As demand for multifamily apartments, condos, and townhouses has expanded, so has demand from developers, owners, and tenants for energy-efficient and sustainable buildings. This is particularly true for projects in the urban core coveted by supposedly environmentally conscious Millennials, and in locales where energy and water regulations are stiffening.
In New York, Mayor Bill de Blasio’s “80 by 50” Committee has set a goal of reducing the city’s greenhouse gas emissions by 80% below 2005 levels by 2050. “They’re talking about a lot of changes to codes,” says committee member Ilana Judah, International Associate AIA, OAQ, LEED AP BD+C, CPHD, Principal and Director of Sustainability with FXFowle.
“Cities are heightening their standards for efficient energy usage and sustainability, as they look to reduce resource consumption,” says Kelly Farrell, AIA, LEED AP BD+C, Vice President, RTKL Associates, Los Angeles (whose brand is now merged with Callison’s). This push at the municipal level has resulted in a noticeable increase in demand for smart design solutions. “For us, the real opportunity is in finding a way to meet these new regulations and ensure that the result translates into added value for our clients,” she says.
Kevin Smith, Senior Project Manager at Balfour Beatty Construction, says ASHRAE now requires more stringent energy modeling for building skin insulation. “The R-values of insulation within the interior wall cavity have been increased,” says Smith. He says EIFS systems installed on extruded polystyrene make for a well-insulated skin. In the 1980s, improperly installed EIFS caused mold problems that led to lawsuits. “Now we know to keep EIFS 48 inches off the ground and utilize an elastomeric finish for the final color coating,” says Smith.
Multifamily developers are using sustainability as a selling point, especially in environmentally conscious markets like California and the Pacific Northwest, says Joe Herzog, AIA, Principal with Shepley Bulfinch in its Phoenix office.
For Uncommon, an 120-unit apartment complex five minutes’ walk from the University of Oregon in Eugene, the firm worked with the client (CA Student Living) and GC (Essex General Construction) to pursue LEED Gold certification, even though it was not required. “We’re responding to changes in the urban housing marketing for college students and graduates,” said JJ Smith, CA Student Living’s COO. “They’re looking for a smaller environmental footprint and well-designed spaces close to life on campus and the city.”
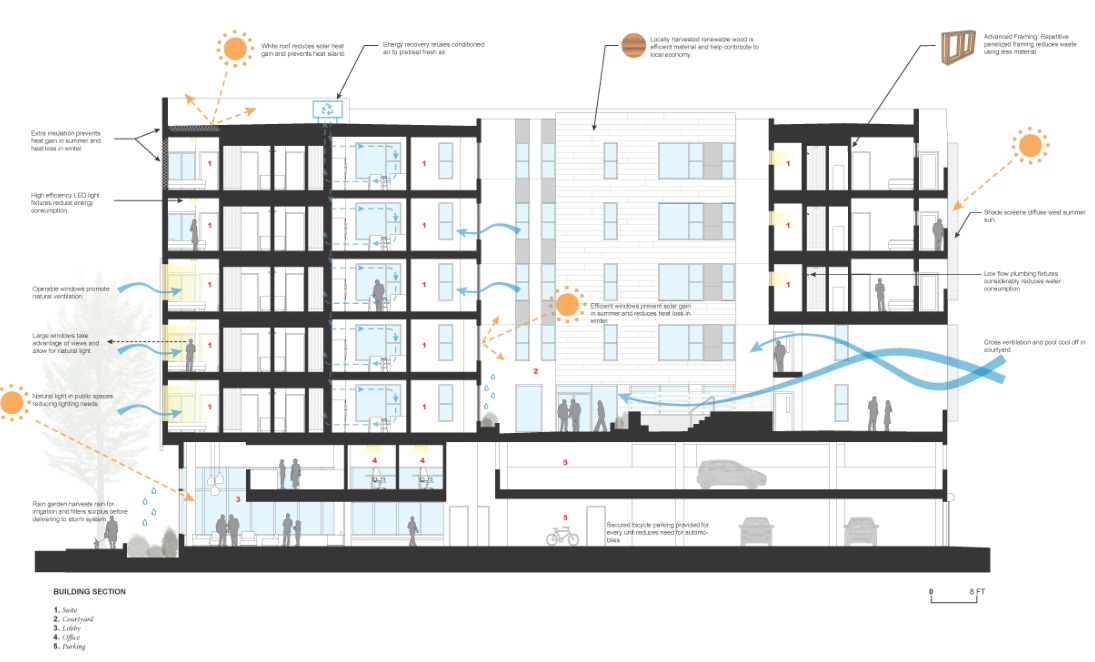 Uncommon, a 120-unit apartment building near the University of Oregon, Eugene, features energy recovery ventilation, which exchanges energy in already conditioned air to pre-treat incoming outdoor air. The Building Team: Shepley Bulfinch (architect), Innovative Air (mechanical contractor), and Essex General Construction (GC). Schematic courtesy Shepley Buifinch.
Uncommon, a 120-unit apartment building near the University of Oregon, Eugene, features energy recovery ventilation, which exchanges energy in already conditioned air to pre-treat incoming outdoor air. The Building Team: Shepley Bulfinch (architect), Innovative Air (mechanical contractor), and Essex General Construction (GC). Schematic courtesy Shepley Buifinch.
A number of “green prerogatives” (Herzog’s term) are having a beneficial impact on multifamily design and construction:
1. The multifamily market remains positive about the value of third-party sustainability certification. “The more LEED projects, the merrier,” says RTKL’s Farrell. But don’t get caught up in chasing LEED points. “If you truly commit to exploring the available options, the scorecard becomes a reflection of the project goals, rather than the other way around,” she says.
FXFowle’s Judah says that 80% of her firm’s high-rise projects in New York and Washington, D.C., are pursuing certification from either LEED or New York’s Enterprise Green Communities. In New York, any such projects built on city-owned land may have additional performance stipulations attached to them.
2. Heating and cooling systems are becoming much more sophisticated. Shepley Bulfinch’s 120-unit Uncommon project incorporates an energy-recovery system, which recycles preconditioned air and mixes it with fresh air. It is expected to save $40,000 a year in energy costs.
Multifamily properties are also providing tenants with the means to monitor their energy (and water) consumption. An RTKL project, The View—which is part of the 2.25-million-sf Liberty Center South mixed-use development in Arlington, Va.—installed Nest thermostats in every unit to meet this need. Some apartment projects even pay end-of-year rebates to tenants with low energy usage.
3. Resiliency comes to the fore in multifamily. After Hurricane Sandy, says Judah, developers suddenly became more interested in buildings that could create their own energy on site, via cogeneration systems that generally use microturbines or reciprocating engines.
4. Water use is a hot topic in almost every community, says Herzog. Rain gardens are collecting water for reuse. Low-flow plumbing fittings are routine. Balfour Beatty’s Smith says he is seeing greater use of graywater recycling for irrigation and sanitary systems.
5. Technology is forging a path in multifamily projects. LED lighting is steadily gaining acceptance in multifamily projects, says Smith. There has been a real evolution in building materials, especially in nontoxic paints, carpeting, and furniture fabric. “Health and wellness are big drivers,” says FXFowle’s Judah. Herzog notes that so-called “smart” plastic membranes can now sense interior humidity and allow an apartment or condo building to breathe and dry out.
6. Reducing heat island effect is growing in importance. Balfour Beatty Construction is working on Alta Midtown, a 369-unit development in Atlanta, which is being built on top of what was once an asphalt parking lot. Balfour Beatty recycled the asphalt and used it as backfill, then built a seven-story parking structure to reduce the overall heat-island effect. The surface will be a combination of white concrete, white TPO roofing membrane, green lawn space, and eco-friendly pavers and walking paths.
7. Passive House principles are attracting attention in multifamily projects. Judah, a Certified Passive House Designer, says her firm recently received a six-month grant to study the feasibility of passive design in taller buildings. Judah says there’s a “big movement” in New York toward passive design, which relies heavily on having a low window-to-wall ratio. She says her firm is encouraging multifamily developers to get off what she calls “their addiction” to predominantly glass façades.
FXFowle is pursuing LEED Silver for a market-rate rental building in Long Island City, N.Y., where the window-to-wall ratio will be less than 40%. Ditto for a 600-unit affordable/market-rate project in Jamaica, Queens, which will include cogeneration capability, green roof terraces, and possibly rainwater recapture.
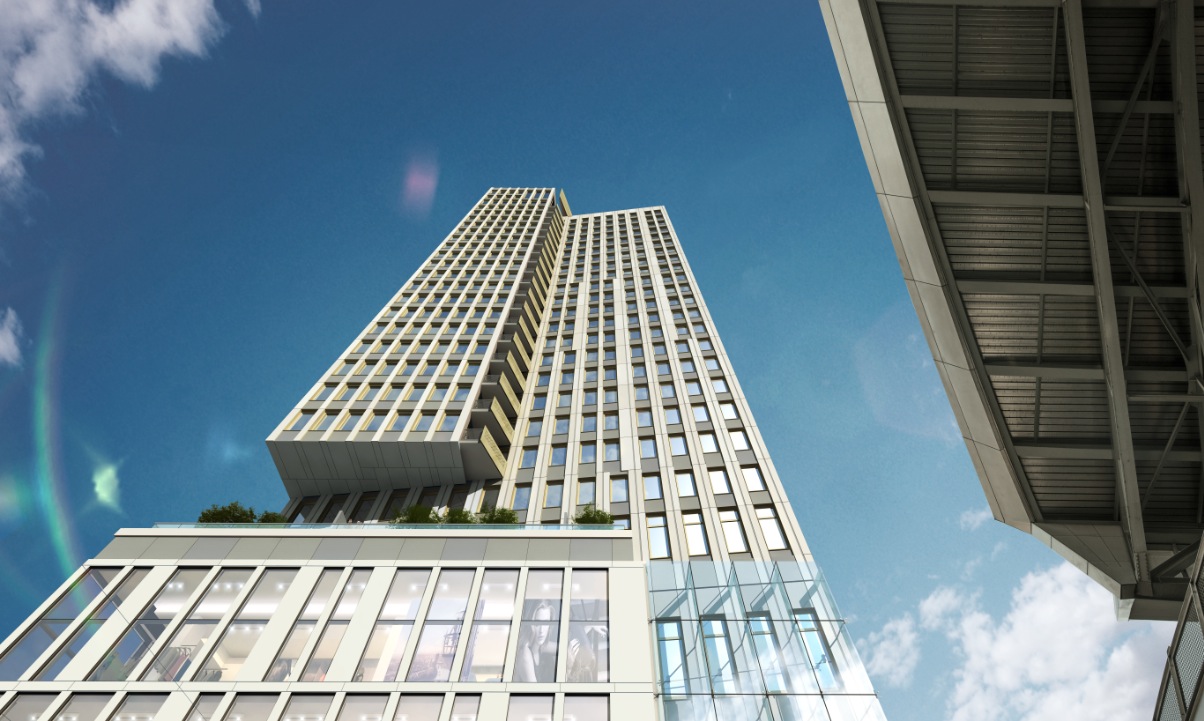
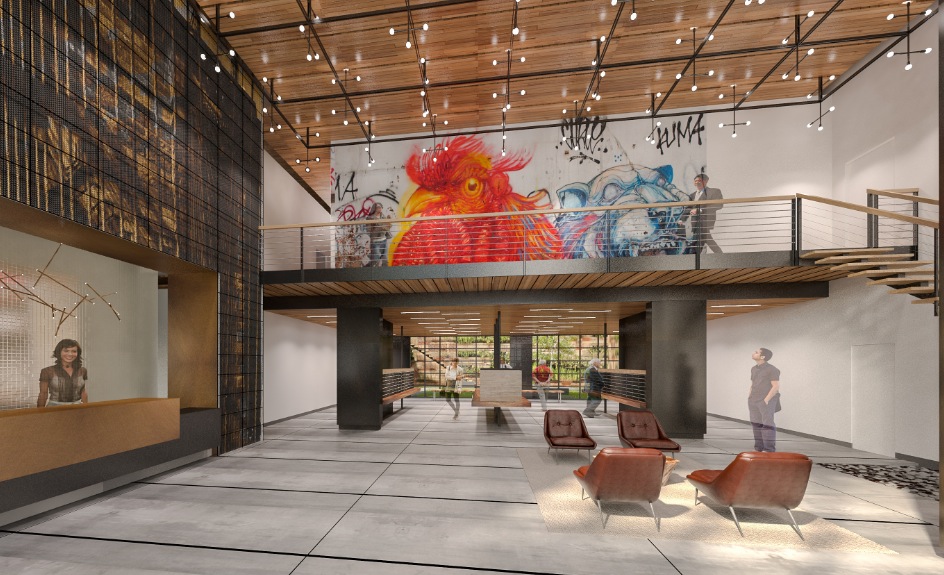 The lobby of the Purves Street Residential Development on Long Island City, N.Y. The 35-story, 266,000-sf building accommodates 270 units, and includes a communal living room, outdoor movie screening area, roof deck with a pool, and sky lounge. FXFOWLE is the architect; Brause Realty and Gotham Organization are the developers. Rendering: FXFOWLE
The lobby of the Purves Street Residential Development on Long Island City, N.Y. The 35-story, 266,000-sf building accommodates 270 units, and includes a communal living room, outdoor movie screening area, roof deck with a pool, and sky lounge. FXFOWLE is the architect; Brause Realty and Gotham Organization are the developers. Rendering: FXFOWLE
Related Stories
| Oct 13, 2010
Apartment complex will offer affordable green housing
Urban Housing Communities, KTGY Group, and the City of Big Bear Lake (Calif.) Improvement Agency are collaborating on The Crossings at Big Bear Lake, the first apartment complex in the city to offer residents affordable, eco-friendly homes. KTGY designed 28 two-bedroom, two-story townhomes and 14 three-bedroom, single-story flats, averaging 1,100 sf each.
| Oct 13, 2010
Residences bring students, faculty together in the Middle East
A new residence complex is in design for United Arab Emirates University in Al Ain, UAE, near Abu Dhabi. Plans for the 120-acre mixed-use development include 710 clustered townhomes and apartments for students and faculty and common areas for community activities.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community center under way in NYC seeks LEED Platinum
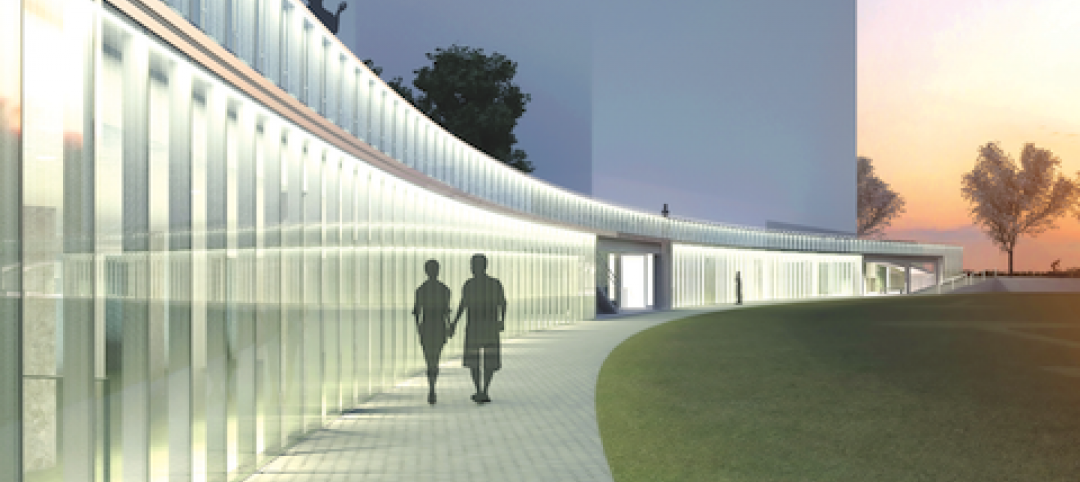
A curving, 550-foot-long glass arcade dubbed the “Wall of Light” is the standout architectural and sustainable feature of the Battery Park City Community Center, a 60,000-sf complex located in a two-tower residential Lower Manhattan complex. Hanrahan Meyers Architects designed the glass arcade to act as a passive energy system, bringing natural light into all interior spaces.
| Oct 12, 2010
The Watch Factory, Waltham, Mass.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards — Gold Award. When the Boston Watch Company opened its factory in 1854 on the banks of the Charles River in Waltham, Mass., the area was far enough away from the dust, dirt, and grime of Boston to safely assemble delicate watch parts.
| Sep 13, 2010
Richmond living/learning complex targets LEED Silver
The 162,000-sf living/learning complex includes a residence hall with 122 units for 459 students with a study center on the ground level and communal and study spaces on each of the residential levels. The project is targeting LEED Silver.
| Sep 13, 2010
Committed to the Core
How a forward-looking city government, a growth-minded university, a developer with vision, and a determined Building Team are breathing life into downtown Phoenix.
| Aug 11, 2010
Brown Craig Turner opens senior living studio
Baltimore-based architecture and design firm Brown Craig Turner has significantly expanded its housing design capabilities and expertise with the launch of its new senior living studio.
| Aug 11, 2010
CTBUH changes height criteria; Burj Dubai height increases, others decrease
The Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH)—the international body that arbitrates on tall building height and determines the title of “The World’s Tallest Building”—has announced a change to its height criteria, as a reflection of recent developments with several super-tall buildings.
| Aug 11, 2010
Morphosis builds 'floating' house for Brad Pitt's Make It Right New Orleans foundation
Morphosis Architects, under the direction of renowned architect and UCLA professor Thom Mayne, has completed the first floating house permitted in the U.S. for Brad Pitt’s Make It Right Foundation in New Orleans.The FLOAT House is a new model for flood-safe, affordable, and sustainable housing that is designed to float securely with rising water levels.













