The terms “desire path” and “line of desire” bring with them a bit of a mystical feeling, as if they were something Indiana Jones would need to find a way to cross to get to the Ark of the Covenant or the Holy Grail that awaits on the other side. In reality, desire paths are not quite so fantastical.
Even if you have never heard the term desire path, odds are you’ve seen one at some point. If you’ve ever been walking around a college campus, public park, or downtown area, you have probably seen an informal dirt path that cuts a corner, or through a field, or even through a few small shrubs or bushes. This path isn’t paved and clearly wasn’t part of the original plan, but thanks to the desire of many to find the path of least resistance from point A to point B, it has emerged over the years from repeated use.
Desire paths don’t necessarily have to be so rustic, either. Lines of desire can also be represented by people using formalized roads or paths in ways they were not intended to be used, such as a service road that has become a main pedestrian thoroughfare.
In general, a desire path or line of desire represents any path that end users have determined to be the most efficient way to travel, regardless of its intended use.
“They reflect the natural tendency of where people want to move. These lines are predicated on there being barrier-free environments,” says Caitlyn Clauson, Principal, Chair at Large on Board of Directors, and Planner at Sasaki. “If areas are inaccessible, for example with a steep slope or a discontinuous sidewalk, individuals will find other routes. Desire lines are often informed by adjacent land uses, especially uses with active ground floor functions and high levels of transparency and shade that make spaces inviting and habitable.”
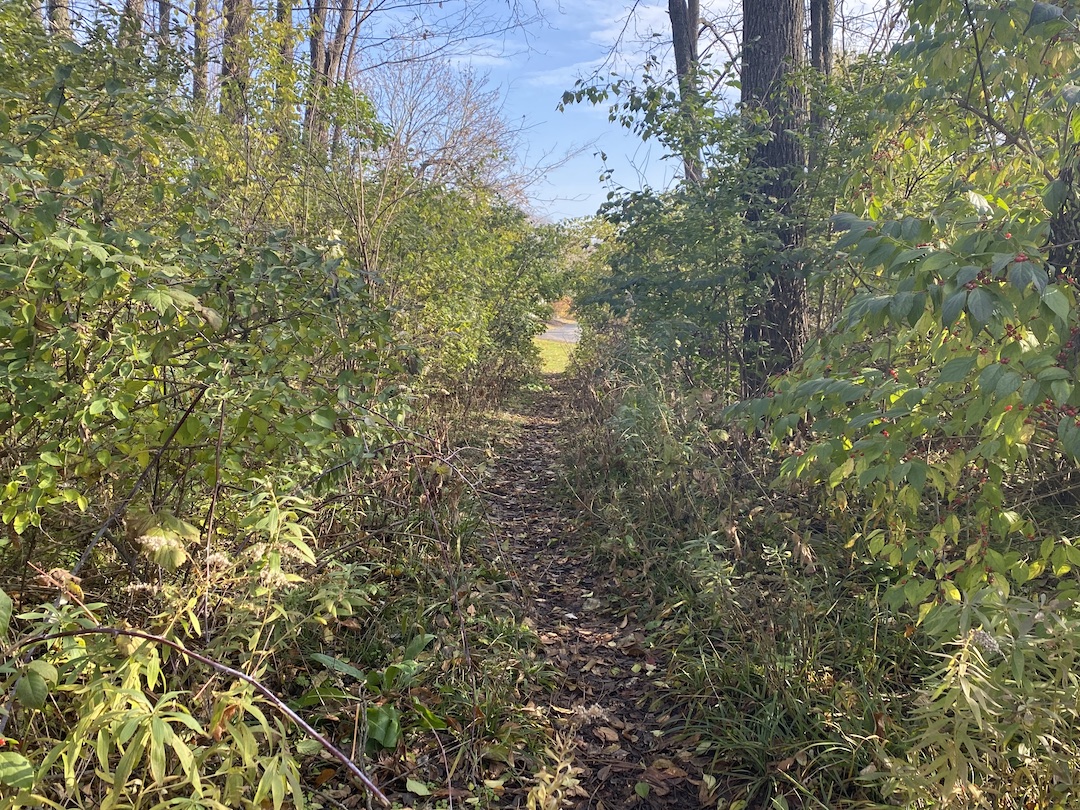

For many, especially planners and designers, a desire path is an unsightly reminder that a campus or downtown design plan was not as efficient and pedestrian-friendly as it could have, or perhaps should have, been. It proves just because something was designed to function a certain way, it doesn’t mean end users will necessarily follow suit.
There are two solutions to the scourge of the desire path: find a way to create a space so optimally designed desire paths won’t ever rear their ugly heads, or create a space so flexible that if a desire path does appear, it can be formalized and integrated into the design.
Sasaki’s CoMap helps spot ‘desire paths’ before they start
In order to prevent desire paths from taking shape, they need to be taken into consideration during a project’s earliest phases. “We did a feasibility study for UC San Diego in 2019 involving some developer land adjacent to campus and the campus architect was intrigued by my use of the term ‘line-of-desire’ in our initial meeting,” says Paul Schlapobersky, AIA, Associate Principal, Urban Designer, and Architect with Sasaki. “The entire study became about trying to ‘complete’ that line through a system of walkways and bridges connecting important nodes on the campus to this off-campus site and to newly-installed public transit beyond.”
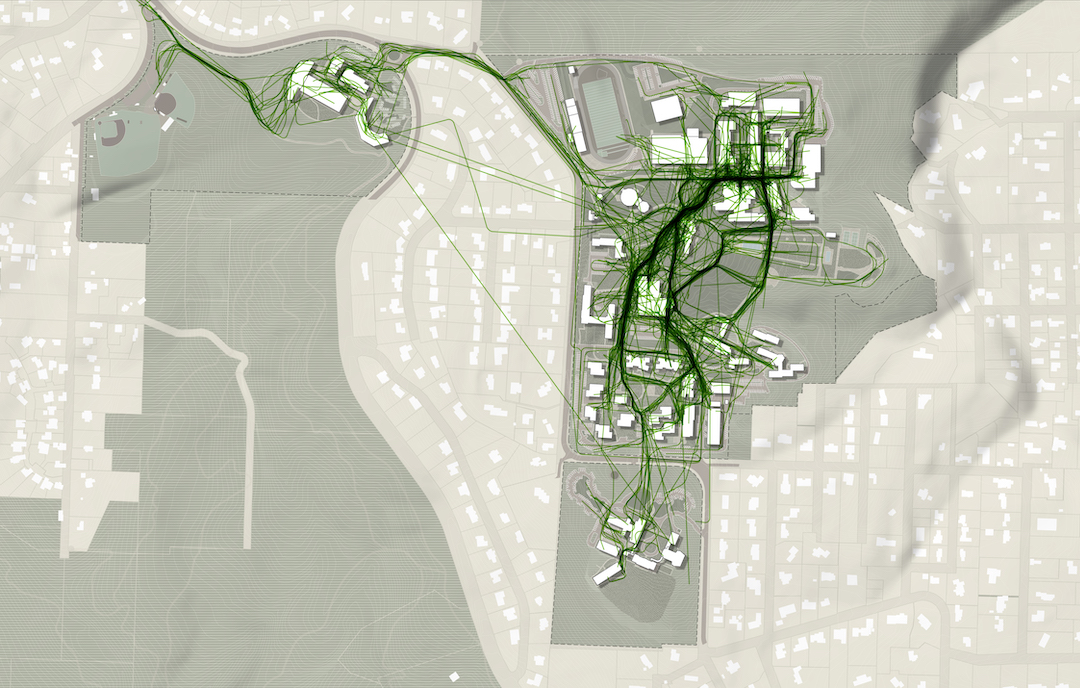
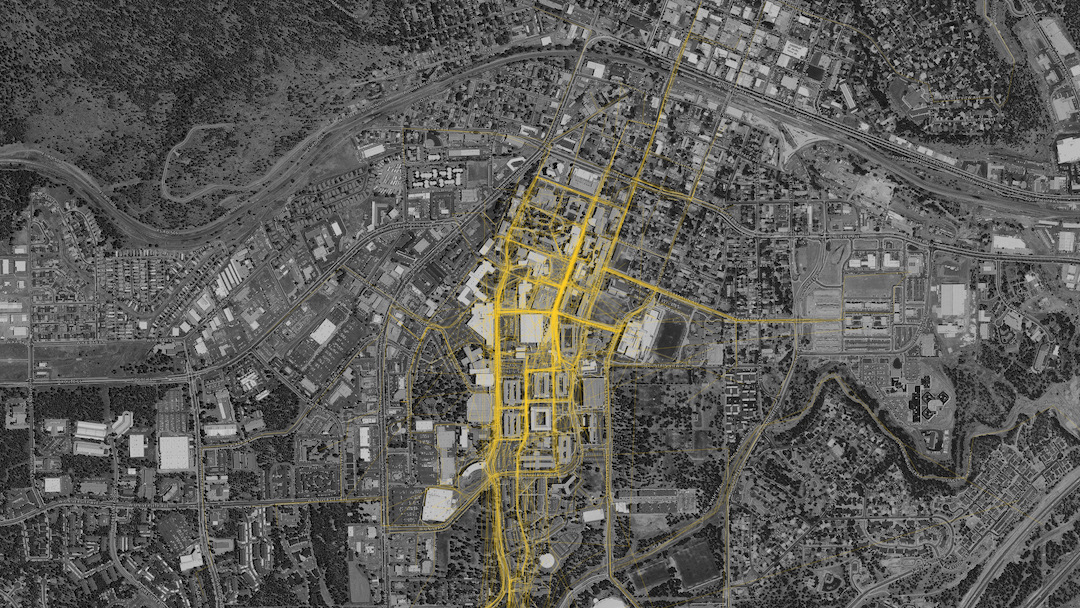
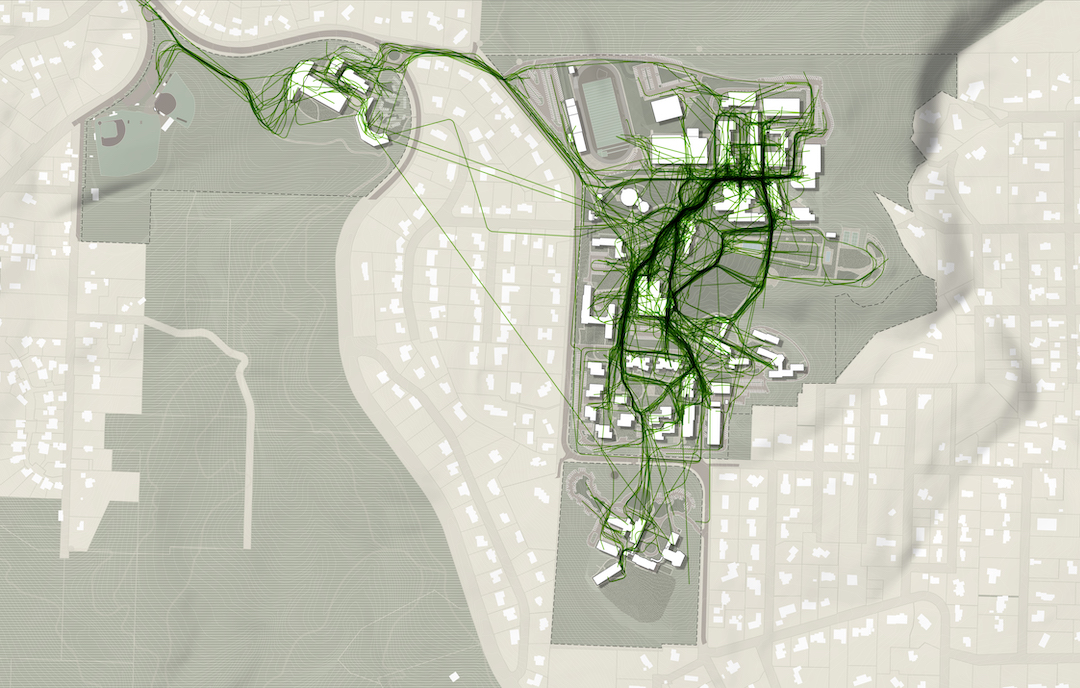
One of the main tools Sasaki uses to mitigate the informal desire path is a proprietary program developed by its in-house data and design tools group called CoMap. This collaborative mapping program generates a spatial visualization of how people experience a campus or region. When used at institutions, CoMap’s survey function allows campus communities to add notes about places or trace routes on a map of the campus. Sasaki then uses the data to inform planning recommendations.
“Many times the paths most traveled by students are not necessarily formally designed paths. The planning recommendation might therefore be to strengthen a desire line path by widening it, resurfacing it, removing an impediment, or lining it with active uses,” says Tyler Patrick, AICP, Principal, Chair of Planning and Urban Design on Board of Directors, and Planner with Sasaki. “For example, sometimes we find that service drives that are designed for vehicles are also heavily used by pedestrians, so we can instead redesign the path as more of a shared-use amenity, with aesthetic improvements to paving, lighting, etc.”
At one university, Sasaki used CoMap to learn that the formal entry to the campus was rarely used and the service drive actually served as the primary pedestrian route into campus. The design team took this information and reoriented the campus and created a new “front door” where the service drive used to be, with service access still accommodated, but in a more understated manner.
Sasaki also used CoMap in a master planning effort the firm led for Lewis & Clark College. The CoMap survey highlighted a strong north-south pedestrian route along an existing road. In response to the user feedback from CoMap, Sasaki turned the route into a primary pedestrian promenade on campus, surrounded by new residential and student life facilities.
CoMap is just one strategy the firm uses to create efficient plans without any informal desire paths. “We employ a range of strategies that include analyzing the existing system of pathways (what forms of mobility they support, their width, condition, amenities, etc.); collecting a variety of data (for instance, looking at where the concentration of classrooms is, as well as classroom utilization, to see key areas between which students may be moving); and conducting interviews and surveys to learn how pathways are used, deficiencies in the overall system, and desire paths that have not been formalized,” says Patrick.
Desire paths do not always equal good design
Just because an informal desire path appears, it does not mean it should always be formalized. Especially if the path is in direct conflict with the greater overall design scheme. “For instance, students may want to formally cross through a recreation field, but we want to maintain the field’s integrity for recreation and so we wouldn’t want to formalize that kind of desire path,” Patrick says.
Other instances may include environmental or safety concerns, such as wanting to keep a stream side riparian system intact as opposed to introducing formalized pedestrian pathways. “If a desire line promotes a path that isn’t accessible, we likely would not want to promote that movement,” adds Clauson.
The key is to balance how people want to use a given space without it turning into a free-for-all. Desire paths can, and often times do, suggest improvements for pedestrian circulation, but blindly formalizing any desire path can easily lead to a one step forward, two steps back situation. As Patrick said above, a desire path that cuts through a recreation field may prove that it is the most efficient way to traverse a campus, but formalizing it would certainly lead to more complaints about a now fractured field that is much more of an inconvenience than the lack of a formal path ever was.
As is often the case in modern design, the benefits of flexibility should never be understated. “A good campus plan should be flexible enough to accommodate evolving patterns of use and allow for the campus to integrate new ideas into the framework,” Patrick says.
The desire path, then, is representative of a larger point: There is no such thing as a perfect design, but there can be a perfectly adaptable one. Having the ability to continually adjust and formally adapt to the desires of end users is the best way to achieve the highest possible efficiency for any design.
Related Stories
Cultural Facilities | Aug 21, 2024
Baltimore’s National Aquarium opens 10,000-sf floating wetland that mimics the harbor’s original tidal marsh habitat
The National Aquarium in Baltimore has opened the National Aquarium Harbor Wetland, a 10,000-sf floating wetland that mimics the Inner Harbor’s original Chesapeake Bay tidal marsh habitat. Located between Piers 3 and 4 on Baltimore’s Inner Harbor, the $14 million project features more than 32,000 native shrubs and marsh grasses.
Building Materials | Aug 19, 2024
Federal 'buy clean' construction materials label program unveiled
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced a plan for implementing a new label program to boost American production of more climate-friendly construction materials and products. The label program will prioritize steel, glass, asphalt and concrete.
Museums | Aug 19, 2024
The Tampa Museum of Art will soon undergo a $110 million expansion
In Tampa, Fla., the Tampa Museum of Art will soon undergo a 77,904-sf Centennial Expansion project. The museum plans to reach its $110 million fundraising goal by late 2024 or early 2025 and then break ground. Designed by Weiss/Manfredi, and with construction manager The Beck Group, the expansion will redefine the museum’s surrounding site.
Reconstruction & Renovation | Aug 19, 2024
Movement to protect historic buildings raises sharp criticism
While the movement to preserve historic buildings has widespread support, it also has some sharp critics with well-funded opposition groups springing up in recent years. Some opponents are linked to the Stand Together Foundation, founded and bankrolled by the Koch family’s conservative philanthropic organization, according to a column in Governing magazine.
Government Buildings | Aug 19, 2024
GSA posts new RFI for enabling energy efficiency, decarbonization in commercial buildings
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy, recently released a new Request For Information (RFI) focused on enabling energy efficiency and decarbonization in commercial buildings. GSA wants to test innovative technologies through GSA’s Center for Emerging Building Technologies.
MFPRO+ New Projects | Aug 16, 2024
At 60 stories, the Paramount multifamily development will stand as Nashville’s tallest high rise
When complete, the 60-story Paramount building, at 750 feet high, will be the tallest high rise tower in Nashville, Tenn., surpassing the city’s current record holder, the 617-foot AT&T Building. The $390 million Paramount project recently launched condo sales after securing more than $230 million in construction financing.
Urban Planning | Aug 15, 2024
New York City begins first large-scale porous pavement installation
New York City is installing its first large-scale porous pavement installation along seven miles of roadway in Brooklyn. The project will keep 35 million gallons of stormwater out of the combined sewer system each year, according to a news release.
Urban Planning | Aug 15, 2024
The magic of L.A.’s Melrose Mile
Great streets are generally not initially curated or willed into being. Rather, they emerge organically from unintentional synergies of commercial, business, cultural and economic drivers. L.A.’s Melrose Avenue is a prime example.
Curtain Wall | Aug 15, 2024
7 steps to investigating curtain wall leaks
It is common for significant curtain wall leakage to involve multiple variables. Therefore, a comprehensive multi-faceted investigation is required to determine the origin of leakage, according to building enclosure consultants Richard Aeck and John A. Rudisill with Rimkus.
MFPRO+ News | Aug 14, 2024
Report outlines how Atlanta can collaborate with private sector to spur more housing construction
A report by an Urban Land Institute’s Advisory Services panel, commissioned by the city’s housing authority, Atlanta Housing (AH), offered ways the city could collaborate with developers to spur more housing construction.