Western Michigan University (WMU) is a dynamic, student-centered research university with an enrollment of 25,000. According to the U.S. News & World Report, WMU consistently ranks among the top 100 public universities in the nation. A key factor in these rankings is the university’s commitment to delivering high-quality, industry-relevant undergraduate instruction. That is one of the reasons why the Department of Civil and Construction Engineering introduced the building information modeling (BIM) process and Autodesk Revit Architecture software to the curriculum in 2008. Soon afterward, WMU initiated a much wider implementation of BIM to support the many building design projects that the planning, engineering and construction divisions were working on across the campus.
“We knew that BIM was the way to go,” says Peter Strazdas, associate vice president of facilities at WMU. “However, before using BIM on a new construction project, we wanted to explore its potential on some of our existing, in-house renovation projects.”
The Challenge
To support this effort, WMU initiated a plan to have a group of engineering students model the campus’ existing buildings in Revit Architecture.
“We wanted hands-on experience with buildings that we already understood before we used BIM on new construction,” says Mike Hodgkinson, building commissioning administrator at WMU. “It was a great learning opportunity for the students—and allowed us to stay within a reasonable budget.”
The initial plan was for the students, working 30 to 40 hours per week, to model two-thirds of the 8-million-sf campus between May and September. One of Strazdas’ ultimate goals was to use these models for energy analysis and to help with the subsequent identification of those buildings on campus most in need of renovation and retrofitting. To help demonstrate the project’s feasibility to stakeholders and facilitate whole-project review, the team used the software and its conflict resolution, visualization and planning capabilities.
The Solution
WMU turned to Autodesk reseller Kal-Blue for early guidance and training. Kal-Blue modeled the first campus building, showing the facility management team and students how the process worked. Kal-Blue also developed best practices that the design team could follow and introduced WMU to AIA E202, a document that helped determine how much detail to include in the models.
“If we drafted every detail, the process would have taken too long,” says Strazdas.
After deliberation, WMU used the graduated scale from the AIA E202 document and selected a baseline of Level 200 out of 500 for most of the buildings.
Leverage Existing Drawings
To help accelerate model creation, the design team based its work on the extensive collection of AutoCAD DWG files that WMU maintained.
“Much of the 2D information transferred easily into 3D,” says Hodgkinson. “We also updated the original designs to ensure that our models included all recent building modifications.”
The Result
The WMU design team succeeded in modeling 80% of the campus—115 buildings—by September.
“We easily surpassed our goals,” says Strazdas. “With help from Revit Architecture, our students accomplished an impressive amount very quickly.”
Others were equally impressed; several students have had inquiries from potential employers. Another group of students will complete the remaining buildings in 2011.
Make Better Decisions
Strazdas believes the models will have tremendous value on future renovations.
“We’ll share visualizations with our in-house customers during the review process,” says Strazdas. “That is much easier with Revit Architecture, Navisworks Manage, and a BIM process.”
WMU will also integrate data from the models with energy analysis software for better decisions about energy consumption and effective identification of targets for renovation and retrofitting.
WMU has already begun using the models on a renovation project that requires adding two chillers to an existing building. WMU is enhancing the model with data from a laser scan, and also piping data from an engineering consultant—raising the detail level in that part of the model to 400.
Ultimately, WMU will consolidate all campus buildings into a unified model.
“We own and operate our buildings for 50 years or more—and approximately 90% of the costs occur after construction,” says Strazdas. “We need to make smarter decisions with those assets—and to have access to real-time information about them. BIM is how we access and maintain that information.”
For more information, visit www.autodesk.com/revitarchitecture.
Related Stories
| Apr 15, 2013
Using software and the power of the cloud to connect your back office to your field operations [webinar]
This webinar will focus on a new software subscription service that will help construction companies, general and specialty contractors connect their back office infrastructure with all of their field operations. The service will help capture, manage and report on the progress of existing construction jobs and help in the planning of new ones.
| Apr 8, 2013
Most daylight harvesting schemes fall short of performance goals, says study
Analysis of daylighting control systems in 20 office and public spaces shows that while the automatic daylighting harvesting schemes are helping to reduce lighting energy, most are not achieving optimal performance, according to a new study by the Energy Center of Wisconsin.
| Apr 5, 2013
'My BIM journey' – 6 lessons from a BIM/VDC expert
Gensler's Jared Krieger offers important tips and advice for managing complex BIM/VDC-driven projects.
| Apr 3, 2013
5 award-winning modular buildings
The Modular Building Institute recently revealed the winners of its annual Awards of Distinction contest. There were 42 winners in all across six categories. Here are five projects that caught our eye.
| Mar 27, 2013
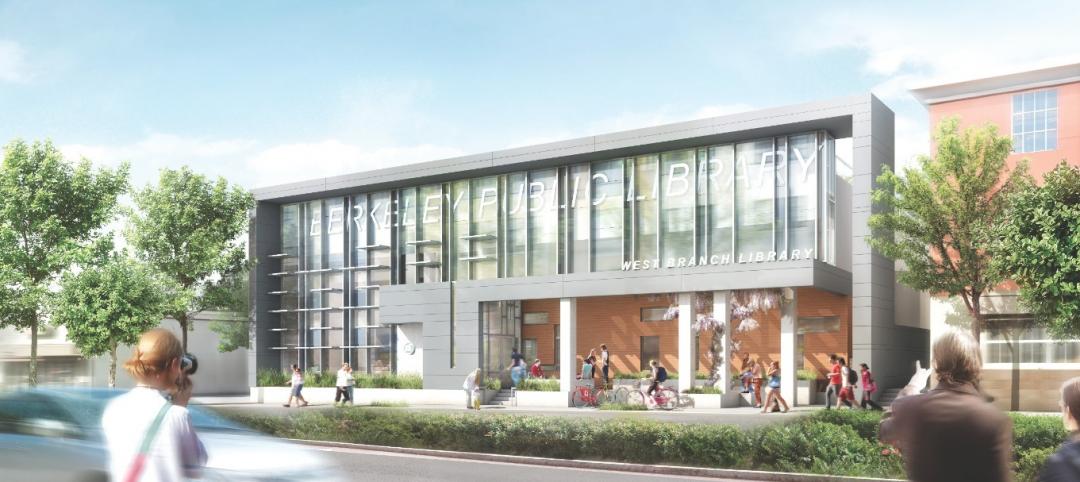
Small but mighty: Berkeley public library’s net-zero gem
The Building Team for Berkeley, Calif.’s new 9,500-sf West Branch library aims to achieve net-zero—and possibly net-positive—energy performance with the help of clever passive design techniques.
| Mar 26, 2013
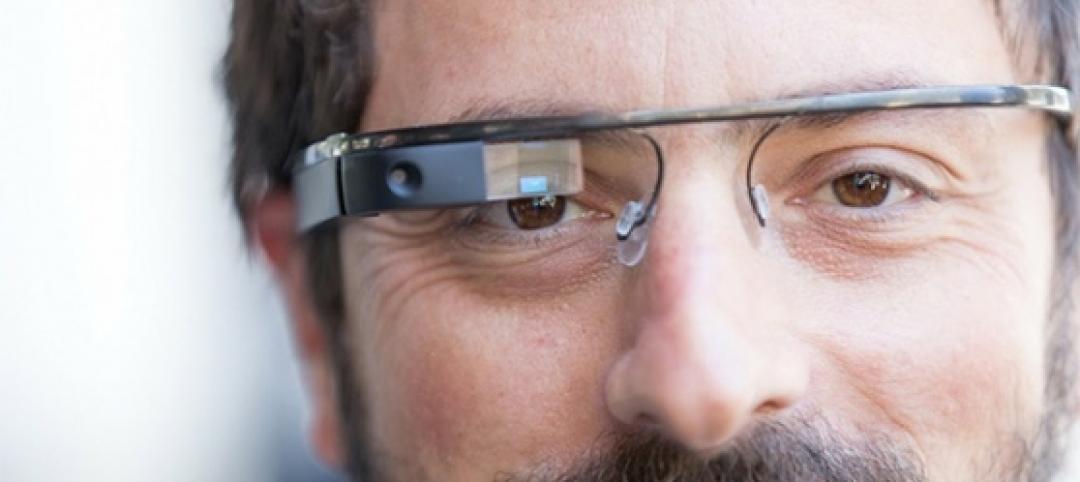
Will Google Glass revolutionize the construction process?
An Australian architect is exploring the benefits of augmented reality in the design and construction process.
| Mar 24, 2013
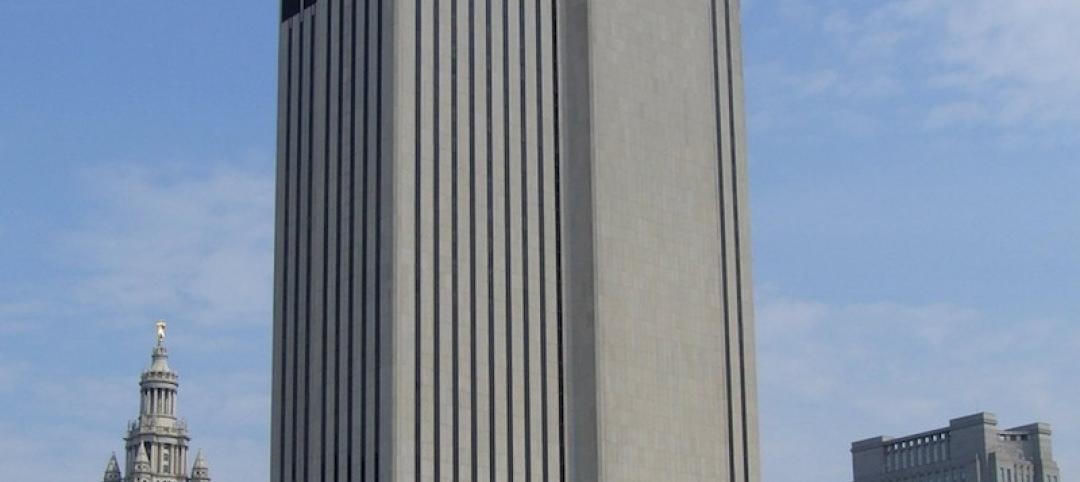
World's tallest data center opens in New York
Sabey Data Center Properties last week celebrated the completion of the first phase of an adaptive reuse project that will transform the 32-story Verizon Building in Manhattan into a data center facility. When the project is completed, it will be the world's tallest data center.
| Mar 20, 2013
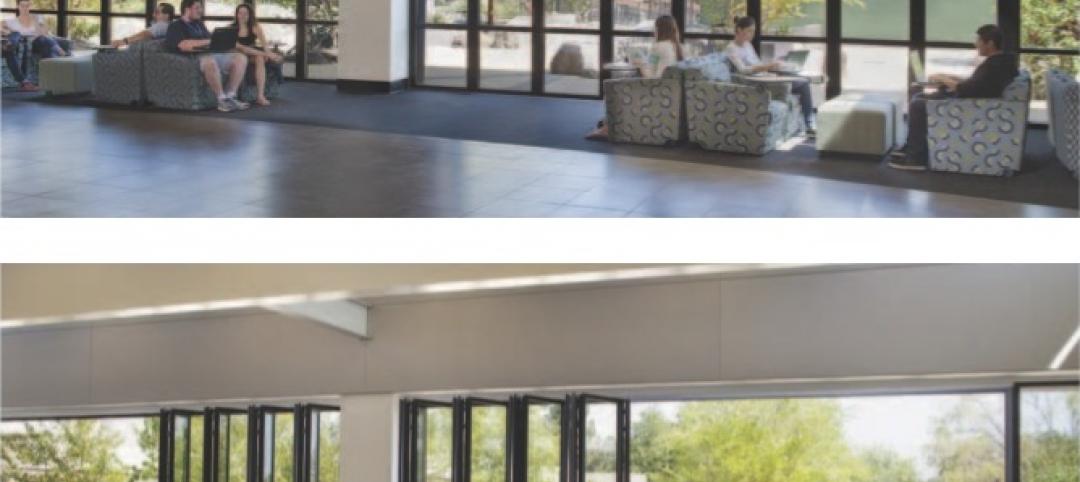
Folding glass walls revitalize student center
Single-glazed storefronts in the student center at California’s West Valley College were replaced with aluminum-framed, thermally broken windows from NanaWall in a bronze finish that emulates the look of the original building.