More than 11% of the world’s electricity is produced by 447 commercial nuclear power reactors operating in 31 countries. The U.S. alone generates just under one-fifth of its electricity—19.7%—from 99 nuclear reactors operating in 30 states that produce 805.3 billion kilowatt-hours of power. At the end of last year, there were 61 nuclear plants under construction worldwide, the equivalent of 16% of existing capacity, and another 160 that have been firmly planned.
These statistics, from the World Nuclear Association and the Nuclear Energy Institute, would suggest that nuclear power—despite ongoing issues related to safety, security, regulations, and radioactive waste storage—is an ascending alternative to fossil fuels as a source of low-carbon power in a world that is increasing concerned about the impact of climate change.
In an opinion piece that Forbes published in early September, nuclear advocate and scientist James Conca noted that two nuclear power plants near Houston—which provide 2,700 MW of power to two million customers in the area—stayed fully operational during Hurricane Harvey, which caused oil refineries to shut down.
The next generation of nuclear plants will be smaller—the plants under construction range from 70 to 1,750 gross MWs—and resilient. But groups that promote nuclear as an essential ingredient of any cocktail of alternative energy sources “don’t have a large bank of imagery to draw upon” to show the public nuclear’s capabilities, says Suzanne Baker, a spokesperson for Third Way, a neoliberal think tank in Washington D.C.
Earlier this year, Third Way commissioned Gensler to come up with sketches and renderings that can be used to explain the role that advanced reactors could play in a variety of energy systems that enable the world to reach its goals for reducing CO2 emissions. Those renderings were exhibited at D.C.’s Fathom Gallery on Oct. 28. The images can be downloaded from Third Way’s website.
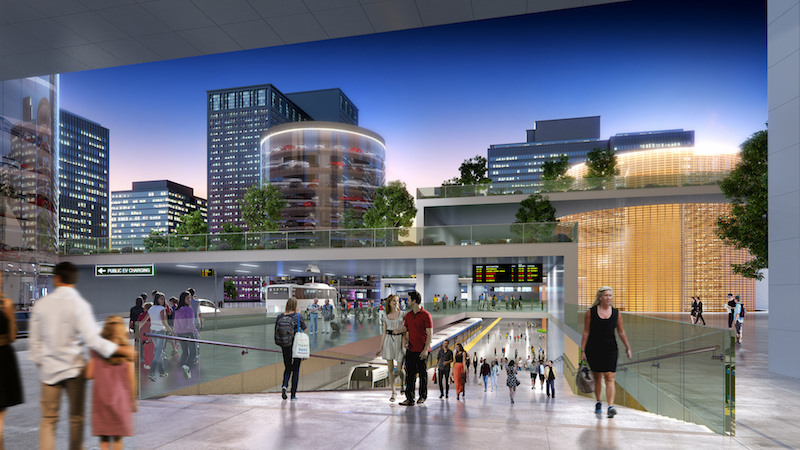

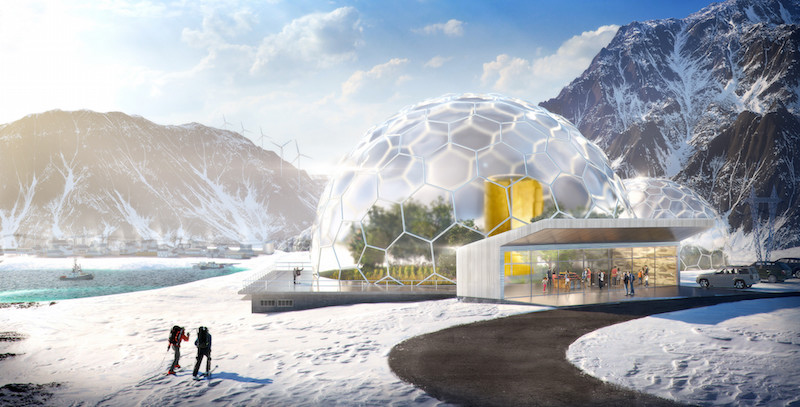
The rendering of a transit hub, where a nuclear reactor provides zero-emissions power for rail and electric vehicles. Image: Third Way
Gensler worked up images for six “scenarios” where nuclear could provide low-carbon power. These include
•A remote arctic community, off the power grid, where electricity is extremely pricey;
•A clean transit hub, where a small reactor powers rail lines, personal electric vehicles, shared autonomous vehicles, and electric buses;
•Growing communities in the developing world where large-scale reactors provide power, and whose excess capacity is used for an onsite desalination plant to provide clean water;
•A high-temperature reactor to power and heat for local industries;
•A Naval base, where advanced reactors generate around the clock electricity and power ships docked at port; and
•Powering data centers, upon which many of life’s daily functions are increasingly dependent.
While much of the growth in nuclear energy technology is occurring overseas, specifically in Russia, China, and the United Arab Emirates, Third Way believes the renderings can help spur innovation in the U.S.—which in recent years has all but ceased building nuclear plants in favor of other forms of alternative energies—“and help American nuclear companies and technologies become more competitive in international energy markets,” says Baker.
She acknowledges that Gensler’s portfolio does not include a broad range of nuclear power plant designs. But, she explains, “We wanted a fresh eye on the topic.” Baker adds that Gensler’s designs typically emphasize sustainability, so the commission “was an alignment of values.”
Earlier this year Baker “cold called” Gensler’s D.C. office about its interest in this project. “Our receptionist went over the public address system and said 'would someone from the Green Team dial zero?,' ” recalls Liz Resenic, LEED AP BD+C, WELL AP, a sustainability specialist at Gensler.
The firm doesn’t have a “green team,” per se; Resenic, on its sustainability team, took the called and spoke with Baker for about 15 minutes about visualization.
At that point, Gensler’s most notable experience in the nuclear power arena was its master planning and urban design for its K.A. CARE project, which stands for the King Abdullah City for Atomic and Renewable Energy in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
The firm agreed to accept Third Way’s commission “because we’re interested in being part of this conversation,” says Duncan Lyons, RIBA, LEED AP BD+C, a Senior Associate and Office Building Developers Practice Area Leader, who was the lead designer on this project. (Other Gensler associates who worked on the renderings and sketches include Gregory Plavcan, Matthew Boland, and Katie Costa.)
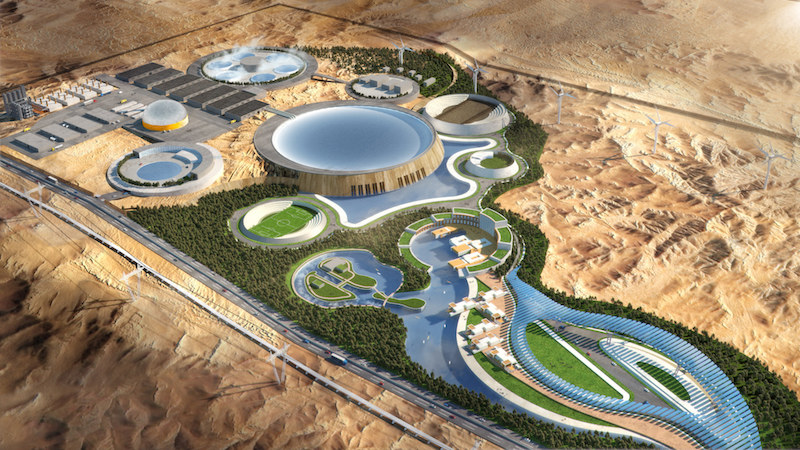

A desert compound whose advanced nuclear reactor pumps out 1,000-plus MW of capacity that supplies a nearby growing city. Image: Third Way
The project operated under a tight schedule: Visualizing sessions were conducted in August, for which Gensler pulled images from the nuclear industry as well as related examples of energy produced by hydro, solar and wind, says Lyons.
Gensler started producing the renderings and sketches in September, and completed them last month.
Baker says Third Way is targeting three audiences with its renderings: policy makers, the press, and the nuclear sector itself, which could use the illustrations in debates about the efficacy of nuclear power.
Related Stories
| Nov 3, 2010
Senior housing will be affordable, sustainable
Horizons at Morgan Hill, a 49-unit affordable senior housing community in Morgan Hill, Calif., was designed by KTGY Group and developed by Urban Housing Communities. The $21.2 million, three-story building will offer 36 one-bed/bath units (773 sf) and 13 two-bed/bath units (1,025 sf) on a 2.6-acre site.
| Nov 3, 2010
Virginia biofuel research center moving along
The Sustainable Energy Technology Center has broken ground in October on the Danville, Va., campus of the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research. The 25,000-sf facility will be used to develop enhanced bio-based fuels, and will house research laboratories, support labs, graduate student research space, and faculty offices. Rainwater harvesting, a vegetated roof, low-VOC and recycled materials, photovoltaic panels, high-efficiency plumbing fixtures and water-saving systems, and LED light fixtures will be deployed. Dewberry served as lead architect, with Lord Aeck & Sargent serving as laboratory designer and sustainability consultant. Perigon Engineering consulted on high-bay process labs. New Atlantic Contracting is building the facility.
| Nov 3, 2010
Dining center cooks up LEED Platinum rating
Students at Bowling Green State University in Ohio will be eating in a new LEED Platinum multiuse dining center next fall. The 30,000-sf McDonald Dining Center will have a 700-seat main dining room, a quick-service restaurant, retail space, and multiple areas for students to gather inside and out, including a fire pit and several patios—one of them on the rooftop.
| Nov 2, 2010
A Look Back at the Navy’s First LEED Gold
Building Design+Construction takes a retrospective tour of a pace-setting LEED project.
| Nov 2, 2010
Wind Power, Windy City-style
Building-integrated wind turbines lend a futuristic look to a parking structure in Chicago’s trendy River North neighborhood. Only time will tell how much power the wind devices will generate.
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 2, 2010
Historic changes to commercial building energy codes drive energy efficiency, emissions reductions
Revisions to the commercial section of the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) represent the largest single-step efficiency increase in the history of the national, model energy. The changes mean that new and renovated buildings constructed in jurisdictions that follow the 2012 IECC will use 30% less energy than those built to current standards.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 27, 2010
Grid-neutral education complex to serve students, community
MVE Institutional designed the Downtown Educational Complex in Oakland, Calif., to serve as an educational facility, community center, and grid-neutral green building. The 123,000-sf complex, now under construction on a 5.5-acre site in the city’s Lake Merritt neighborhood, will be built in two phases, the first expected to be completed in spring 2012 and the second in fall 2014.