A new report from researchers at UCLA and France's University Paris–Dauphine claims that workers at environmentally conscious - i.e., green - companies in France are 16% more productive than their counterparts at nongreen companies.
Before anyone starts applying these findings to buildings, note that nowhere in the report do the authors attribute increased worker productivity to sustainably designed and constructed buildings. There have been a lot of claims to that effect in the past, but no one has proved it definitively. If it could be proven, it would be a huge breakthrough for green buildings, since employers would more or less be obligated to provide green workplaces for their employees.
The 16% increase in productivity also seems pretty high. That would mean an additional hour and 15 minutes in productivity per day, or more than six hours a week - nearly an extra day of worker productivity every week. Sounds too good to be true.
Here's the press release from UCLA, with a link to the full report:
Employees at 'green' companies are significantly more productive, study finds
By Alison Hewitt
September 10, 2012
Bucking the idea that environmentalism hurts economic performance, a new UCLA-led study has found that companies that voluntarily adopt international "green" practices and standards have employees who are 16 percent more productive than the average.
Professor Magali Delmas, an environmental economist at UCLA's Institute of the Environment and Sustainability and the UCLA Anderson School of Management, and Sanja Pekovic from France's University Paris–Dauphine are the first to study how a firm's environmental commitment affects its productivity.
Their findings were published online Sept. 10, 2012, in the Journal of Organizational Behavior.
"Adopting green practices isn't just good for the environment," Delmas said. "It's good for your employees and it's good for your bottom line. Employees in such green firms are more motivated, receive more training, and benefit from better interpersonal relationships. The employees at green companies are therefore more productive than employees in more conventional firms."
For their study, "Environmental Standards and Labor Productivity: Understanding the Mechanisms That Sustain Sustainability," Delmas and Pekovic collected data from a survey of employees at 5,220 French companies, randomly selecting two employees from each company for a pool of more than 10,000 people. Companies that had voluntarily adopted international standards and eco-labels such as "fair trade" and "organic" or the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 14001 certification were identified as green.
The researchers determined each company's productivity by taking a logarithm of its value added (revenue minus costs), divided by the number of employees, which produced the average value of production per employee. They discovered a difference of one standard deviation, which corresponded to 16 percent higher-than-average labor productivity, in firms that voluntarily adopted environmental standards.
The employee surveys showed how much training employees received and how often they interacted with co-workers — which Delmas and Pekovic found also correlated with green companies.
"It's truly a big difference between firms that have adopted these practices and firms that haven't," Delmas said. "I expected a contrast, but not such a strong, robust jump in productivity."
Green certifications should be used by managers to increase productivity, by potential employees as a sign of a better work environment, and by investors as an indicator of good management practices, Delmas said. Previous research has already shown that sustainable business practices can result in cost-efficiencies, but Delmas and Pekovic are the first to explore the link to labor productivity.
"It's a counterpoint to people thinking that environmental practices are detrimental to the firm," Delmas said. "Green practices make a company more attractive because so many employees want to work for a company that is green, but we also argue in this paper that it's more than just wanting to work there — it's working more."
The findings reflect a change in attitudes, according to Delmas.
"When you talk now to M.B.A. students, there's a big change in the way they look at their future job," she said. "They don't want to work just to make money. They also want to make a difference. There's a little more social consciousness than there was before."
The 'virtuous circle'
Because fair trade, organic and ISO 14001 are international certifications that are commonly used in the United States, the findings are applicable in the U.S. and around the world, the authors said.
All three eco-labels are third-party certified: Fair trade certification requires fair wages and treatment for employees; organic certification recognizes commitments such as working without pesticides and other chemicals; and ISO 14001 certification requires firms to set up an organizational structure to investigate the company's environmental impact and how to reduce it.
The higher-productivity effect stems from employees' appreciation for their workplace, Delmas said. The certifications, especially ISO 14001, include educating employees about a firm's environmental commitment and require employees to work together across departments to reduce the organization's environmental impact. This education and training helps increase employees' identification with their office, while interdepartmental cooperation increases employees' engagement.
"It's a virtuous circle," Delmas said — the opposite of a vicious cycle. "You attract the best people, and because you're open-minded, then you adopt green standards, and then you attract even better people, and this continues to feed itself. Companies that adopt these policies tend to be better. It could be they were better to start with, but there are mechanisms built into these policies that mean they continue to get better."
Real-life examples
Although the companies from the survey retain confidentiality, it's an effect Delmas said she has seen elsewhere many times. At Patagonia, a sports clothing company well known for its sustainable practices, every job opening receives an average of 900 applicants eager to work for a green company, she said. At the Ambrose Hotel, a boutique hotel in Santa Monica, Calif., adopting wide-ranging sustainability measures made employees happier and healthier, Delmas found in a case study. Housekeeping workers reported fewer headaches, allergies and sick days after switching from chemical cleaners to non-toxic, green cleaning products.
In her research, Delmas has found that wineries also adopt the organic label to improve employees' health.
"I hope managers look at this and see the potential for their firms and employees," she said. "Socially responsible investors say green practices are a proxy for good management. It's also important for regulators to see that some voluntary practices can have beneficial effects."
Related Stories
| Jan 3, 2014
World’s tallest vegetated façade to sprout in Sri Lanka [slideshow]
Set to open in late 2015, the 46-story Clearpoint Residences condo tower will feature planted terraces circling the entire structure.
| Jan 2, 2014
Measuring whole building energy use among big changes in LEED v4
A new prerequisite in LEED v4 calls for each project to measure whole building energy use, and then share that data with USGBC.
| Dec 26, 2013
WDMA launches project to create ISO-compliant architectural doors
WDMA's National Architectural Door Council has initiated a project to create ISO-compliant Product Category Rules for architectural wood flush and stile and rail doors
| Dec 20, 2013
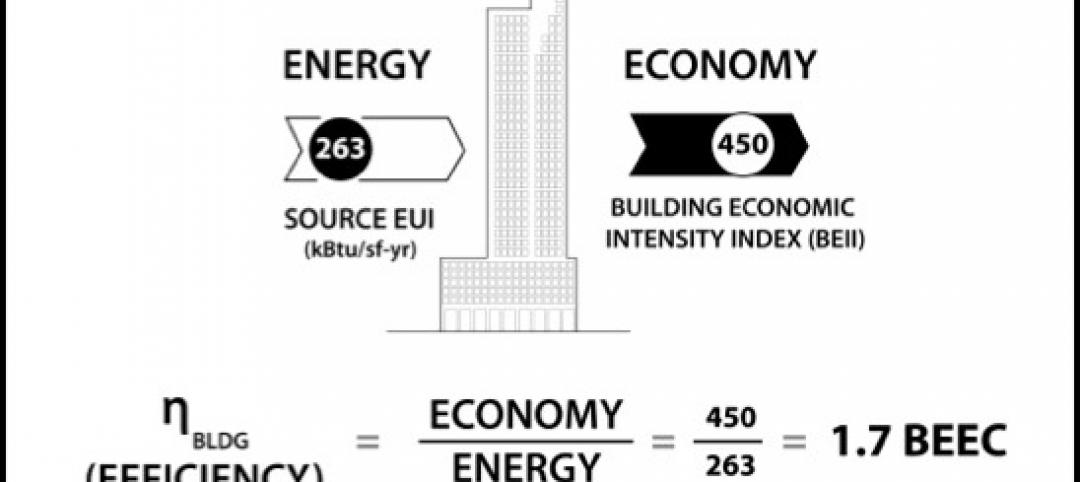
Can energy hogs still be considered efficient buildings? Yes, say engineers at Buro Happold
A new tool from the engineering firm Buro Happold takes into account both energy and economic performance of buildings for a true measure of efficiency.
| Dec 19, 2013
NRDC report relates green infrastructure investments to commercial property value [Infographic]
The Natural Resources Defense Council has released The Green Edge: How Commercial Property Investment in Green Infrastructure Creates Value -- a first-ever illustrative and well-documented report that helps demonstrate the value of green infrastructure. It draws from available published material to capture the multitude of tangible, monetizable non-water quality and water quality benefits that green infrastructure investments (trees, rain gardens, and porous pavement, rainwater harvesting cisterns, bioswales, etc.) can unlock for the commercial real estate sector, including commercial property owners and their tenants.
| Dec 19, 2013
Urban populations, climate change demand resilient design: Report
With over fifty percent of the population already living in urban areas, cities must grapple with the potentially catastrophic effects of climate change (think: Superstorm Sandy in New York). In a new report, Jones Lang LaSalle has identified steps cities can take to make their infrastructure more resilient to changing climate conditions.
| Dec 17, 2013
Nation's largest net-zero K-12 school among winners of 2013 Best of Green Schools award
The Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, was named a winner of USGBC's annual award, along with nine other schools, individuals and communities working toward the common goal of healthy, high-performing learning places.
| Dec 10, 2013
16 great solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
From a crowd-funded smart shovel to a why-didn’t-someone-do-this-sooner scheme for managing traffic in public restrooms, these ideas are noteworthy for creative problem-solving. Here are some of the most intriguing innovations the BD+C community has brought to our attention this year.
| Dec 9, 2013
What is life cycle cost optioneering?
Life cycle cost optioneering is a way of assessing alternative design options, analyzing their long-term capital and operational costs to identify those with the lowest price tag, over the entire life cycle.
| Nov 27, 2013
LEED for Healthcare offers new paths to green
LEED for Healthcare debuted in spring 2011, and certifications are now beginning to roll in. They include the new Puyallup (Wash.) Medical Center and the W.H. and Elaine McCarty South Tower at Dell Children’s Medical Center of Central Texas in Austin.