The 1939 Hinman Research Building on the campus of the Georgia Institute of Technology, in Atlanta, is undergoing an $8.5 million renovation to adapt and expand its capacity to serve the program objectives of the university’s College of Architecture. The renovation, which is being designed using building information modeling (BIM) and related software systems, will also produce flexible and functional interior space that encourages interaction and collaboration by architecture students and faculty.
The 35,000-sf Hinman Building was last renovated in 1951. As a result, the project, which is expected to achieve LEED-EB Gold certification from the U.S. Green Building Council, required significant interior improvement to create adequate studio and classroom space for the architecture school. The scope of work for the general contractor on the design-build project, the Dallas-based Beck Group, included demolition and abatement of the existing interior and completion of the new interior finishes.
The design for the reconstructed building, by the architecture firms Office da of Boston (design architect) and Lord Aeck & Sargent of Atlanta (architect of record), used elaborate interior millwork to create the kind of flexible and functional spaces that the College of Architecture desired. Not only was it necessary to manufacture the thousands of new interior millwork pieces at reasonable cost and within the schedule. They also had to fit the tight tolerances at their interfaces with the existing structure, as mandated by the design (which was modeled in Autodesk Revit). To accomplish this difficult task, the designers used Rhino 3D, a design tool that uses NURBS, or non-uniform rational b-splines, to create curvilinear pieces and other sophisticated shapes that other 3D design software can’t touch.
“We generally use Rhino for studying design and generating freeform geometry on most of our projects,” said Tom Beresford, project architect for Office da on the Hinman Building project. Beresford said his firm had also used the software in previous work involving custom millwork packages.
The 3D architectural models worked for design purposes, but once the Beck Group got them on site they noticed several existing conditions that made installation difficult. In particular, the staircases in the post-demolition interior of the building were mostly in the wrong locations.
“Dealing with unknowns was adding contingencies,” said Josh Oakley, BIM manager for the Beck Group. “The price of installation was starting to escalate because it would take time to figure out how to install all of these pieces, and it was getting to the point that stairs and millwork may have had to be value-engineered out. Our field people were not used to spending days on installation.”
Oakley and his Beck colleagues—notably assistant project manager Frank Fralick and project engineer Jesse Plata—came up with a plan to import the geometries of the existing Rhino models into Autodesk Inventor and then transfer that data to EdgeCAM, a computer-aided machining program that can apply CNC tooling paths to the model geometry. With these paths the model information could be used to create G code, a series of numbers used to program a CNC milling machine to create the thousands of millwork pieces needed for the project. They hoped this process could meet the $547,000 millwork budget and deliver it on time.
“If there was a way to make these models only once, we were going to do it,” Oakley said. “We needed to mitigate risk and meet budget.”
Oakley and Fralick also took a point-cloud scan of the preconstruction Hinman Building and put that information into their Autodesk Revit and Rhino models to ensure accuracy in the as-built model. In a matter of one day all the existing conditions were imported into the design model.
This workflow also allowed the Building Team to create animated DWF files as instructions for the installation of each piece of millwork from the Autodesk Inventor model. These “IKEA-like” graphical representations showed how each piece fit and where holes needed to be drilled to create the finished, ornate millwork. Oakley said having these detailed animations allowed Beck to reduce the time needed to put together the thousands of unlabeled pieces of millwork and keep the project on track and under budget.
The next step was finding a CNC fabricator who could create the custom millwork pieces using CNC machines. The modified workflow made it likely that using a traditional commercial project fabricator would be out of the question. The Building Team would also need space to store the thousands of pieces necessary to create the new interior millwork. The scope of work and the storage problem would require a different approach entirely.
The Beck team approached Amir Nejad, president and CEO of residential custom cabinetmaker Royal Custom Cabinets in Norcross, Ga., a suburb of Atlanta, to take on the millwork project. Using Royal Custom’s CNC production capability, the fabrication process was quickly commoditized. The EdgeCAM data was easily fed into Royal Custom Cabinets’ four-axis router machines. The millwork pieces began rolling out and were stored in a 15,000-sf warehouse in Norcross that the Beck Group leased.
The millwork was recently completed, and the Beck Group will be returning $30,000 in a change order fund to owner Georgia Tech. The Building Team is using the same process to build custom furniture for the project, which is expected to be completed, with the rest of the interior fit-out, in time for the Hinman Building’s reopening in January.
Related Stories
Office Buildings | Feb 9, 2023
Post-Covid Manhattan office market rebound gaining momentum
Office workers in Manhattan continue to return to their workplaces in sufficient numbers for many of their employers to maintain or expand their footprint in the city, according to a survey of more than 140 major Manhattan office employers conducted in January by The Partnership for New York City.
Giants 400 | Feb 9, 2023
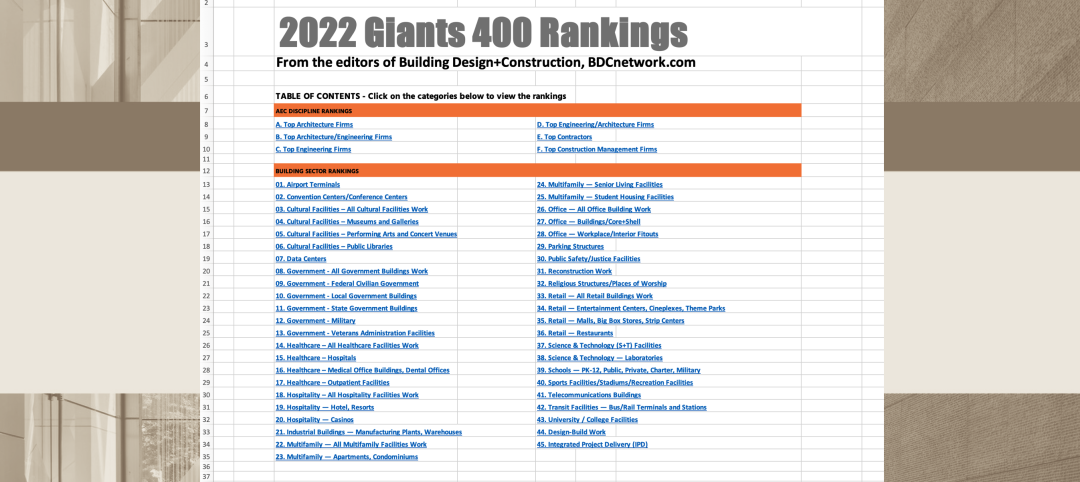
New Giants 400 download: Get the complete at-a-glance 2022 Giants 400 rankings in Excel
See how your architecture, engineering, or construction firm stacks up against the nation's AEC Giants. For more than 45 years, the editors of Building Design+Construction have surveyed the largest AEC firms in the U.S./Canada to create the annual Giants 400 report. This year, a record 519 firms participated in the Giants 400 report. The final report includes 137 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
University Buildings | Feb 8, 2023
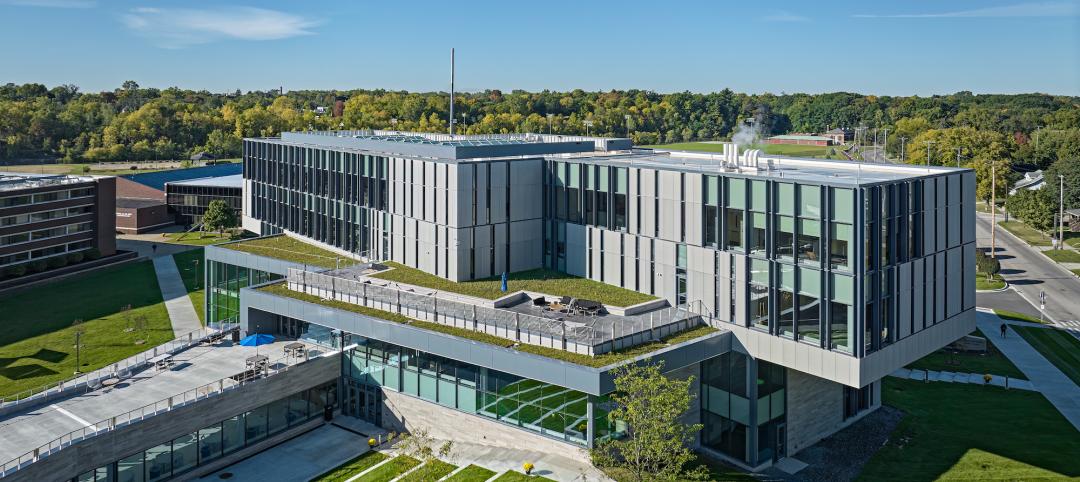
STEM-focused Kettering University opens Stantec-designed Learning Commons
In Flint, Mich., Kettering University opened its new $63 million Learning Commons, designed by Stantec. The new facility will support collaboration, ideation, and digital technology for the STEM-focused higher learning institution.
Sustainability | Feb 8, 2023
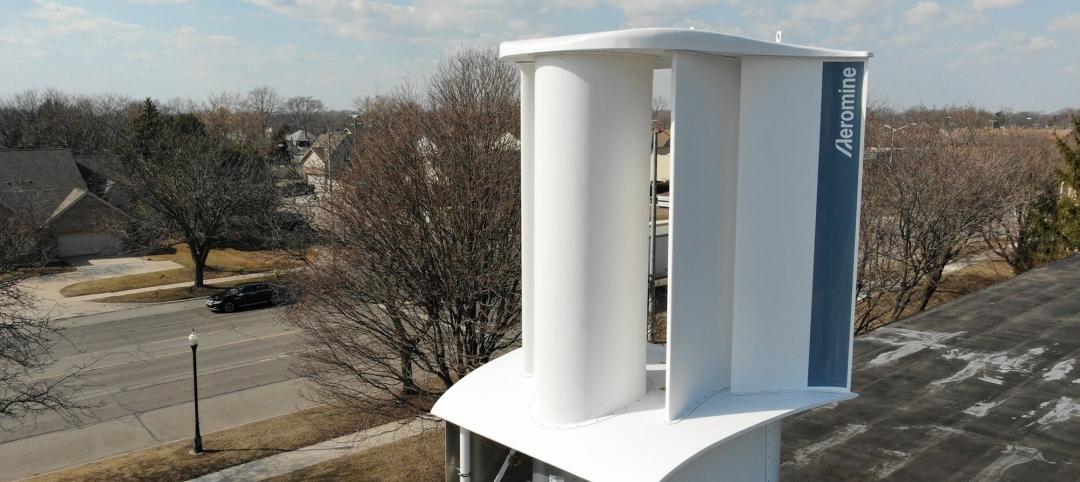
A wind energy system—without the blades—can be placed on commercial building rooftops
Aeromine Technologies’ bladeless system captures and amplifies a building’s airflow like airfoils on a race car.
Codes and Standards | Feb 8, 2023
GSA releases draft of federal low embodied carbon material standards
The General Services Administration recently released a document that outlines standards for low embodied carbon materials and products to be used on federal construction projects.
University Buildings | Feb 7, 2023
Kansas City University's Center for Medical Education Innovation can adapt to changes in medical curriculum
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) at Kansas City University was designed to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy. The project program supported the mission of training leaders in osteopathic medicine with a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 7, 2023
Multifamily housing rents flat in January, developers remain optimistic
Multifamily rents were flat in January 2023 as a strong jobs report indicated that fears of a significant economic recession may be overblown. U.S. asking rents averaged $1,701, unchanged from the prior month, according to the latest Yardi Matrix National Multifamily Report.
Giants 400 | Feb 6, 2023
2022 Reconstruction Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. building reconstruction and renovation sector
Gensler, Stantec, IPS, Alfa Tech, STO Building Group, and Turner Construction top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest reconstruction sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Feb 6, 2023
2022 Transit Facility Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. transit facility sector
Walsh Group, Skanska USA, HDR, Perkins and Will, and AECOM top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest transit facility sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Feb 6, 2023
2022 Telecommunications Facility Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. telecommunications facility sector
AECOM, Alfa Tech, Kraus-Anderson, and Stantec head BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest telecommunications facility sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2022 Giants 400 Report.