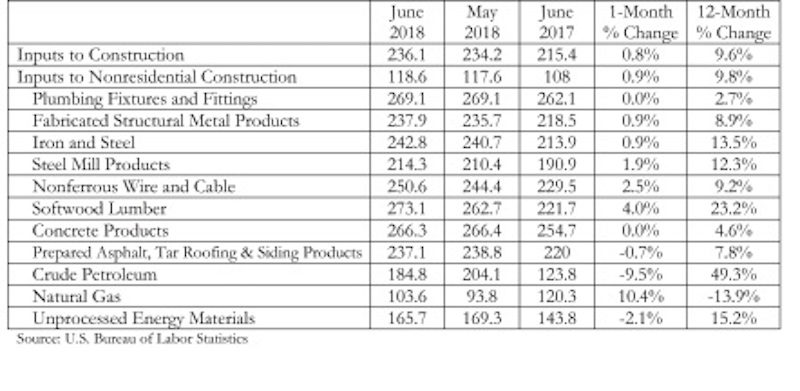
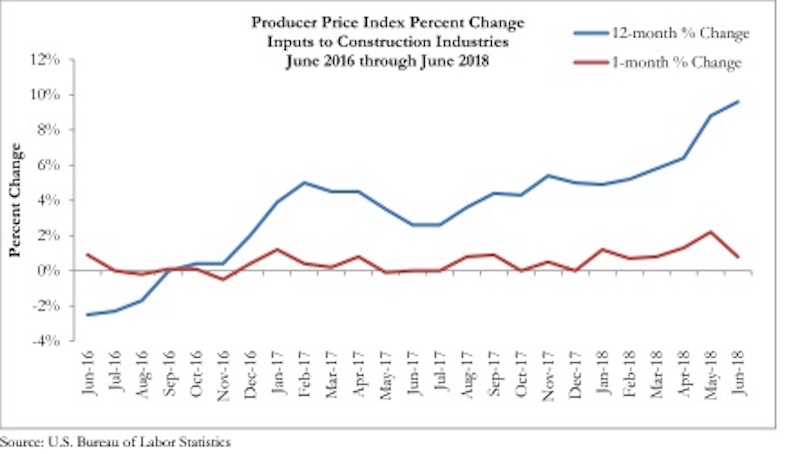
According to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data released today, construction material prices rose another 0.8% in June and are 9.6% higher than they were at the same time one year ago.
June represents the latest month associated with rapidly rising construction input prices. Nonresidential construction materials prices effectively mirrored overall construction prices by rising 0.9% on a month-over-month basis and 9.8% on a year-over-year basis.
“In general, this emerging state of affairs is unfavorable,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “Rapidly rising materials prices interfere with economic progress in numerous ways, including by making it less likely that a particular development will move forward. They also increase the cost of delivering government-financed infrastructure, raise costs for final consumers such as homeowners, renters and office tenants, and exacerbate overall inflationary pressures, which serves to push nominal borrowing costs higher.
“Materials prices are up roughly 10% in just one year, and certain categories have experienced significant rates of price increase,” said Basu. “Among these are key inputs that appear to have been impacted by evolving policymaking, including the price of crude petroleum, which is up 49% over the past year, iron and steel, which is up nearly 14%, and softwood lumber, up 23%.
“Some contractors may note the similarities between the current period and the period immediately preceding the onset of the global financial crisis,” said Basu. “Materials prices, for instance, were rising rapidly for much of 2006 and 2007 as the economic expansion that began in 2001 reached its final stages. Today’s data will provide further ammunition for policymakers committed to tightening monetary policy and raising short-term interest rates.
“With no end in sight regarding the ongoing tariff spat between the United States and a number of leading trading partners, and with the domestic economy continuing to expand briskly, construction input prices are positioned to increase further going forward, though the current rate of increase appears unsustainable.”
Related Stories
Market Data | Dec 2, 2020
Nonresidential construction spending remains flat in October
Residential construction expands as many commercial projects languish.
Market Data | Nov 30, 2020
New FEMA study projects implementing I-Codes could save $600 billion by 2060
International Code Council and FLASH celebrate the most comprehensive study conducted around hazard-resilient building codes to-date.
Market Data | Nov 23, 2020
Construction employment is down in three-fourths of states since February
This news comes even after 36 states added construction jobs in October.
Market Data | Nov 18, 2020
Architecture billings remained stalled in October
The pace of decline during October remained at about the same level as in September.
Market Data | Nov 17, 2020
Architects face data, culture gaps in fighting climate change
New study outlines how building product manufacturers can best support architects in climate action.
Market Data | Nov 10, 2020
Construction association ready to work with president-elect Biden to prepare significant new infrastructure and recovery measures
Incoming president and congress should focus on enacting measures to rebuild infrastructure and revive the economy.
Market Data | Nov 9, 2020
Construction sector adds 84,000 workers in October
A growing number of project cancellations risks undermining future industry job gains.
Market Data | Nov 4, 2020
Drop in nonresidential construction offsets most residential spending gains as growing number of contractors report cancelled projects
Association officials warn that demand for nonresidential construction will slide further without new federal relief measures.
Market Data | Nov 2, 2020
Nonresidential construction spending declines further in September
Among the sixteen nonresidential subcategories, thirteen were down on a monthly basis.
Market Data | Nov 2, 2020
A white paper assesses seniors’ access to livable communities
The Joint Center for Housing Studies and AARP’s Public Policy Institute connect livability with income, race, and housing costs.