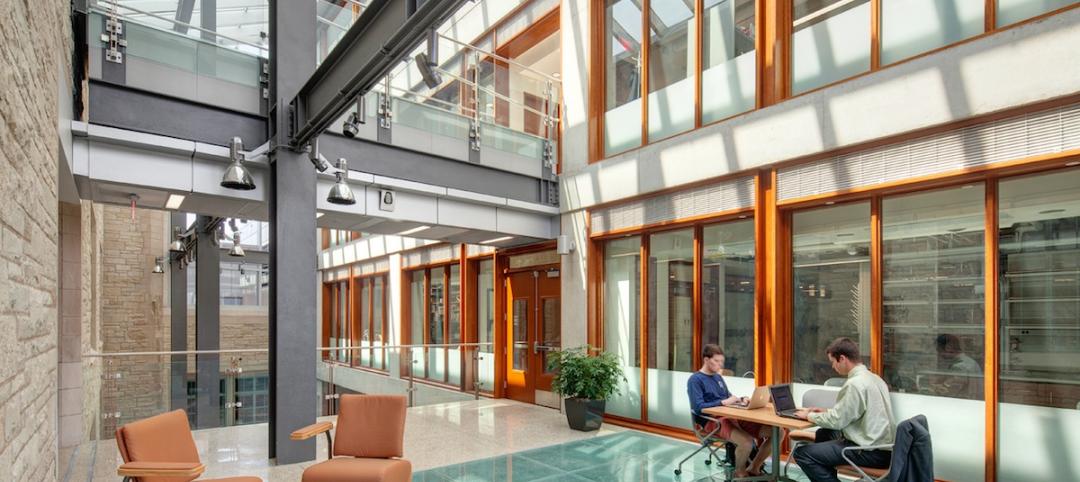
When the University of Wisconsin School of Business officially opened the Learning Commons last May, it kicked off the first step in realizing the university’s grand masterplan to renovate the library buildings across the Madison campus. “The design strategy for this Learning Commons space included connecting the east and the west wings of Grainger Hall. Transparency was a key principle for making this happen,” says Scott Kammer, AIA at Potter Lawson. Incorporating transparency between spaces extended to the stairwells as well. To meet the design intent and code requirements, the architects decided to use clear, fire resistive glass walls.
Traditionally, stairwells have been relegated to the back of the building and usually reserved for emergencies as their dark, isolated surroundings made it unappealing for everyday use. The lack of vision and transparency also made it a prime spot for attacks. This all changed with the advent of clear, fire resistive glazing able to meet the ASTM E-119/UL 263 wall standard up to 2 hours. Using transparent building materials that incorporate vision and code-compliance made it possible to design stairwells that are more centrally located instead of being tucked away in the back.
This was the case for the Learning Commons. “The existing building had two separate stairs that only connected two floors each. The centrally located stairwell connected all three levels of the Learning Commons and contributed to the wayfinding experience for the users. It was critical for this stairwell to be as clear as possible to see through the space,” adds Scott.
 Image created by MSR.
Image created by MSR.
During the design phase, Scott worked with Mike White at SAFTI FIRST to explore his options. “Mike was very responsive and answered our questions in a timely manner. He included photos of similar projects, which helped us specify exactly what we needed. He was very helpful in determining if the products would work with our budget at an early stage of design,” says Scott.
To achieve maximum transparency while meeting code requirements, the architects specified 9 ft. tall, clear, fire resistive butt-glazed walls using SuperLite II-XLM in GPX Architectural Series perimeter framing. Instead of vertical mullions, SuperLite II-XLM uses a slim, 6mm butt-joint between the fire resistive glass panels to allow as much transparency as possible while still meeting the fire resistive ASTM E-119/UL 263 wall requirement.
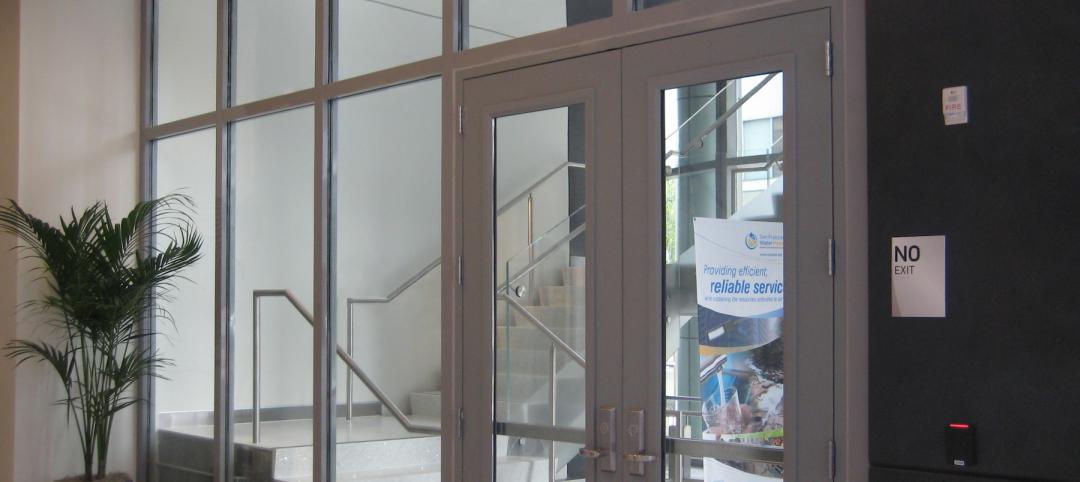
The entrances to the stairwell also maximized vision and transparency without sacrificing safety. Building codes in the USA limit ceramics and other fire protective glazing to 100 sq. in. in the vision panels of 60-90 minute doors in interior exit stairways, ramps and exit passageways regardless if the building is fully sprinklered. To exceed the 100 sq. in. door vision panel limitation, fire resistive glazing tested to ASTM E-119/UL 263 must be used.
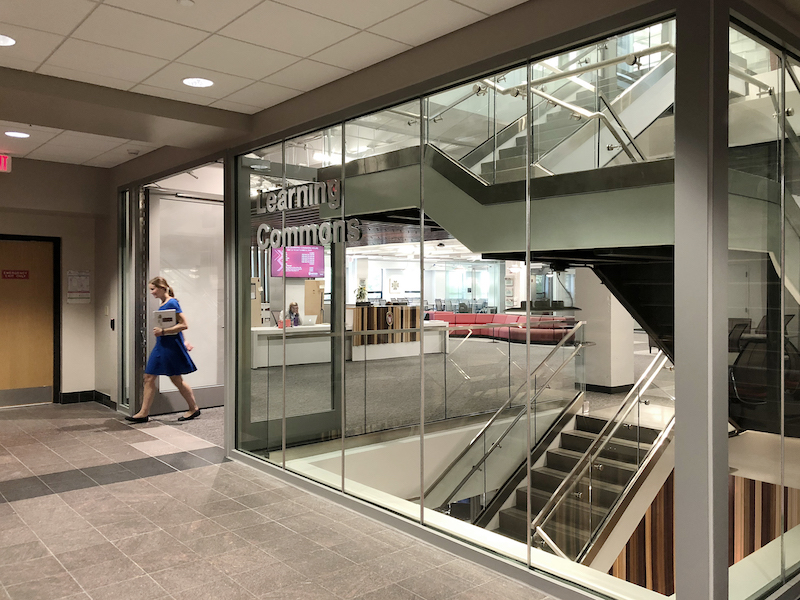 Photo: Olivia Nass.
Photo: Olivia Nass.
That’s exactly what the architects did for this project. For maximum vision and transparency, they specified full-vision temperature rise doors using an ASTM E-119/UL 263 rated assembly comprised of GPX Architectural Series Doors with SuperLite II-XL glazing. The doors also matched the 9-ft. height of the clear, fire resistive butt-glazed panels adjacent to it. With other aluminum temperature rise doors having a maximum height of 8 ft. tall, going with the GPX Architectural Series aluminum temperature rise door at the full 9 ft. height eliminated the need for a transom above the door. These doors do not require a mid-rail and were supplied with custom access hardware at the architect’s request for enhanced security.
SAFTI FIRST worked closely with Omni Glass & Paint during the installation phase. Even though fire resistive butt-glazed walls are a relatively new product in the market, the installation was a pretty smooth process. “I spoke with our installers and they did not see much of a difference in the captured and butt-glazed systems as far as ease of installation,” says Robert Leffel of Omni Glass & Paint. “The service from SAFTI FIRST was good. They did all they could to minimize delays,” he adds. SAFTI FIRST’s sales and project management teams were in constant communication with Omni throughout the bidding, submittal, fabrication and delivery stages.
The result is a visually stunning, code-compliant stairwell enclosure that helps connect the various spaces in this state-of-the-art Learning Commons that is sure to be enjoyed by students, faculty and visitors for years to come.
Related Stories
Sponsored | | May 3, 2014
Fire-rated glass floor system captures light in science and engineering infill
In implementing Northwestern University’s Engineering Life Sciences infill design, Flad Architects faced the challenge of ensuring adequate, balanced light given the adjacent, existing building wings. To allow for light penetration from the fifth floor to the ground floor, the design team desired a large, central atrium. One potential setback with drawing light through the atrium was meeting fire and life safety codes.
| Apr 25, 2014
Recent NFPA 80 updates clarify fire rated applications
Code confusion has led to misapplications of fire rated glass and framing, which can have dangerous and/or expensive results. Two recent NFPA 80 revisions help clarify the confusion. SPONSORED CONTENT
Sponsored | | Apr 23, 2014
Ridgewood High satisfies privacy, daylight and code requirements with fire rated glass
For a recent renovation of a stairwell and exit corridors at Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Ill., the design team specified SuperLite II-XL 60 in GPX Framing for its optical clarity, storefront-like appearance, and high STC ratings.
| Apr 8, 2014
Fire resistive curtain wall helps The Kensington meet property line requirements
The majority of fire rated glazing applications occur inside a building to allow occupants to exit the building safely or provide an area of refuge during a fire. But what happens when the threat of fire comes from the outside? This was the case for The Kensington, a mixed-use residential building in Boston.
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
Sponsored | | Mar 30, 2014
Ontario Leisure Centre stays ahead of the curve with channel glass
The new Bradford West Gwillimbury Leisure Centre features a 1,400-sf serpentine channel glass wall that delivers dramatic visual appeal for its residents.
| Mar 13, 2014
Austria's tallest tower shimmers with striking 'folded façade' [slideshow]
The 58-story DC Tower 1 is the first of two high-rises designed by Dominique Perrault Architecture for Vienna's skyline.
| Mar 7, 2014
Thom Mayne's high-tech Emerson College LA campus opens in Hollywood [slideshow]
The $85 million, 10-story vertical campus takes the shape of a massive, shimmering aircraft hangar, housing a sculptural, glass-and-aluminum base building.
| Feb 27, 2014
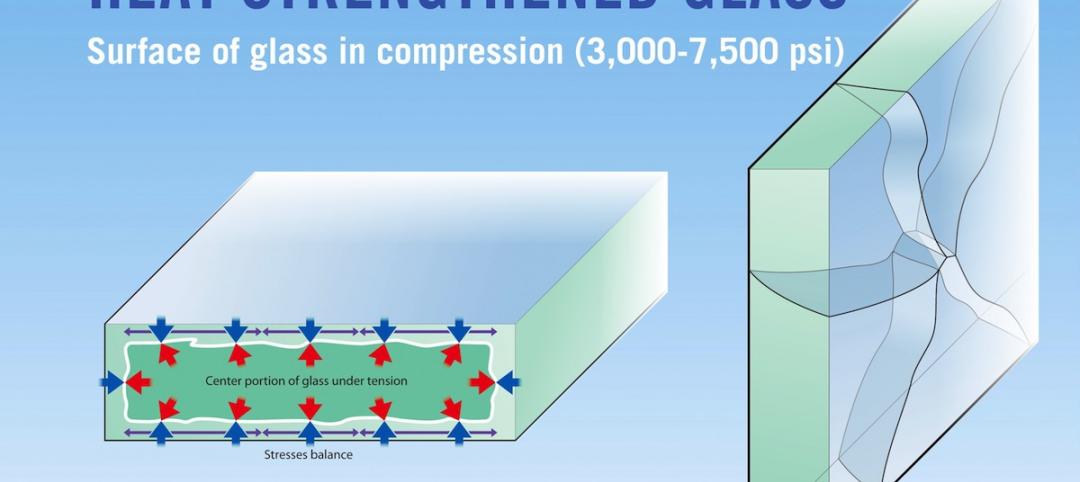
12 facts about heat-treated glass: Why stronger isn’t always better
Glass is heat-treated for two reasons: the first is to increase its strength to resist external stresses such as wind and snow loads, or thermal loads caused by the sun’s energy. The second is to temper glass so that it meets safety glazing requirements defined by applicable codes or federal standards.
| Feb 27, 2014
PPG earns DOE funding to develop dynamically responsive IR window coating Technology aims to maintain daylighting, control solar heat gain
PPG Industries’ flat glass business has received $312,000 from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to develop a dynamically responsive infrared (IR) window coating that will block heat in the summer to reduce air-conditioning costs and transmit solar heat in the winter to reduce heating costs.