamily housing can reshape our cities
Often referred to as “five-over-ones,” the mid-rise apartment type is typically comprised of five stories of apartments on top of a concrete “podium” of ground-floor retail. The main criticism of the “five-over-one” is that they are often too predictable.
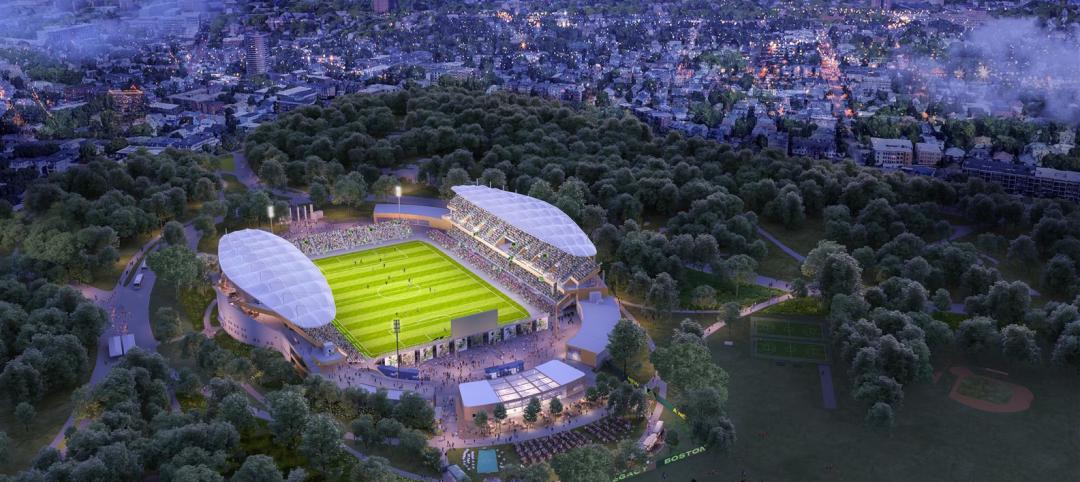
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Oct 24, 2024
Stadium renovation plans unveiled for Boston’s National Women’s Soccer League
A city-owned 75-year-old stadium in Boston’s historic Franklin Park will be renovated for a new National Women’s Soccer League team. The park, designed by Fredrick Law Olmsted in the 1880s, is the home of White Stadium, which was built in 1949 and has since fallen into disrepair.
Laboratories | Oct 23, 2024
From sterile to stimulating: The rise of community-centric life sciences campuses
To distinguish their life sciences campuses, developers are partnering with architectural and design firms to reimagine life sciences facilities as vibrant, welcoming destinations. By emphasizing four key elements—wellness, collaboration, biophilic design, and community integration—they are setting their properties apart.