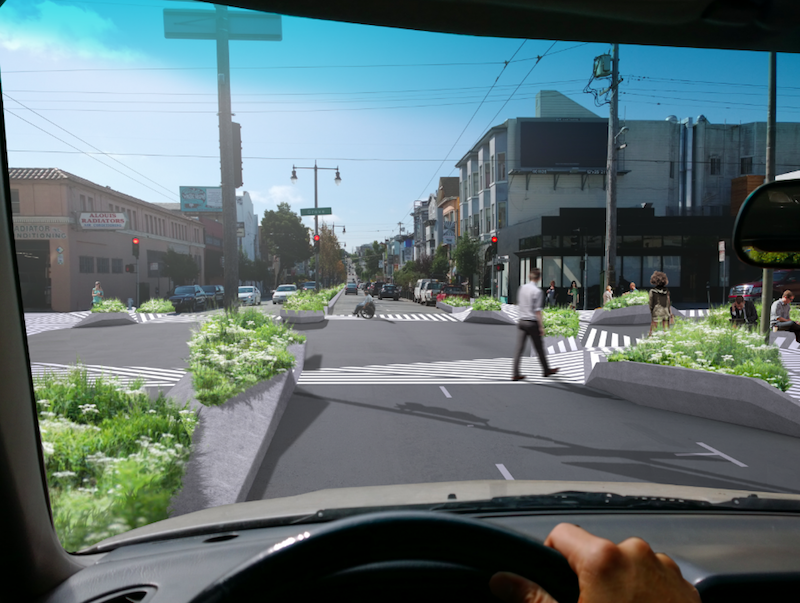
In San Francisco, an average of three people are hit by cars everyday, with 70 percent of these collisions occurring in crosswalks. It makes sense that the majority of these incidents occur in the space were cars and pedestrians converge the most, but is there a way to make crosswalks safer and lower the number of people who get hit by cars everyday?
The city of San Francisco believes so, which is why it has just broken ground on a $26 million project to renovate Masonic Avenue, one of the more accident prone streets in the city. Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects (OPA) believes so, as well. OPA has gone beyond focusing on just a single intersection or crosswalk, instead, creating a new design proposal for all crosswalks that takes surrounding green space and pulls it into the street, Curbed reports.
The idea behind the proposal is that people tend to drive differently, meaning more carefully, in a park than they do on an urban street. The redesign consists of two main components. The first component proposes adding highly visible black and white hatchings to the street at crosswalks in order to blur the edges between pedestrian and vehicle zones. The hatch pattern would go beyond the street and connect the four corners of the surrounding buildings, putting the pedestrians on center stage and alerting drivers to their presence.
The second component is a change to the actual physical space of city crosswalks. The plan proposes a three-dimensional kit of parts that would use geometric concrete curb extensions to not only define the curbs, but also be provide built-in benches and planters, extending the green space provided by parks into a more urban locale.
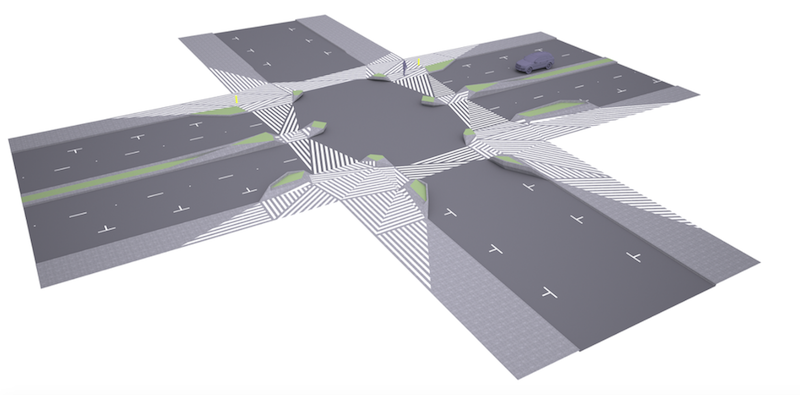 Image courtesy of Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects
Image courtesy of Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects
The combination of the hatchings and extended concrete curbs make pedestrians more visible while also providing them with more time to cross.
However, when looking at the renderings of the proposal, the new crosswalks appear to complicate a driver’s line of sight and the curb extensions provide new blind spots for pedestrians to pop out from behind, completely unseen. And, surely, turning crosswalks into green space suitable for sitting and having lunch or relaxing is not the way to reduce pedestrian versus vehicle accidents while simultaneously improving the flow of traffic.
The new road markings to increase pedestrian visibility are a good idea, but the second aspect of the proposal seems to be based on the idea that by increasing pedestrian presence around a crosswalk, drivers will be forced to be more careful. It seems a bit counterintuitive, like saying a traffic jam will result in fewer accidents than an open road because drivers will need to pay more attention to their surroundings in heavy traffic.
OPA, however, says it has the statistics to back up their proposal. According to the architect, each of the tactics its design uses has been proven to reduce pedestrian collisions by around 50%.
The proposal began as a design challenge, but according to the architecture firm, the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency is interested in exploring the idea more deeply.
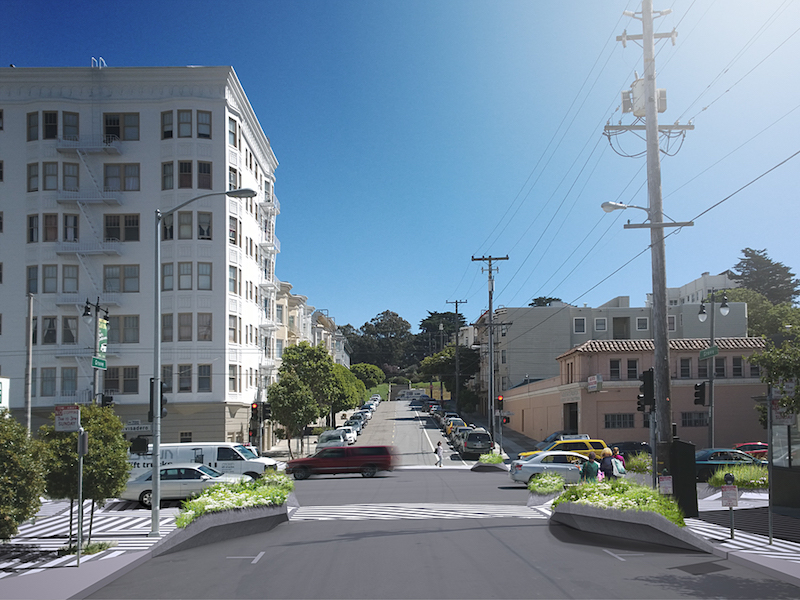 Image courtesy of Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects
Image courtesy of Ogrydziak Prillinger Architects
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Dec 4, 2017
Sports ‘districts’ are popping up all over America
In downtown Minneapolis, the city’s decision about where to build the new U.S. Bank Stadium coincided with an adjacent five-block redevelopment project.
Urban Planning | Dec 4, 2017
Can you spark an urban renaissance?
Thoughtful design, architecture, and planning can accelerate and even create an urban renaissance.
Urban Planning | Nov 20, 2017
Creating safer streets: Solutions for high-crash locations
While there has been an emphasis on improving safety along corridors, it is equally important to focus on identifying potential safety issues at intersections.
Urban Planning | Nov 16, 2017
Business groups present a new vision of Downtown Houston as that city’s unavoidable hub
The plan, which took 18 months to complete, emphasizes the centrality of downtown to the metro’s eight counties.
Architects | Oct 30, 2017
City 2050: What will your city look like in 2050?
What do we think the future will look like 30 years or so from now? And what will City: 2050 be like?
Great Solutions | Oct 17, 2017
Loop NYC would reclaim 24 miles of park space from Manhattan’s street grid
A new proposal leverages driverless cars to free up almost all of Manhattan’s Park Avenue and Broadway for pedestrian paths.
Mixed-Use | Aug 2, 2017
Redevelopment of Newark’s Bears Stadium site receives team of architects
Lotus Equity Group selected Michael Green Architecture, TEN Aquitectos, Practice for Architecture and Urbanism, and Minno & Wasko Architects and Planners to work on the project.
Urban Planning | Jul 21, 2017
Streets as storytellers: Defining places and connecting people
“In a city the street must be supreme. It is the first institution of the city. The street is a room by agreement, a community room, the walls of which belong to the donors, dedicated to the city for common use.” – Louis Kahn
Urban Planning | Jun 26, 2017
Convenience and community lead the suburban shift
As the demand for well-connected urban locales increases, so too has the cost of property and monthly rent; and as suburbs typically offer a bargain on both, more people are looking for a compromise.
Office Buildings | Jun 12, 2017
At 11.8 million-sf, LG Science Park is the largest new corporate research campus in the world
The project is currently 75% complete and on schedule to open in 2018.

















