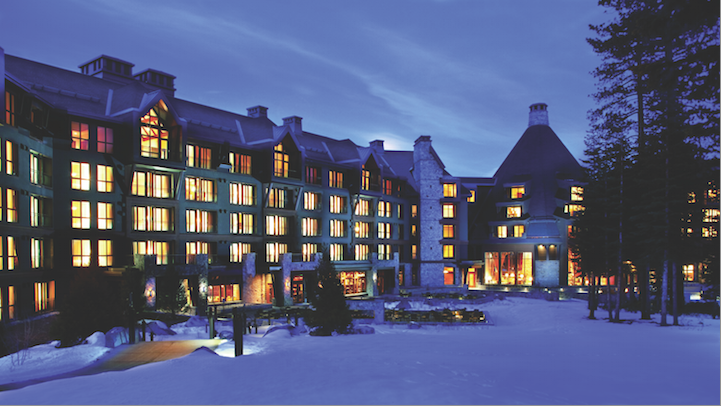
If you think your jobsite is problematic, wait until you hear what the Building Team for the 380,800-sf Ritz-Carlton Highlands resort in Lake Tahoe, Calif., had to contend with.
The project started off in mid-2006 on the wrong foot. Q&D/Swinerton, the joint venture general contractor, came in with an initial budget that was 10% higher than expected, a result of construction prices being driven up dramatically by a shortage of skilled carpenters and materials shortages, especially for concrete. These issues weighed heavily on the Building Team throughout the project.
To address the issue of the limited availability of concrete supplies and skilled carpentry trades, the general contractor ran estimates comparing the number of carpenters and the amount of material needed to build the project using concrete versus steel frame construction. Steel came out on top in this calculation, and the scales tipped for good in steel's favor when it was determined that the steel framing could be erected in a single season. Concrete construction was used for the four-level underground parking garage and the conference center above it.
Then there were the sheer physical demands of building seven thousand feet up in the Sierra Nevada. Access to the site was so limited that the team had to build a new four-and-a-half-mile access road-at an average grade of 10%-plus six bridges and tunnels before construction could begin on the hotel itself. Water mains and conduit for phones and cable were being laid at the same time, further complicating the roadwork.
In the summer, with the road only partially completed, construction crews found themselves sharing the right-of-way with mountain bikers, outdoor adventurers, trailside workers, and ski-resort repair and safety crews.
Getting 500 trade workers a day to the remote site over a three-year period meant that general contractor Q&D/Swinerton had to rent parking at nearby Truckee Tahoe Airport in the winter and at the Northstar-at-Tahoe resort in the summer and bus everyone up and down the mountain in all kinds of weather. This turned the task of scheduling and coordinating subcontractors into an intricate exercise.
The Building Team found itself working on the sensitive issue of erosion control with a community that's ultra-protective of their lake-these are the same people who bring you the "Keep Tahoe Blue" bumper stickers. The team consulted with local environmentalists and the Lahontan Conservation District on a runoff prevention plan that went well beyond the usual silt fences and waddles: the entire building site perimeter was temporarily paved to prevent soil disruption. Local regulations further stipulated that no soil could be moved from October 15 to April 15, so the team had to work around that restriction as well.
The Lake Tahoe region is blessed with an average 16 feet of snow each season, which can put the freeze on construction projects. To allow crews and materials to move around the site during winter months, snow was trucked away rather than stockpiled on the grounds.
As the building went up, it was encapsulated in plastic and heated so that construction could go on year-round. Unfortunately, this cozy environment also attracted black bears, which occasionally used the space for rent-free accommodation. Construction crews would find beds made of torn-up building insulation when they arrived in the morning.
Serving as inspiration for the five-star resort's architecture were such great historic lodges as the Ahwahnee (Yosemite National Park), the Timberline Lodge (Mt. Hood National Forest), and the Tahoe Tavern (Lake Tahoe). The new Ritz-Carlton has a steeply pitched roof, shallow eaves, shiplap siding, and a rustic base of locally sourced granite.
Inside, a modern take on the traditional lodge fireplace is constructed of weathered granite with a chimney that rises 55 feet above the hotel lobby. The massive four-sided fireplace-with its eight-sided chimney-serves as the focal point of the lobby and head-house. The chimney is not merely decorative: it is the central support column for both the head-house roof and the spiral entry staircase. The fireboxes alone took two months to build due to the intricate herringbone pattern used to lay the 200 tons of stone from which it was fashioned.
A BIM model was used to help coordinate design and construction processes. This cut down the need for frequent visits to the remote site which, along with savings on printing and mail, saved an estimated $285,000. Another $8 million in savings came from the detection of 450 design discrepancies, which the team estimates greatly reduced the number of change orders.
The Building Team of Q&D/Swinerton; East West Partners (owner); Hornberger + Worstell (architect); OZ Architects (architect of record); BraytonHughes Design Studio (interior architect); and S.A. Miro Inc. Consulting Engineers (structural engineers) and many other dedicated professionals surmounted all these challenges to create a 170-room luxury hotel and spa with 23 private residences and a 14,000-sf convention center that earned the project a Silver Award from our judging panel. The project is also awaiting LEED certification from the Green Building Certification Institute.
Although the initial cost estimate came in 10% over budget, the Building Team reworked every facet of the building, shaving almost $22 million from the price tag and bringing the project in at a construction cost of $226 million. The Ritz-Carlton Highlands opened on schedule last December, just in time for the winter ski season.
PROJECT SUMMARY
Silver Award
The Ritz-Carlton Highlands, Lake Tahoe
Truckee, Calif.
Building Team
Submitting firm: Q&D/Swinerton (joint venture GC)
Owner: East West Partners
Architect: Hornberger + Worstell
Architect of record: OZ Architects
Interior architect: BraytonHughes Design Studio
Structural engineer: S.A. Miro Inc. Consulting Engineers
MEP engineer: Beaudin Ganze Consulting Engineers
General Information
Project size: 380,800 sf
Construction cost: $226 million
Construction time: July 2006 to December 2009
Delivery method: CM at risk
Related Stories
Building Technology | Jun 18, 2024
Could ‘smart’ building facades heat and cool buildings?
A promising research project looks at the possibilities for thermoelectric systems to thermally condition buildings, writes Mahsa Farid Mohajer, Sustainable Building Analyst with Stantec.
University Buildings | Jun 18, 2024
UC Riverside’s new School of Medicine building supports team-based learning, showcases passive design strategies
The University of California, Riverside, School of Medicine has opened the 94,576-sf, five-floor Education Building II (EDII). Created by the design-build team of CO Architects and Hensel Phelps, the medical school’s new home supports team-based student learning, offers social spaces, and provides departmental offices for faculty and staff.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Mass Timber | Jun 17, 2024
British Columbia hospital features mass timber community hall
The Cowichan District Hospital Replacement Project in Duncan, British Columbia, features an expansive community hall featuring mass timber construction. The hall, designed to promote social interaction and connection to give patients, families, and staff a warm and welcoming environment, connects a Diagnostic and Treatment (“D&T”) Block and Inpatient Tower.
Concrete Technology | Jun 17, 2024
MIT researchers are working on a way to use concrete as an electric battery
Researchers at MIT have developed a concrete mixture that can store electrical energy. The researchers say the mixture of water, cement, and carbon black could be used for building foundations and street paving.
Codes and Standards | Jun 17, 2024
Federal government releases national definition of a zero emissions building
The U.S. Department of Energy has released a new national definition of a zero emissions building. The definition is intended to provide industry guidance to support new and existing commercial and residential buildings to move towards zero emissions across the entire building sector, DOE says.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 14, 2024
AEC inspections are the key to financially viable office to residential adaptive reuse projects
About a year ago our industry was abuzz with an idea that seemed like a one-shot miracle cure for both the shockingly high rate of office vacancies and the worsening housing shortage. The seemingly simple idea of converting empty office buildings to multifamily residential seemed like an easy and elegant solution. However, in the intervening months we’ve seen only a handful of these conversions, despite near universal enthusiasm for the concept.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 13, 2024
Top 10 trends in the hospital facilities market
BD+C evaluated more than a dozen of the nation's most prominent hospital construction projects to identify trends that are driving hospital design and construction in the $67 billion healthcare sector. Here’s what we found.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 13, 2024
4 ways to transform old buildings into modern assets
As cities grow, their office inventories remain largely stagnant. Yet despite changes to the market—including the impact of hybrid work—opportunities still exist. Enter: “Midlife Metamorphosis.”
Affordable Housing | Jun 12, 2024
Studio Libeskind designs 190 affordable housing apartments for seniors
In Brooklyn, New York, the recently opened Atrium at Sumner offers 132,418 sf of affordable housing for seniors. The $132 million project includes 190 apartments—132 of them available to senior households earning below or at 50% of the area median income and 57 units available to formerly homeless seniors.