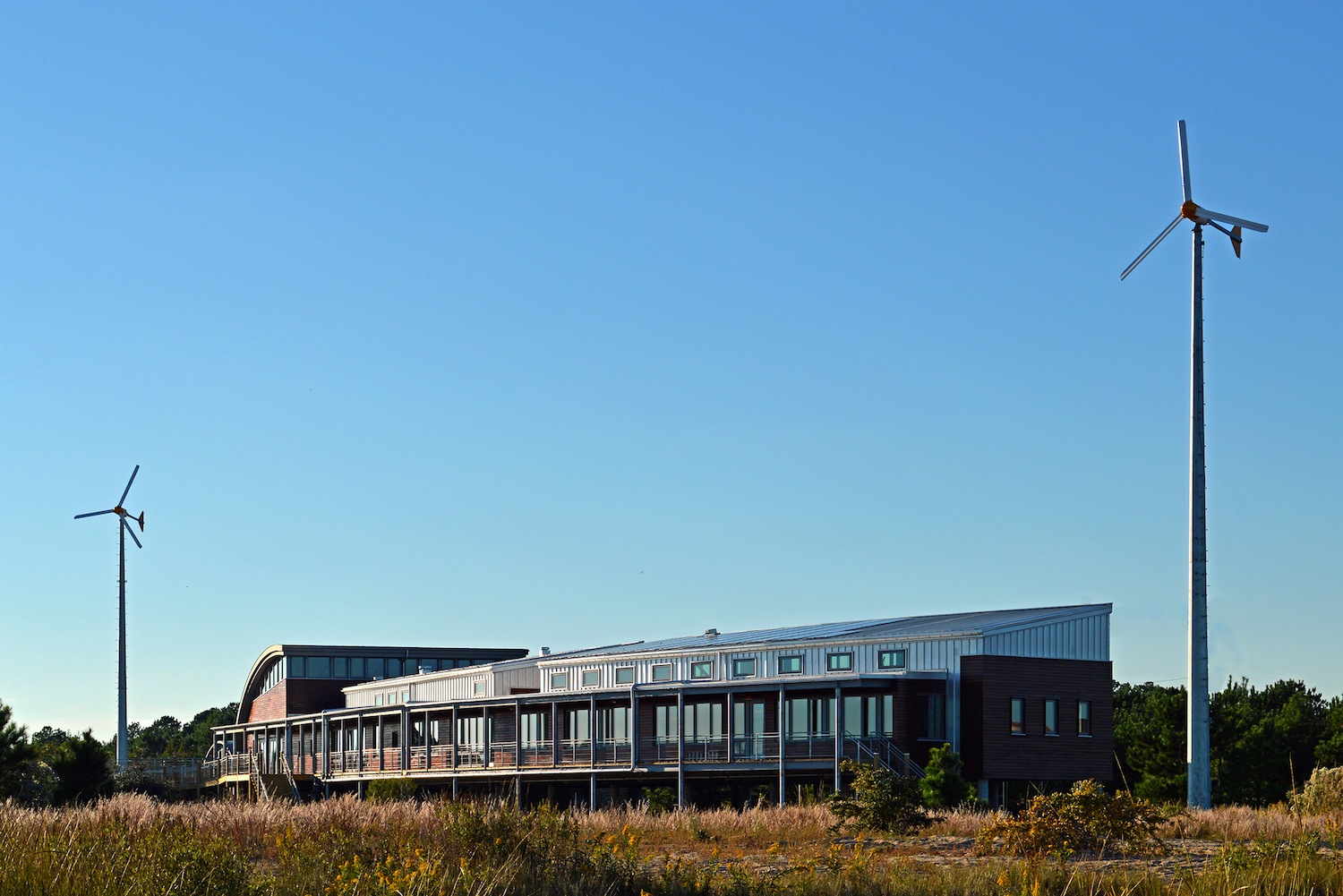
The Chesapeake Bay Foundation’s (CBF) Brock Environmental Center reached construction completion today in Virginia Beach, Va. Designed by SmithGroupJJR and constructed by Hourigan Construction, the Center is an international model for energy and water efficiency and climate change resiliency.
The 10,000-sf, one-story building will serve as the hub for CBF’s Hampton Road office and support its Chesapeake Bay education, outreach, advocacy and restoration initiatives. In addition to offices for CBF and partner groups, the Center provides meeting rooms and exhibit display areas, and an 80-seat conference room designed to express CBF’s mission to defend one of the nation’s most valuable and threatened natural resources—the Chesapeake Bay.
Every aspect of the Center—location, materials, utilities, operation and use—meets the strictest environmental standards. “With the Brock Environmental Center, CBF is raising the bar for sustainability,” said Greg Mella, FAIA, LEED AP, SmithGroupJJR project manager and design architect.
“The Brock Center is a model for environmental awareness in our industry,” commented Mark Hourigan, president of Hourigan Construction.
The Center is targeting LEED Platinum designation and also strives to meet the strict standards of the Living Building Challenge (LBC), a green building certification program promulgated by the International Living Future Institute that defines the most advanced measure of sustainability in the built environment possible today. LBC standards require the facility to have “net zero” impact on the environment. The Brock Environmental Center would become the first building in Virginia to earn LBC certification; to-date, only five projects in the world have achieved Full Certification through the Living Building Challenge.
Designed for Resiliency on a Preserved Site
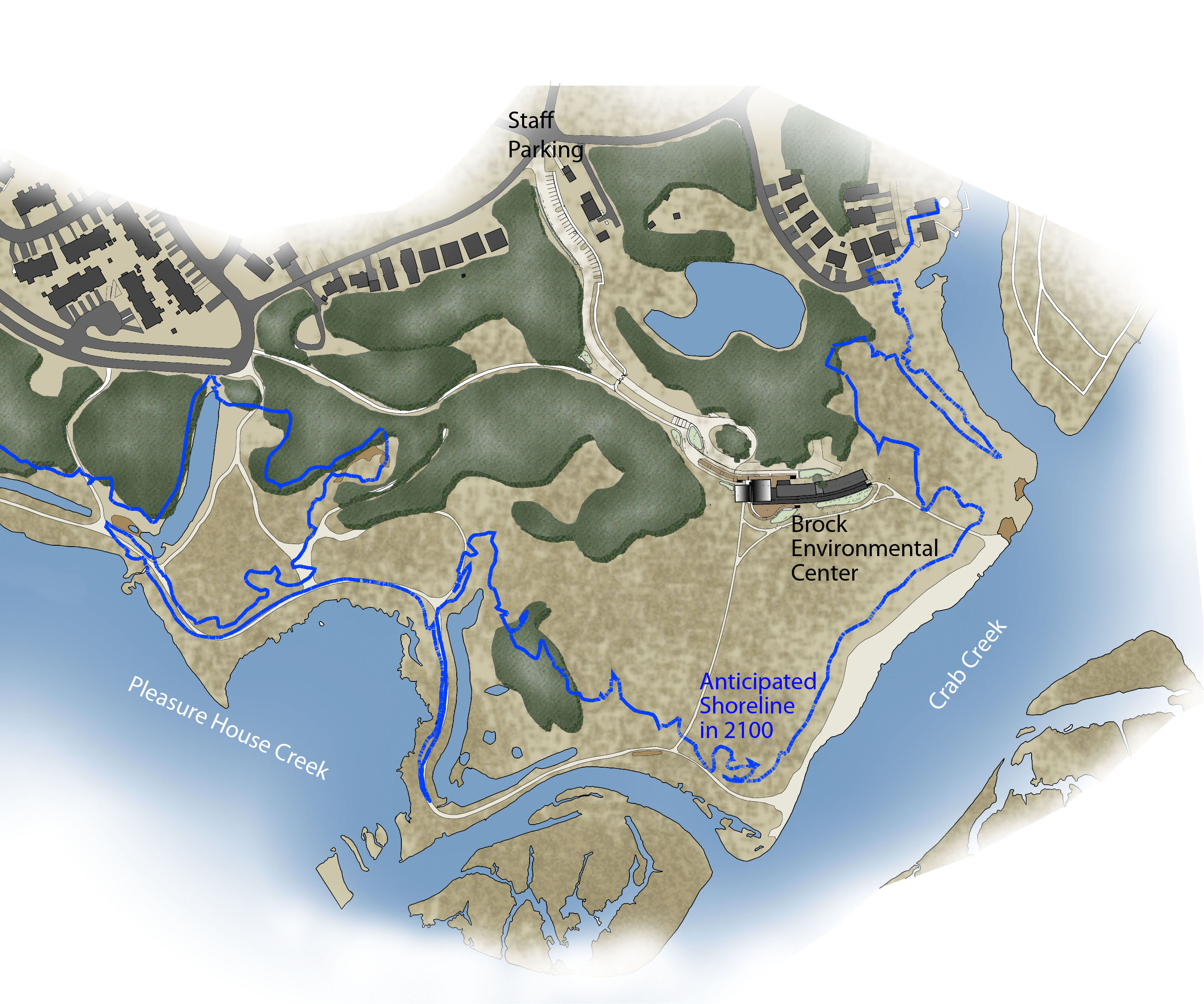
Completion of the Center concludes a successful community effort to save Virginia Beach’s 118-acre Pleasure House Point tract from development. As recently as 2008, developers intended to build more than 1,100 new high-rise condos and townhouses on the property. The collapse of the housing market in 2009, however, led to bank foreclosure of the property.
A community partnership with CBF, the City of Virginia Beach and the Trust for Public Land purchased the land from the bank in 2012, preserving it for open space and environmental education. The new Center, the only major structure on the entire 118 acres, takes up only one-half acre of CBF’s 10-acre parcel. Preserving the local ecology was paramount upon development of the site, which includes a boat pier with floating dock and an open-air education pavilion.
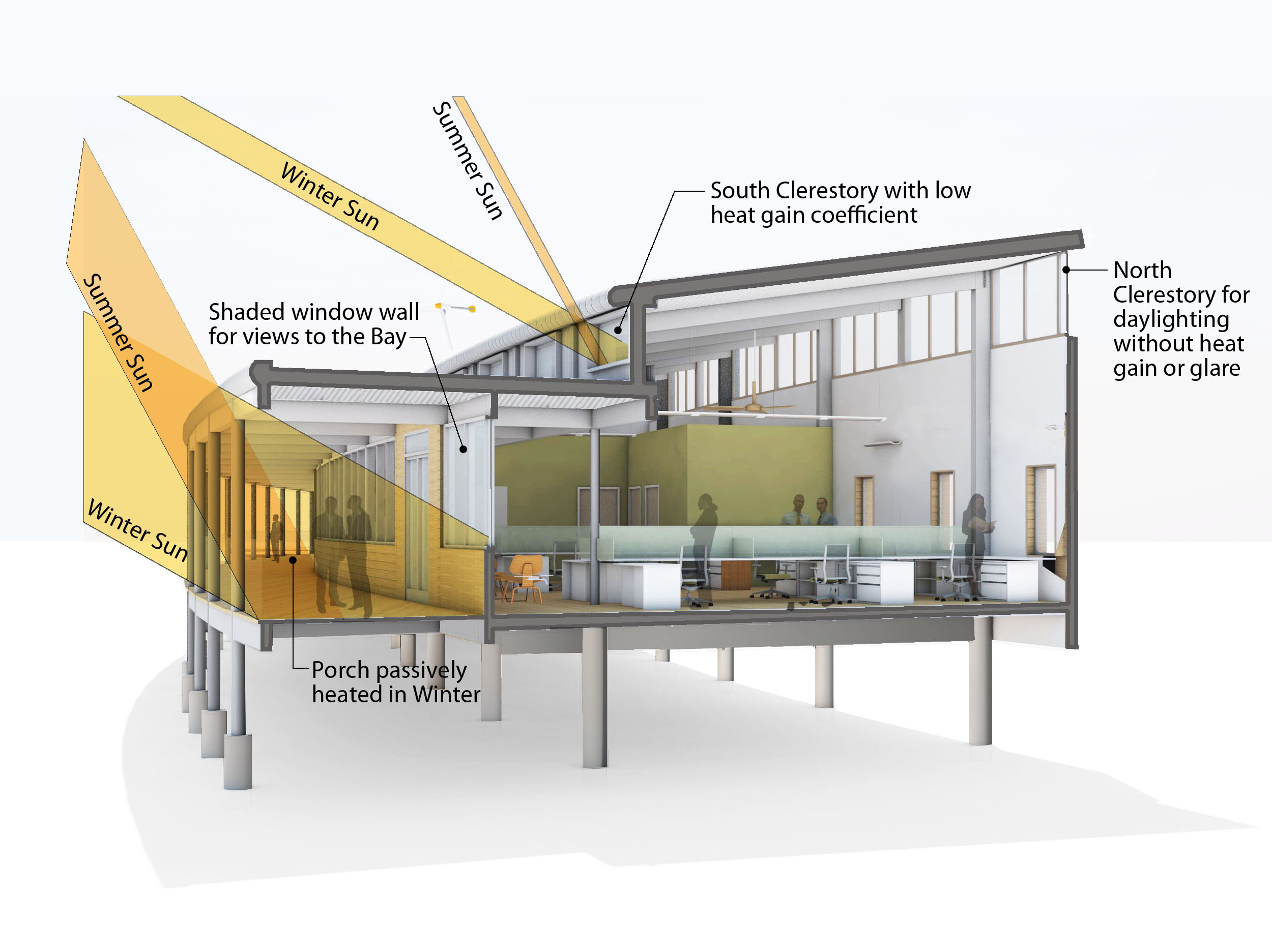
The project is situated on a coastal site to facilitate the client’s outdoor education program. The design anticipated the onset of sea-level rise and hurricanes: the building is set back 200 feet from the shore and sits on pylons 14 feet above sea level. Even the building’s structural steel system was designed to be capable of resisting 120-mph hurricane force winds.
“We had the opportunity to push the envelope on innovative and creative methods,” said Chris Brandt, executive vice president of Hourigan Construction. “There were so many certification levels that needed to be met that it was a job in itself to keep track of them all.”
Targeting Net-Zero Water, Energy and Waste
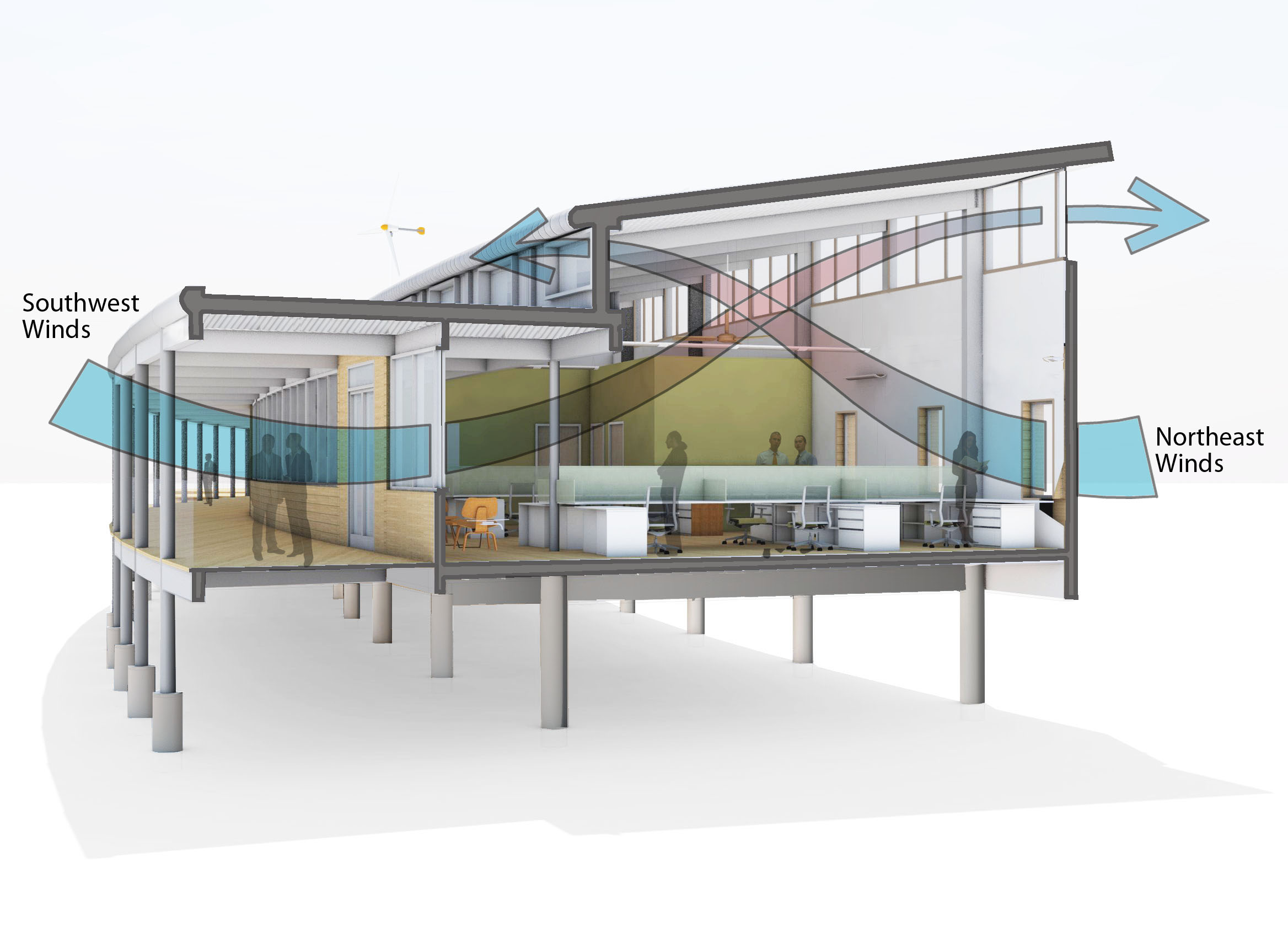
SmithGroupJJR designed the building to use very little energy by incorporating a series of aggressive, energy-saving features such as natural ventilation, natural daylighting and sunshading, highly efficient geo-thermal heating and cooling, and super insulation.
The Center is on track to be the first commercial-scale building in the continental U.S. to earn net-zero water status. A rainwater collection system will store rainwater in tanks under the building and then filter it for hand-washing and drinking through a state-of-the-art water filtration system licensed by the State of Virginia’s Office of Drinking Water. The Center features waterless, composting toilets, and all grey water (wastewater generated from sinks and showers) will be channeled through a wetland constructed of native plants where natural processes will clean and return it to the underground aquifer.
Net-zero energy status will be realized as the building generates its own electricity via solar and wind-powered renewable energy. The Center’s array of 38.8 kW rooftop photovoltaic panels will produce 60 percent of the building’s energy needs by converting the sun’s energy to electricity. Two small, 10-kilowatt wind turbines, 80’ tall, will contribute the remaining 40 percent of the building’s energy needs. Using only as much energy as it generates over the course of a year will enable the Center to earn net-zero energy certification. Surplus energy will be returned to the power grid.
Materials: Natural and Salvaged, “Red List” Chemicals Avoided
For the Center, construction materials were selected for their natural and simple properties. Preference was given to materials that are bio-based instead of those heavily processed, complex, synthetic and chemical-based. In specifying building materials, the design and construction team took special care to not use any materials on the International Living Future Institute’s “Red List,” which identifies chemicals and materials considered harmful to humans and the environment.
As a LBC requirement, recycled, salvaged and reclaimed materials were used extensively throughout the project. Examples include cypress siding from reclaimed sinker logs, wood flooring made from old fence posts and barn siding, interior wood trim from salvaged high school bleachers, and mirrors and toilet accessories from a local hospital demolition. The Rainwater Cistern and reception desk millwork were constructed from salvaged pickle barrels, and cabinet hardware consists of used champagne corks.
Hourigan Construction used cutting-edge building techniques in constructing the Center in order to minimize environmental impacts. In addition to using toxin-free building materials, sustainable measures used during construction included solar-powered tools and paperless construction documents. Normal construction equipment noise was reduced by the use of filters and baffles on the exhaust systems of all operating equipment, and slings or, in effect, construction equipment diapers were used so no equipment discharge would be deposited on the building site.
Even Hourigan’s on-site construction offices used less energy and water than normal systems. Instead of piping in treated water from the public grid, a deep fresh water well was installed to utilize existing water for construction use.
CBF: Continuing to Push the Boundaries of Sustainability
The Chesapeake Bay Foundation will occupy the building by the end of 2014. Prior, building occupants will be trained in the day-to-day operations and measurements of the renewable technologies. A 12-month measurement period is planned to commence in early 2015 and continue until early 2016. LBC certification is targeted for mid-2016.
The ultra-green Brock Environmental Center is the latest CBF initiative to push the boundaries of sustainability. The Foundation started with the 2000 completion of its Annapolis, Maryland headquarters building, the Philip Merrill Environmental Center, also designed by SmithGroupJJR. In 2001, the Merrill Center became the world’s first LEED Platinum building and was soon-after recognized as an international model of sustainability.
“What LEED Platinum was when we were designing the Philip Merrill Environmental Center, the Living Building Challenge is now,” said SmithGroupJJR’s Mella, who is based at the firm’s Washington, DC office. “Back then, we were designing to do less harm to the environment. Now, we’ve designed a building that could actually improve the environment,” he added.
The Brock Environmental Center is named in honor of Virginia Beach philanthropists Joan and Macon Brock in recognition of their $3.5 million donation toward the $21 million capital campaign to build, operate and endow a new Hampton Roads environmental center.
Joining SmithGroupJJR (architect and MEP engineer) and Hourigan Construction (general contractor) were WPL Site Design, Virginia Beach, civil engineer and landscape architect; and A+F Engineers, Washington, DC, for structural engineering. Skanska, New York, NY, served as the owner’s representative.
SmithGroupJJR (www.smithgroupjjr.com) is a recognized, integrated design firm with 800 employees in 10 offices. With more than 100 LEED certified projects and 343 LEED professionals, SmithGroupJJR is a national leader in sustainable design.
Hourigan Construction (www.houriganconstruction.com) is a full-service construction management company with operations throughout the Southeast U.S. The firm has constructed multiple projects in the Hampton Roads region and across Virginia.
Related Stories
Building Technology | Jun 18, 2024
Could ‘smart’ building facades heat and cool buildings?
A promising research project looks at the possibilities for thermoelectric systems to thermally condition buildings, writes Mahsa Farid Mohajer, Sustainable Building Analyst with Stantec.
University Buildings | Jun 18, 2024
UC Riverside’s new School of Medicine building supports team-based learning, showcases passive design strategies
The University of California, Riverside, School of Medicine has opened the 94,576-sf, five-floor Education Building II (EDII). Created by the design-build team of CO Architects and Hensel Phelps, the medical school’s new home supports team-based student learning, offers social spaces, and provides departmental offices for faculty and staff.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Mass Timber | Jun 17, 2024
British Columbia hospital features mass timber community hall
The Cowichan District Hospital Replacement Project in Duncan, British Columbia, features an expansive community hall featuring mass timber construction. The hall, designed to promote social interaction and connection to give patients, families, and staff a warm and welcoming environment, connects a Diagnostic and Treatment (“D&T”) Block and Inpatient Tower.
Concrete Technology | Jun 17, 2024
MIT researchers are working on a way to use concrete as an electric battery
Researchers at MIT have developed a concrete mixture that can store electrical energy. The researchers say the mixture of water, cement, and carbon black could be used for building foundations and street paving.
Codes and Standards | Jun 17, 2024
Federal government releases national definition of a zero emissions building
The U.S. Department of Energy has released a new national definition of a zero emissions building. The definition is intended to provide industry guidance to support new and existing commercial and residential buildings to move towards zero emissions across the entire building sector, DOE says.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 14, 2024
AEC inspections are the key to financially viable office to residential adaptive reuse projects
About a year ago our industry was abuzz with an idea that seemed like a one-shot miracle cure for both the shockingly high rate of office vacancies and the worsening housing shortage. The seemingly simple idea of converting empty office buildings to multifamily residential seemed like an easy and elegant solution. However, in the intervening months we’ve seen only a handful of these conversions, despite near universal enthusiasm for the concept.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 13, 2024
Top 10 trends in the hospital facilities market
BD+C evaluated more than a dozen of the nation's most prominent hospital construction projects to identify trends that are driving hospital design and construction in the $67 billion healthcare sector. Here’s what we found.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 13, 2024
4 ways to transform old buildings into modern assets
As cities grow, their office inventories remain largely stagnant. Yet despite changes to the market—including the impact of hybrid work—opportunities still exist. Enter: “Midlife Metamorphosis.”
Affordable Housing | Jun 12, 2024
Studio Libeskind designs 190 affordable housing apartments for seniors
In Brooklyn, New York, the recently opened Atrium at Sumner offers 132,418 sf of affordable housing for seniors. The $132 million project includes 190 apartments—132 of them available to senior households earning below or at 50% of the area median income and 57 units available to formerly homeless seniors.