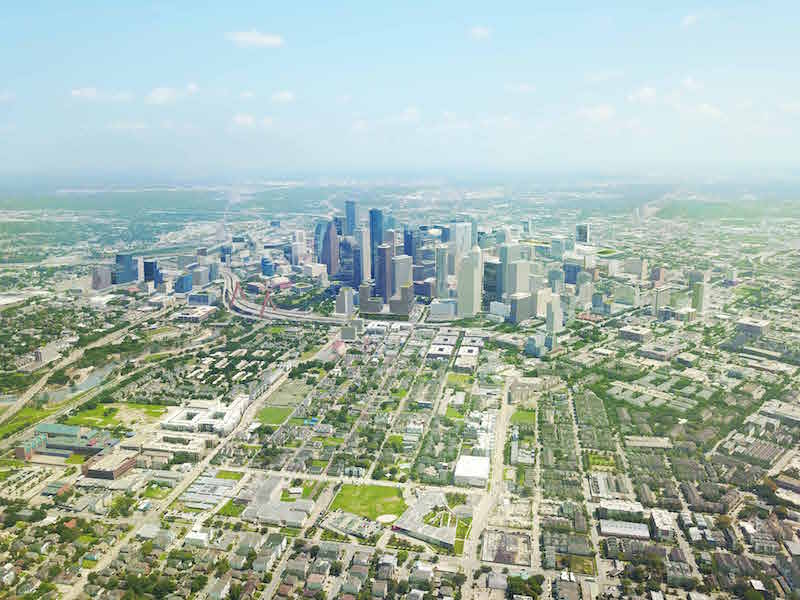
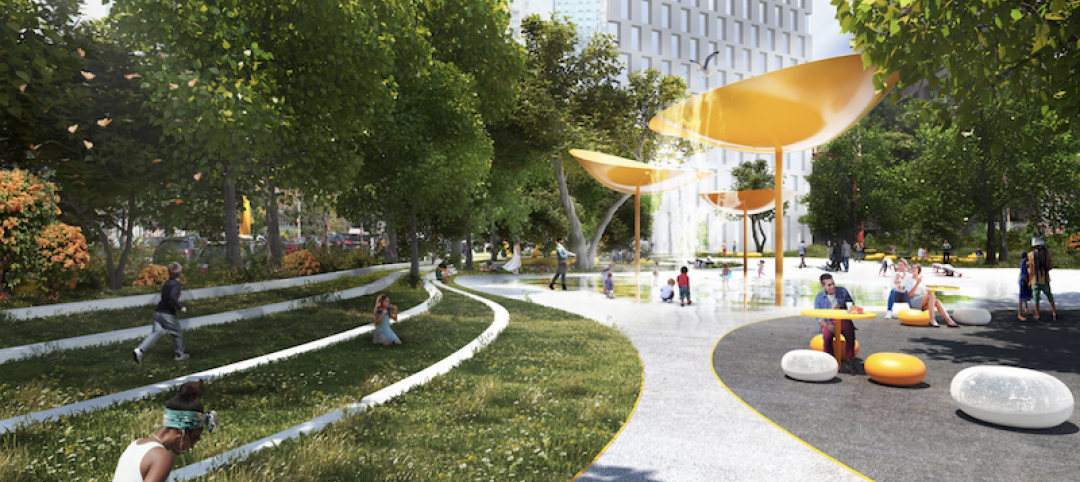
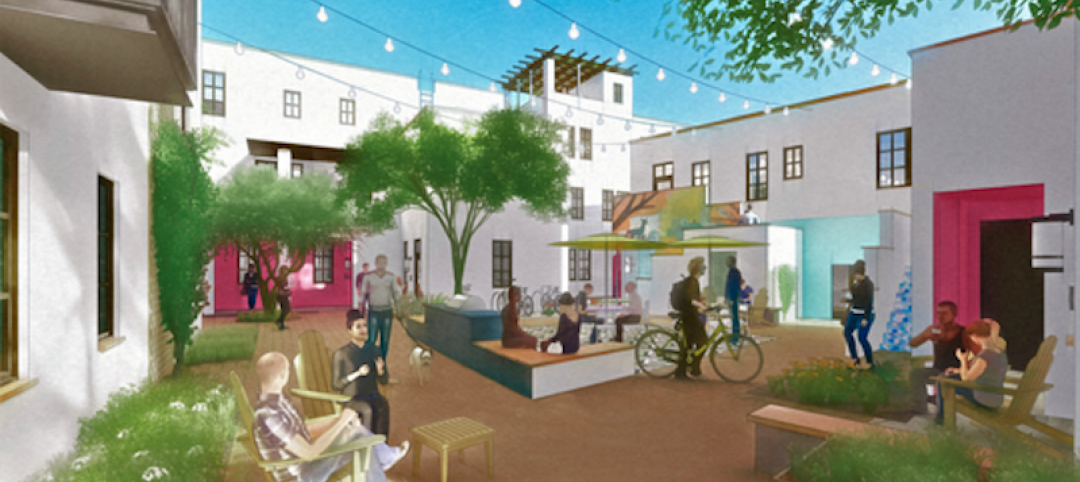
On August 30, 2036, Houston will celebrate its Bicentennial. In preparation for that occasion, city leaders have devised an ambitious plan to make its Downtown the center of its universe, and the focal point of its activities and growth.
The 48-page “Plan Downtown: Converging Culture, Lifestyle & Commerce,” is the product of an 18-month process led by several downtown partner organizations and city, county, and community leaders. It also incorporates “robust” public input. The plan considers nearly 150 recommendations that range from big-picture ideas to small, localized upgrades.
The plan was spearheaded by Asakura Robinson, a planning, urban design and landscape architecture firm, working with AEC consultants Sasaki, Traffic Engineers Inc., and HR&A Advisors. The consultants also tapped a 166-member steering committee of elected officials, community leaders and area residents.
Funding for researching and writing this plan came from the Downtown District, Downtown Redevelopment Authority/TIRZ No. 3, and Houston First Corporation.
It’s not like Houston has been standing still. Since 2004, nearly $6 billion has been invested across a broad range of urban uses that include offices, residences, and parks. Today, more than $1.39 billion in new Downtown construction projects are underway, and another $2.58 billion are in preconstruction or design. An additional 2.86 million sf of office space is being built, as well as eight hotel high rises.
The goal of the new plan is to accentuate Downtown’s “interconnectedness” with this sprawling city, Harris County, and neighboring counties.
At the heart of downtown is the George R. Brown Convention Center, which under this new plan would be upgraded and expanded to include a new South Expo Hall. The construction of two new large hotels near the convention center are also envisioned, along with a “dynamic, elevated pedestrian connection” from the convention center to the eastern sector of downtown.
In East Downtown, the plan calls for adding 4,000 hotel rooms, with the 20-year goal of 12,000 hotel rooms throughout the Downtown area, including no fewer than 8,000 located within a 10-minute walk from the convention center.
Enhancing and expanding Downtown’s activity centers and attractions would also create within Houston’s Theater District “an immersive arts and culture environment.” Housing and mass transit would be expanded in different Downtown quadrants, as would pedestrian and bike trails, and public spaces.
That effort would include the development of a five-mile-long Downtown Green Loop as part of the city’s 24-mile, $7 billion, decade-long infrastructure project that entails a full rebuild of three highways encircling Downtown. The Green Loop would interact with the city’s bayou system and its street grid.
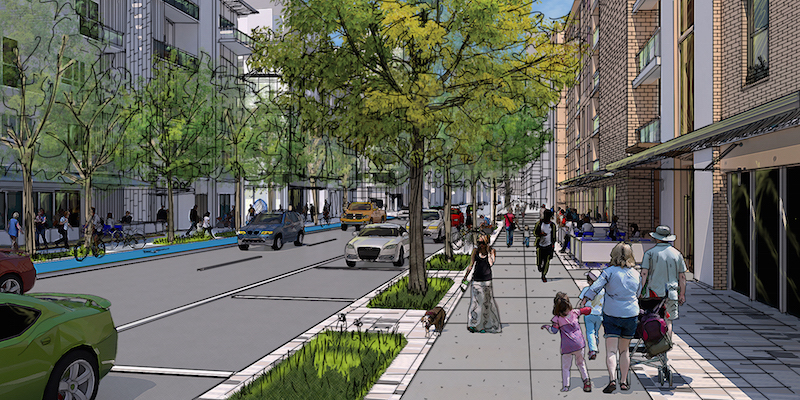

Walkability is a big factor in the redevelopment plan for Downtown Houston, which also calls for a proactive shift toward the support of autonomous vehicles and ride sharing. Image: Courtesy Houston Downtown Management District.
Other highlights of this plan include:
•Working with existing property owners and managers to convert 5% to 10% of Downtown properties into new office spaces for start-up and small businesses at affordable and/or protected rents.
•Creating a Downtown innovation district. (Today, there are more than 250 early-stage software and digital technology companies operating in the Downtown area.)
•Building 12,000 residential units within Downtown to support its projected population growth to 30,000 (from 7,500 today) over the next 20 years. The plan calls for building a public elementary school and public middle school within two or more of the Downtown residential neighborhoods.
•In Downtown’s western quadrant, redeveloping the currently vacant Barbara Jordan Post Office, which takes up eight blocks, into a “one-of-a-kind” multicultural center with food, art, retail, offices, hospitality, educational facilities.
•Becoming a national leader for connectivity innovation. The city would adapt autonomous vehicle technologies by managing Downtown parking with future decreases in demand while adapting new street, garage, and curb space use that include supporting autonomous vehicles with service zones, changing stations, and dedicated transit lanes.
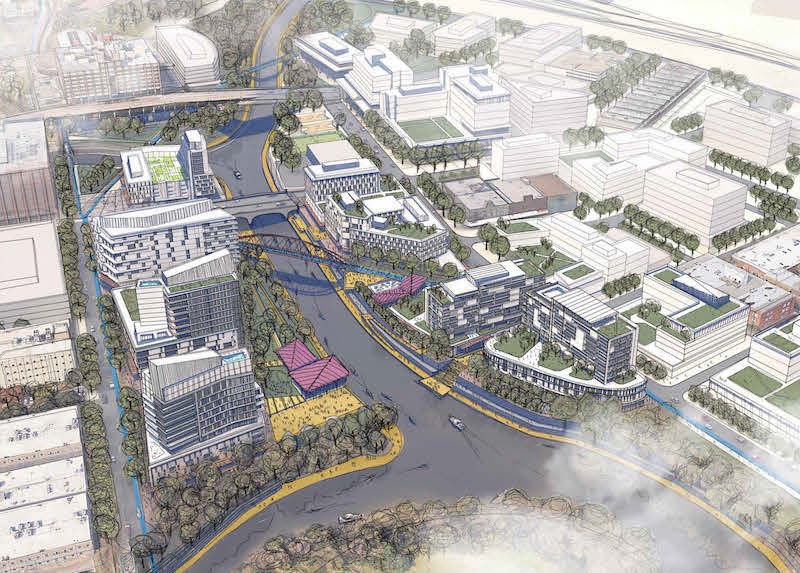

A perspective from Downtown Houston's North Canal, which under the new plan would, among other things, expand student housing for the University of Houston, connect Buffalo Bayou with Allen's Landing, add a North Downtown Transit Center, and establish enhanced stormwater retention centers. Image: Courtesy of Houston Downtown Management District.
This connectivity initiative would ensure the integrity of Downtown’s power grid, expand WiFi service in parks and public spaces, expand shared mobility, and use smart street light systems to collect and disseminate data on traffic, noise, air quality and so forth.
Houston is still drying out from the dunking it received from Hurricane Harvey. But surprisingly little detail is provided in the plan about how the development of Houston’s downtown would contribute to future storm protection and recovery. There are general references, such as the call for civic spaces—libraries, schools, community centers—that front the Green Loop to support resilience and disaster recovery goals. But few specifics; in fact, the word “resilience” appears only seven times in the plan’s text.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Dec 6, 2020
Ford lays out plans for mobility innovation district in Detroit
Its centerpiece is an abandoned train depot whose architecture and decay reflect two sides of this city’s past.
Resiliency | Nov 5, 2020
CRE investors are concerned that cities aren’t resilient enough for climate change
A new ULI-Heitman report states that the biggest challenge to valuation is measuring urban risk mitigation.
Multifamily Housing | Oct 22, 2020
The Weekly show: Universal design in multifamily housing, reimagining urban spaces, back to campus trends
BD+C editors speak with experts from KTGY Architecture + Planning, LS3P, and Omgivning on the October 22 episode of "The Weekly." The episode is available for viewing on demand.
Urban Planning | Jan 23, 2020
Unicorn Island’s first building nears completion
The building is the first on the 67-hectare island.
AEC Tech | Jan 16, 2020
EC firms with a clear ‘digital roadmap’ should excel in 2020
Deloitte, in new report, lays out a risk mitigation strategy that relies on tech.
Urban Planning | Jan 13, 2020
Henning Larsen designs all-timber neighborhood for Copenhagen
The project hopes to set a standard for how modern communities can live in harmony with nature.
Urban Planning | Jan 8, 2020
BIG partners with Toyota to unveil Toyota Woven City
It will be the world’s first urban incubator dedicated to the advancement of all aspects of mobility.
Urban Planning | Jan 3, 2020
BIG unveils Downtown Brooklyn Public Realm vision
BIG and WXY Architects are co-leading the project.
Urban Planning | Nov 22, 2019
Culdesac Tempe will be the country’s first from-scratch, car-free neighborhood
The neighborhood is scheduled to launch in 2020.
Sustainability | Nov 8, 2019
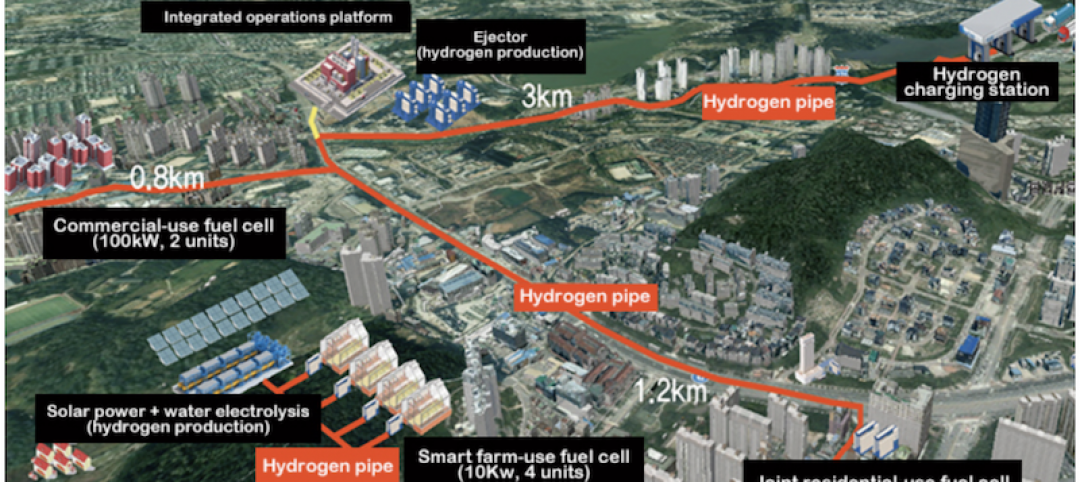
South Korea plans to build three hydrogen-powered cities by 2022
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport is in charge of the project.