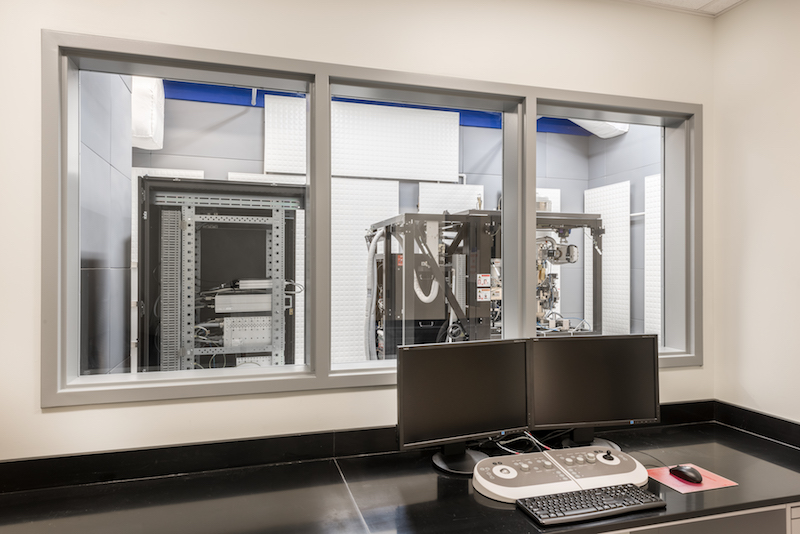
The University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester, Mass., held grand opening ceremonies on October 4 for its new Massachusetts Facility for High-Resolution Cyro-Electron Microscopy, the first of its kind in New England, and one of only a handful of similar facilities nationwide.
TRO Architects designed this $20 million, 4,100-sf facility, for which Consigli was construction manager.
Cryo-Electron Microscopy, or cyro-EM, was recently called the “research method of the year” by Nature magazine. “Cryo-EM is particularly well suited for obtaining structural information for large protein complexes and for systems that exhibit multiple conformational or compositional states,” the magazine explained.
By first plunging particle samples into liquid nitrogen, cyro-EM processes images of particles at near-atomic levels. It is said to be revolutionizing structural biology by helping to identify likely therapeutic approaches to a broad range of diseases, including neurological ailments such as Alzheimer’s. “With cryo-EM, we can look at detailed mechanisms and dynamics in molecules and complexes of molecules to understand their functions, dissecting each step to have a high-resolution picture of how they work,” said UMMS structural biologist Andrei Korostelev, Ph.D, associate professor in the RNA Therapeutics Institute and of biochemistry & molecular pharmacology.
The new facility includes a 2,000-sf microscopy suite for its two microscopes: Titan Krios, which is said to be the most sophisticated cyro-EM in the world, and whose purchase was supported by a $5 million grant from the Massachusetts Life Science Center; and the powerful, versatile Talos-Arctica, whose $4 million cost was funded by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Titan Krios was delivered to the medical school last summer in 19 crates. When assembled, it is nearly 13.5 feet tall.
The building had exacting requirements for vibration, acoustical and climate control (the microscopes’ environment can tolerate only 0.1 degree change in an hour, and relative humidity must always be below 20%.) To meet those requirements, the Building Team built what essentially is a five-roomed box, constructed with eight-layered walls, floors, and ceilings. The nearly two-feet-thick construction isolates and protects the microscopes and adjacent spaces that support their use from noise, sound, and movement.
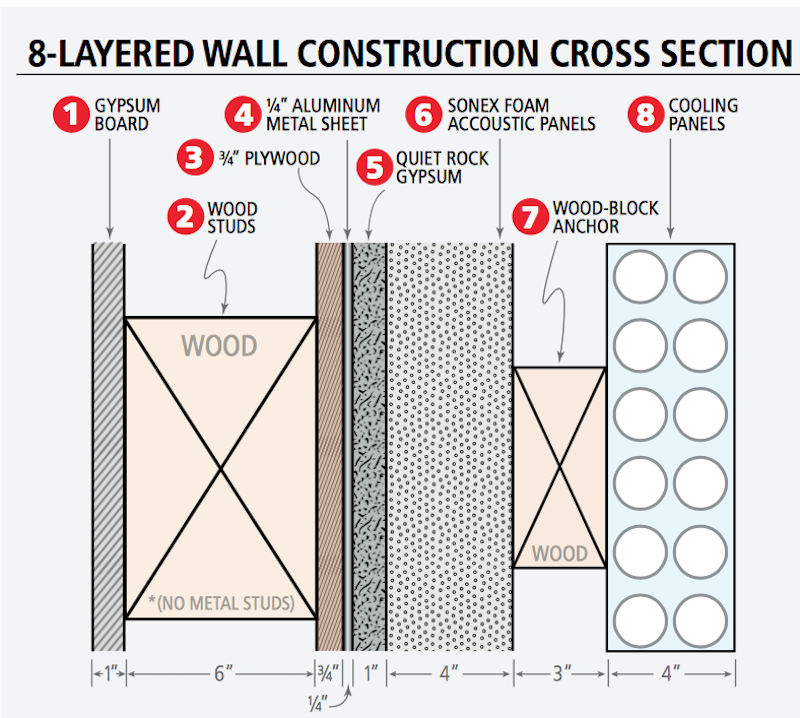
To address sound, vibration, and temperature controls, the Building Team devised this system for walls, floors, and ceilings. Image: Consigli Construction
Mark Morrow, Consigli’s manager on this project, explains that the eight layers include an outer layer of one-inch gypsum wallboard and six-inch wood studs. Consigli used wood, instead of more typical metal studs, to eliminate vibration.
Over the wood studs is a layer of ¾-inch plywood, to which is attached a ¼-inch thickness of aluminum sheeting. Over the aluminum panels Consigli installed 1-inch-thick acoustical drywall panel, “Quiet Rock,” which incorporates a damping technique called “constrained-layer damping,” creating a higher ability to dampen vibrational and acoustical energy. Next came 4-inch-thick “Sonex” foam acoustical panels, to which are attached 3-inch wood block anchors to assure a secure attachment of the final layer, 4-inch-wide cooling panels.
Because the aluminum welding was conducted within a healthcare facility, mitigation that limited smoke and smell was required. Morrow says that coordination with all of the project’s trades and specialty subcontractors—which included the electromagnetic shielding company Vitatech Electromagnetics—was critical to the successful construction of this facility, as was working with the facilities’ director, electron microscopist Chen Xu, Ph.D; and the project’s superintendent Tim Backlin.
The completed facility includes a lab to prepare the research samples, staff offices, a mechanicals room, space for a possible third microscope, and space for computer resources. Chen says that about 100,000 particle projections are needed in order to see a particle structure. “You're talking about a lot of data.”
Related Stories
Public Health Labs | Feb 14, 2019
Merck KGaA is expanding its R&D hub in the U.S.
The 145,000-sf addition will be built to meet LEED and WELL certification standards.
Mixed-Use | Oct 25, 2018
Philadelphia’s uCity Square kicks off major expansion drive
This innovation center has several office, lab, and residential buildings in the works.
Public Health Labs | Dec 19, 2017
10 takeaways from SmithGroup’s ‘lab of the future’ initiative
The LAB2050 initiative digs into the scientific trends, technologies, and economics that will shape tomorrow’s research laboratory environments.
Laboratories | Sep 12, 2017
New York City is positioning itself as a life sciences hub
A new Transwestern report highlights favorable market and regulatory changes.
Laboratories | Aug 8, 2016
The lab of the future: smaller, flexible, tech-enabled, business focused
A new CBRE report emphasizes the importance of collaboration and standardization in lab design.
| Jan 14, 2016
How to succeed with EIFS: exterior insulation and finish systems
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the six elements of an EIFS wall assembly; common EIFS failures and how to prevent them; and EIFS and sustainability.
Building Team Awards | Apr 10, 2015
14 projects that push AEC teaming to the limits
From Lean construction to tri-party IPD to advanced BIM/VDC coordination, these 14 Building Teams demonstrate the power of collaboration in delivering award-winning buildings. These are the 2015 Building Team Award winners.
Public Health Labs | Jan 29, 2015
Breaking out of the box: Pirbright Institute’s radical approach to biocontainment facility design
The novel scheme turns the typical containment lab building inside out, placing the high-containment spaces at the perimeter to provide researchers with daylight and views.
| Jan 2, 2015
Construction put in place enjoyed healthy gains in 2014
Construction consultant FMI foresees—with some caveats—continuing growth in the office, lodging, and manufacturing sectors. But funding uncertainties raise red flags in education and healthcare.
| Dec 28, 2014
AIA course: Enhancing interior comfort while improving overall building efficacy
Providing more comfortable conditions to building occupants has become a top priority in today’s interior designs. This course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.