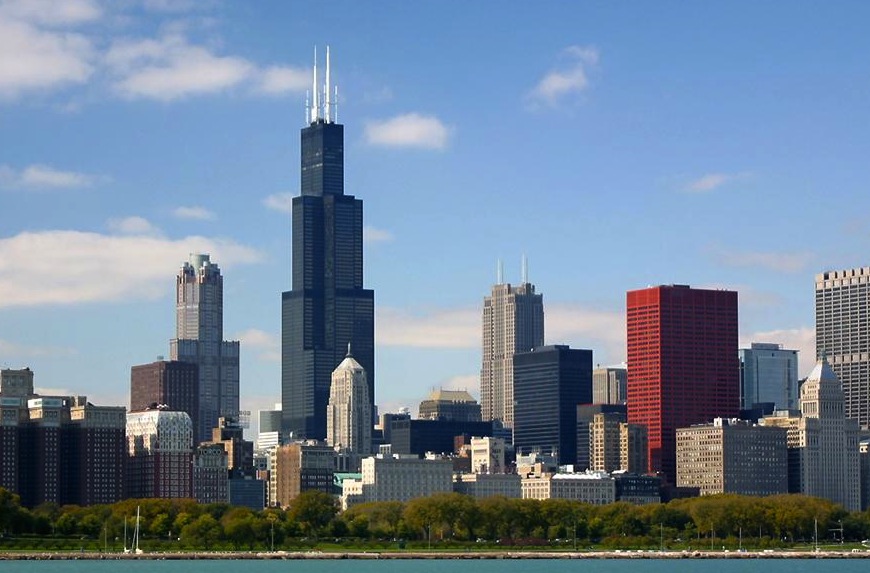
The Windy City is the latest U.S. city to enact legislation that mandates building energy benchmarking and disclosure for owners of large commercial and residential buildings. The ordinance was introduced in June 2013 and passed city council vote on Wednesday.
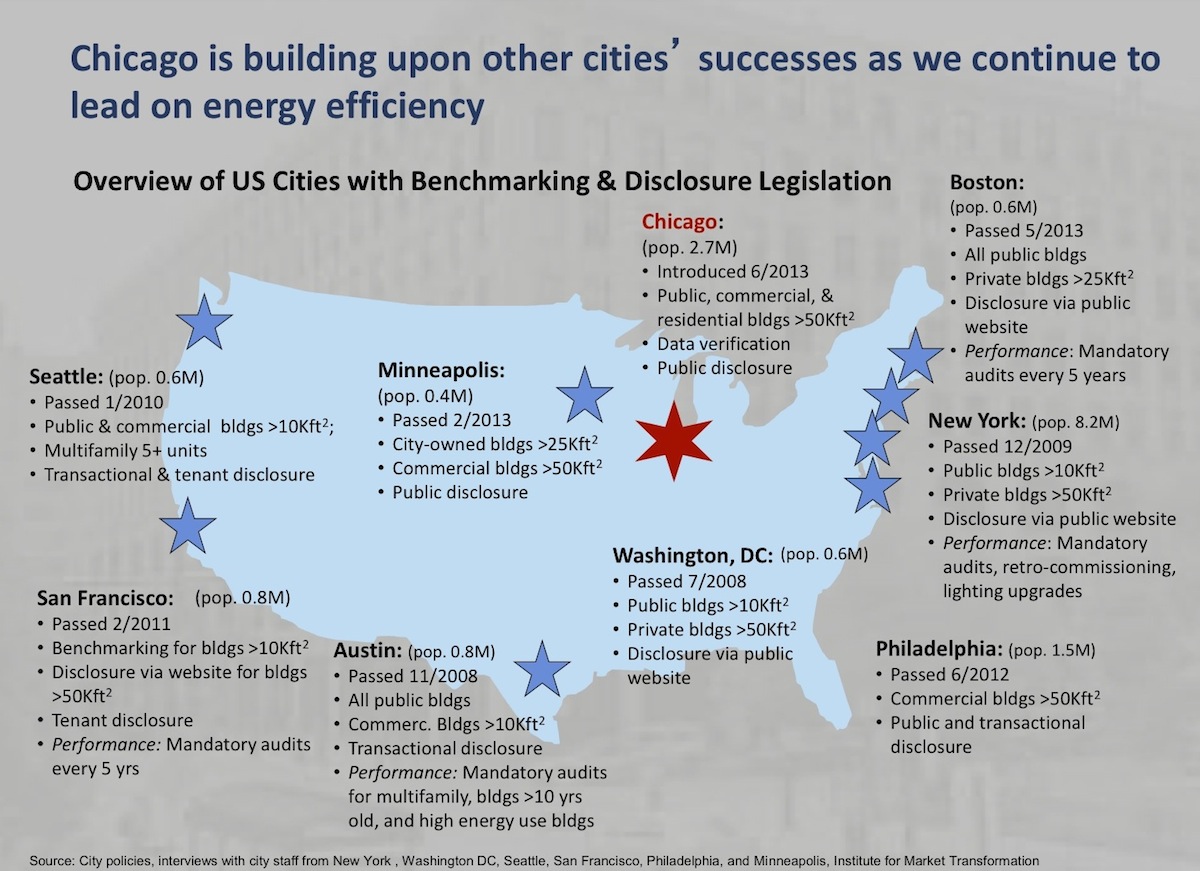
In developing the Chicago Energy Use Benchmarking & Transparency Ordinance, city officials reached out to eight U.S. cities that have enacted similar benchmarking legislation and adopted the best elements of each program.
During a panel discussion at BD+C's BUILDINGChicago conference this week, Jamie Ponce, Chicago City Director of the C40 - Clinton Climate Initiative, outlined the elements that differentiate Chicago's benchmarking ordinance. The most unique element, said Ponce, is a rule that mandates the verification of building energy data every three years. The data must be checked and verified by a registered architect, professional engineer, or other trained professional designated by the city. Chicago will be the only city with such a mandate.
"We asked representatives from the eight other cities what they would add or do differently, and the overwhelming majority mentioned the need for data quality and accuracy," said Ponce. "They said they were getting some questionable data from building owners."
Causes range from errors in data entry to owners not fully considering all aspects of the building in calculating the energy performance. "It's helpful to have an additional data check," added Ponce. The city will offer low- and no-cost verification options for building owners who cannot afford third-party data verification services.
Here's a breakdown of Chicago's benchmarking ordinance (click image to enlarge):
Here's a comparison of the various U.S. city ordinances (click image to enlarge):
For more on Chicago's ordinance, click here.
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | Apr 26, 2022
Investment firm Blackstone makes $13 billion acquisition in student-housing sector
Blackstone Inc., a New York-based investment firm, has agreed to buy student-housing owner American Campus Communities Inc.
Mixed-Use | Apr 22, 2022
San Francisco replaces a waterfront parking lot with a new neighborhood
A parking lot on San Francisco’s waterfront is transforming into Mission Rock—a new neighborhood featuring rental units, offices, parks, open spaces, retail, and parking.
Multifamily Housing | Apr 20, 2022
A Frankfurt tower gives residents greenery-framed views
In Frankfurt, Germany, the 27-floor EDEN tower boasts an exterior “living wall system”: 186,000 plants that cover about 20 percent of the building’s facade.
Multifamily Housing | Apr 20, 2022
Prism Capital Partners' Avenue & Green luxury/affordable rental complex is 96% leased
The 232-unit rental property, in Woodbridge, N.J., has surpassed the 96 percent mark in leases.
Senior Living Design | Apr 19, 2022
Affordable housing for L.A. veterans and low-income seniors built on former parking lot site
The Howard and Irene Levine Senior Community, designed by KFA Architecture for Mercy Housing of California, provides badly needed housing for Los Angeles veterans and low-income seniors
Market Data | Apr 14, 2022
FMI 2022 construction spending forecast: 7% growth despite economic turmoil
Growth will be offset by inflation, supply chain snarls, a shortage of workers, project delays, and economic turmoil caused by international events such as the Russia-Ukraine war.
Wood | Apr 13, 2022
Mass timber: Multifamily’s next big building system
Mass timber construction experts offer advice on how to use prefabricated wood systems to help you reach for the heights with your next apartment or condominium project.
Codes and Standards | Apr 13, 2022
LEED multifamily properties fetch higher rents and sales premiums
LEED-certified multifamily properties consistently receive higher rents than non-certified rental complexes, according to a Cushman & Wakefield study of two decades of data on Class A multifamily assets with 50 units or more.
Multifamily Housing | Apr 7, 2022
Ken Soble Tower becomes world’s largest residential Passive House retrofit
The project team for the 18-story high-rise for seniors slashed the building’s greenhouse gas emissions by 94 percent and its heating energy demand by 91 percent.