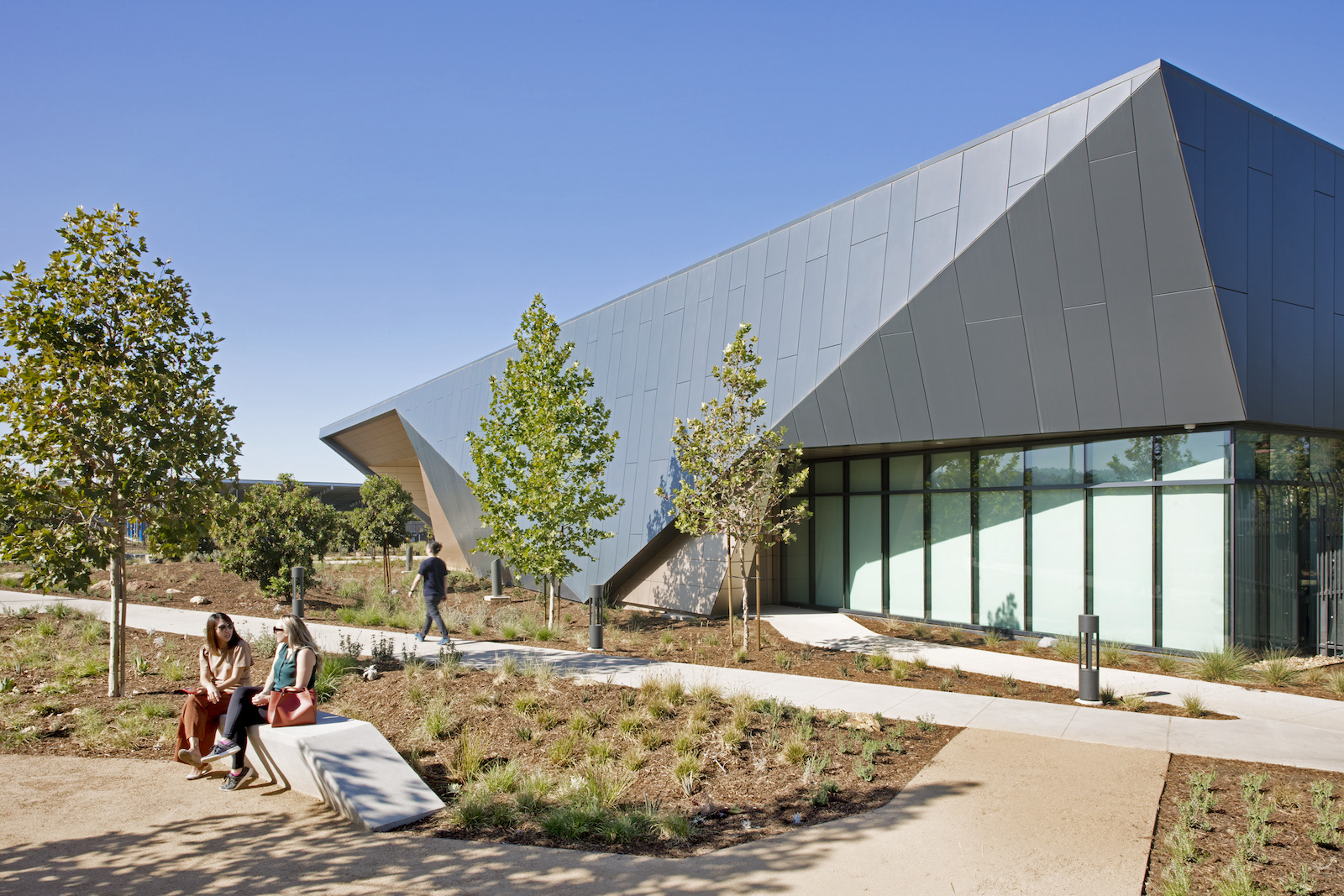
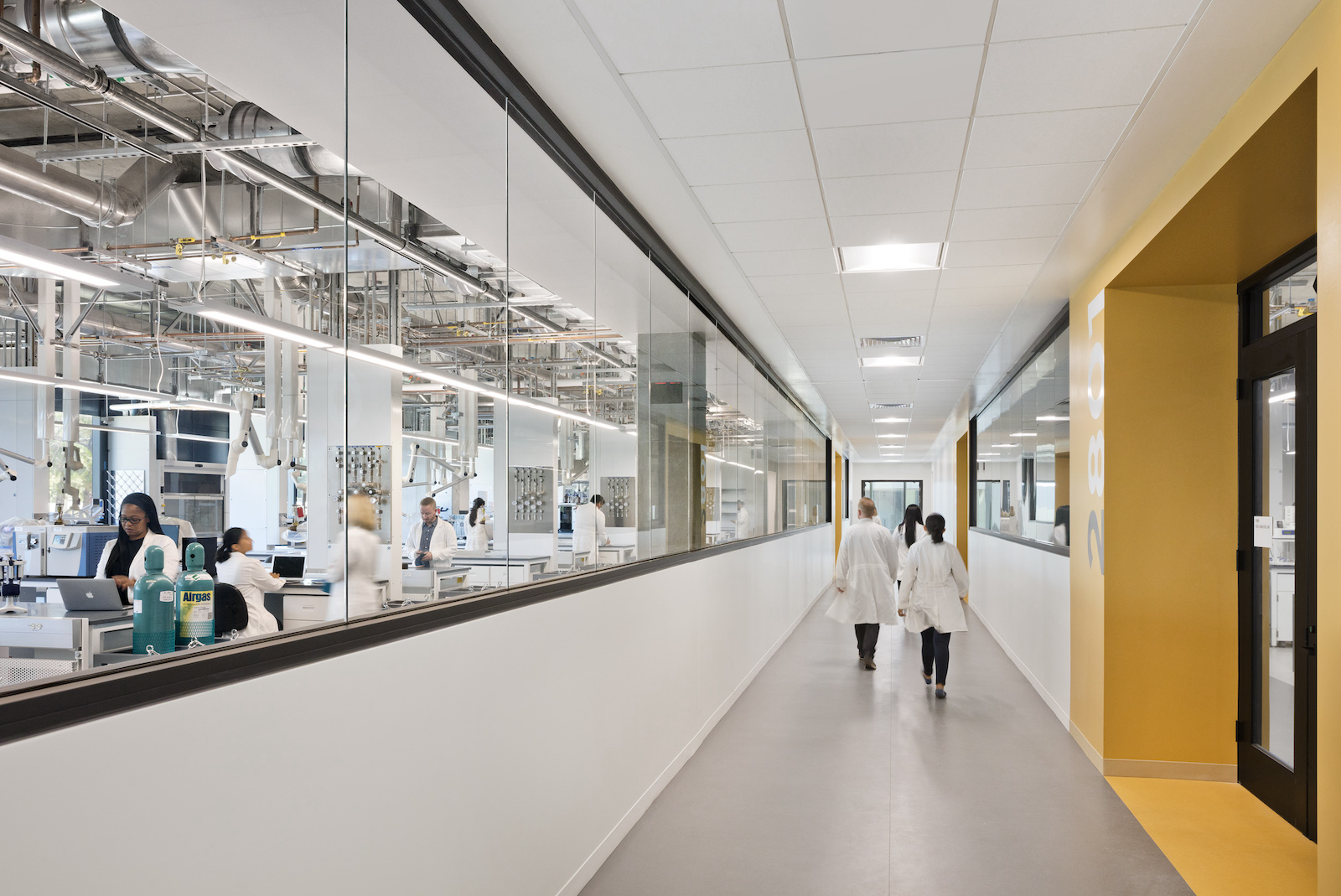
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) Southern California headquarters has been completed in Riverside, Calif. The 403,306-sf is the largest vehicle emissions testing facility in the world and the largest net-zero facility of its kind.
The CARB headquarters exceeds California Title 24 requirements by 30% and lowers energy cost savings by 75%. All of the energy needed is produced onsite, making it resilient to power outages and protecting it from pausing its research operations.
CARB consolidated five existing locations across Southern California into CARB’s headquarters which improves performance and efficiency of operations while also providing a healthy workplace for the organization’s employees. The design team’s focus was not just reaching high-performance targets, but creating a quality environment for CARB’s employees.
The features of the headquarters include a complex program with myriad space types, including a main entrance and lobby, an employee entrance and lounge, a large auditorium, open office, conference room, light-and-heavy-duty vehicular emissions testing wings, specialized chemistry and hydrogen laboratories, and employee amenity spaces such as an expensive breakroom and a gym. The facility is sited on 19 acres to encourage biking, walking, public transit, and use of zero emissions vehicles to reduce transportation impacts.
The facility effectively connects users to the outdoors. The layout and form of the building establishes two principle outdoor spaces: the main courtyard to the east and a more private courtyard to the west. The building is oriented around the courtyards to lend itself to easy circulation, views, daylighting, and self-shading. Coupled with an abundance of low B VOC-emission trees and plantings, comfortable outdoor respite spaces are established for employee enjoyment.
The massing of the office building is consolidated into three stories that extend in three directions parallel to light duty testing, chemistry labs, and toward the conference buildings. This creates a smaller building footprint and shortens horizontal circulation networks, while using vertical connectivity established by a network of bridges and stairs to increase proximity between offices, testing areas, support spaces, and laboratories, resulting in increased flexibility, optimized adjacencies, and greater opportunities for intellectual collisions among employees. A variety of types and scales of meeting spaces, as well as coffee bars and cafés promote interaction and collaboration, especially for staff who circulate between the various departments throughout the day.
The ground floor of the open office atrium features testing control desks where employees conduct and operate the air regulation testing that occurs in the test cells. These inset spaces throughout the office building first floor are open and allow all users to see the AC dynamometers, among other testing equipment, in action.
Beyond putting CARB vehicular testing on display, the energy reduction strategies in the office building also largely contribute to the facility’s net-zero energy status. The integration of chilled beams allowed the atrium ceiling to be kept high, making way for the collection of skylights—a passive lighting strategy—that create expansive views of the naturally lit workspace. Paired with task lighting and daylighting harvesting, the office wing, which accounts for 41% of the total program, uses only 15% of the total energy needed to operate the building.

Energy reduction strategies include:
- Fluid cooler - Using hybrid coolers in conjunction with an elevated 570°F chilled water temperature reduced estimated energy consumption of the facility by approximately 8%.
- Aircuity and demand control ventilation - Continuous indoor air monitoring maximizes ventilation efficiency and energy reduction.
- Adiabatic humidification - Air is humidified without using steam or an additional heat source, reducing energy consumption.
- Active chilled beams - The hydronic air cooling system uses less air, reducing energy requirements and overall operating costs.
- Daylighting - Skylights increase interior daylighting. Motorized interior shades reduce glare.
- Lighting - Site lighting: high efficiency LED site in parking. Interior lighting: interiors incorporate all LED lighting, task-ambient lighting, daylight harvesting control, dual lighting / HVAC occupancy sensors.
- Electrical vehicle charging - 118 EV charging stalls provided on site with the ability to expand to a total of 149 EV parking stalls.
- Fume hood occupancy-based control - Occupancy-based sensors integrated into the chemistry lab fume hoods reduce energy demands.
- Exterior louvers - Exterior louvers integrated into the southeast and west facades reduce solar heating and glare.
- High-performance glazing - Low-e insulated glazing with exterior louvers increase operational energy efficiency.
The facility was completed in August 2021. ZGF worked with Hensel Phelps and Affiliated Engineers on the project.
Related Stories
| Apr 30, 2014
Visiting Beijing's massive Chaoyang Park Plaza will be like 'moving through a urban forest'
Construction work has begun on the 120,000-sm mixed-use development, which was envisioned by MAD architects as a modern, urban forest.
| Apr 29, 2014
Best of Canada: 12 projects nab nation's top architectural prize [slideshow]
The conversion of a Mies van der Rohe-designed gas station and North Vancouver City Hall are among the recently completed projects to win the 2014 Governor General's Medal in Architecture.
| Apr 29, 2014
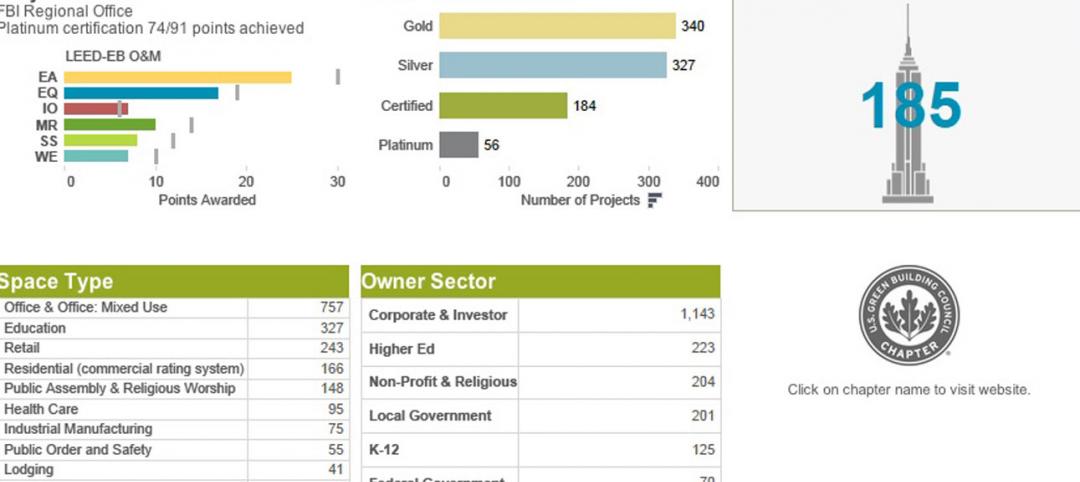
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
| Apr 23, 2014
Mean and Green: Top 10 green building projects for 2014 [slideshow]
The American Institute of Architects' Committee on the Environment has selected the top ten examples of sustainable architecture and ecological design projects that protect and enhance the environment. Projects range from a project for Portland's homeless to public parks to a LEED Platinum campus center.
| Apr 16, 2014
Upgrading windows: repair, refurbish, or retrofit [AIA course]
Building Teams must focus on a number of key decisions in order to arrive at the optimal solution: repair the windows in place, remove and refurbish them, or opt for full replacement.
| Apr 15, 2014
12 award-winning structural steel buildings
Zaha Hadid's Broad Art Museum and One World Trade Center are among the projects honored by the American Institute of Steel Construction for excellence in structural steel design.
| Apr 9, 2014
Steel decks: 11 tips for their proper use | BD+C
Building Teams have been using steel decks with proven success for 75 years. Building Design+Construction consulted with technical experts from the Steel Deck Institute and the deck manufacturing industry for their advice on how best to use steel decking.
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
| Mar 26, 2014
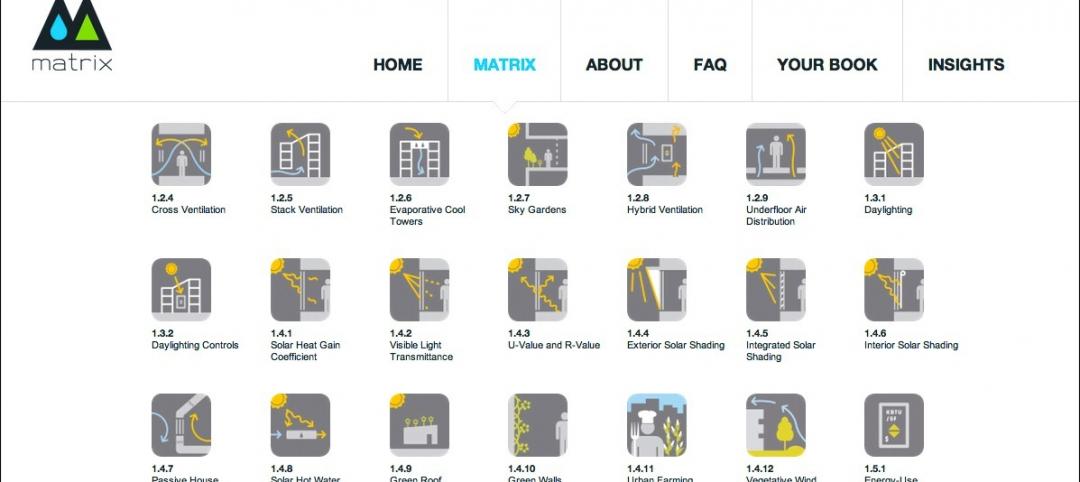
Callison launches sustainable design tool with 84 proven strategies
Hybrid ventilation, nighttime cooling, and fuel cell technology are among the dozens of sustainable design techniques profiled by Callison on its new website, Matrix.Callison.com.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.