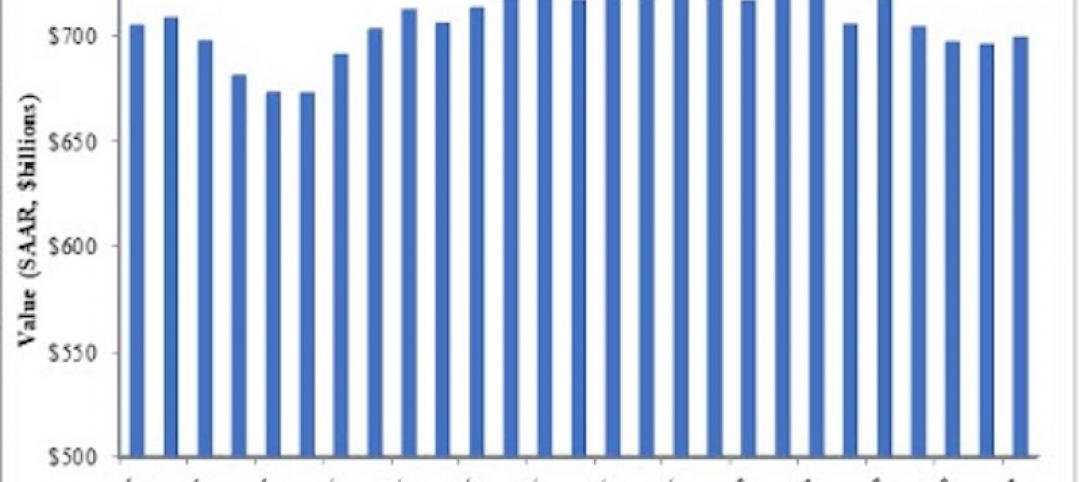
Through the first half of 2022, nonresidential construction spending returned to “nomimal growth.” But JLL, in its Construction Outlook for the second half of the year, foresees nonresidential spending being flat, on an inflation-adjusted basis, and year-over-year growth returning to historical levels in 2024, “as disruptions are likely to persist into 2023.”
Those disruptions include supply-chain issues that contributed to construction materials costs increasing by 42.5 percent from prepandemic levels. Labor costs related to workforce shortages were 10.5 percent higher than they were in March 2020.
“Labor availability remains a deep-set structural challenge for the industry and will be a larger issue as construction demand persists and shifts focus,” JLL observes. “Estimates of future need based on these upcoming expenditures show the gap will only widen, with a particular need for nonbuilding and public workers.”
Too much work, too few workers
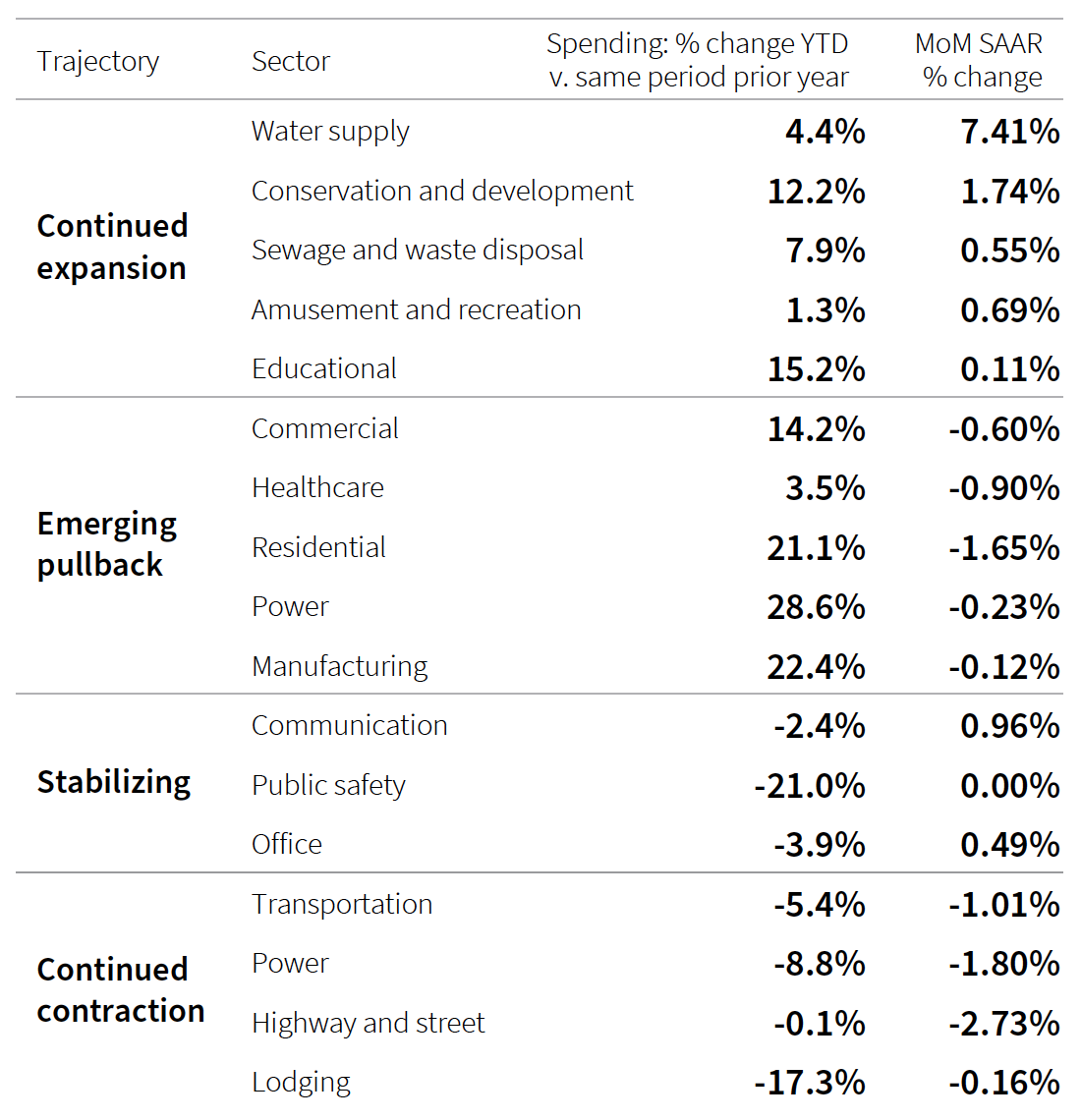
Job openings for construction labor have been consistently elevated, even as hiring expanded above prepandemic rates and separations fell to extremely low levels. In June 2022, unemployment fell to 3.7 percent, just 0.1 percent above the national average and job openings finally pulled back, dropping by 109,000 openings to 330,000. As such, the pullback is likely to continue, as firms stabilize backlogs and plan for difficult times.
Wage growth in the first half of 2022 was modest as well, significantly outpaced by inflation. Workers in the construction industry have actually experienced real wage losses of roughly 1.9 percent since the start of the pandemic. That gap widened in the first half of 2022 for construction employees.
“It is unlikely that the pullback will result in significantly lower demand side pressure in the construction labor market, as the current volume and array of work are sufficient to keep demand high for the next several years,” states JLL, especially once spending from the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) is in full swing.
The industry’s dilemma, however, is that it doesn’t have the capacity to fill every construction job that’s expected to be added in the next few years. At current forecasts of incoming IIJA funds bumping public spending by 10 percent or more annually from 2024 on, the increased need for construction employment equates to roughly 350,000 jobs from that spending alone —well above capacity identified in the historical record.
The largest impacts could be continued wage pressure and potential delays in projects. JLL predicts that the favorable situation for labor is expected to accelerate wage growth in the second half of the year, continuing to pressure margins. Though outright cancellations have remained limited, delays due to labor shortages are a nearly universal experience “with no relief in sight.”
Uneven price stability
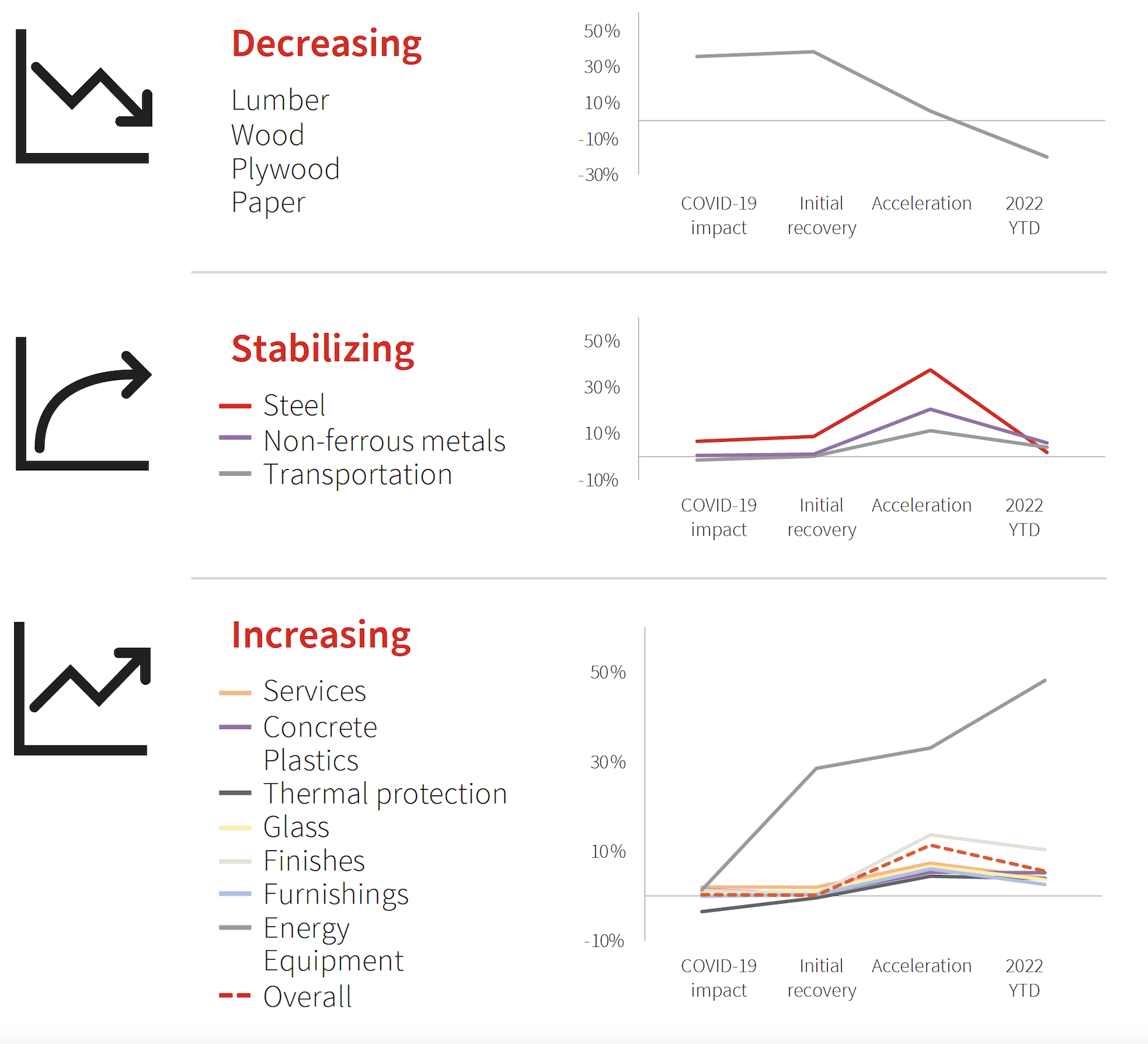
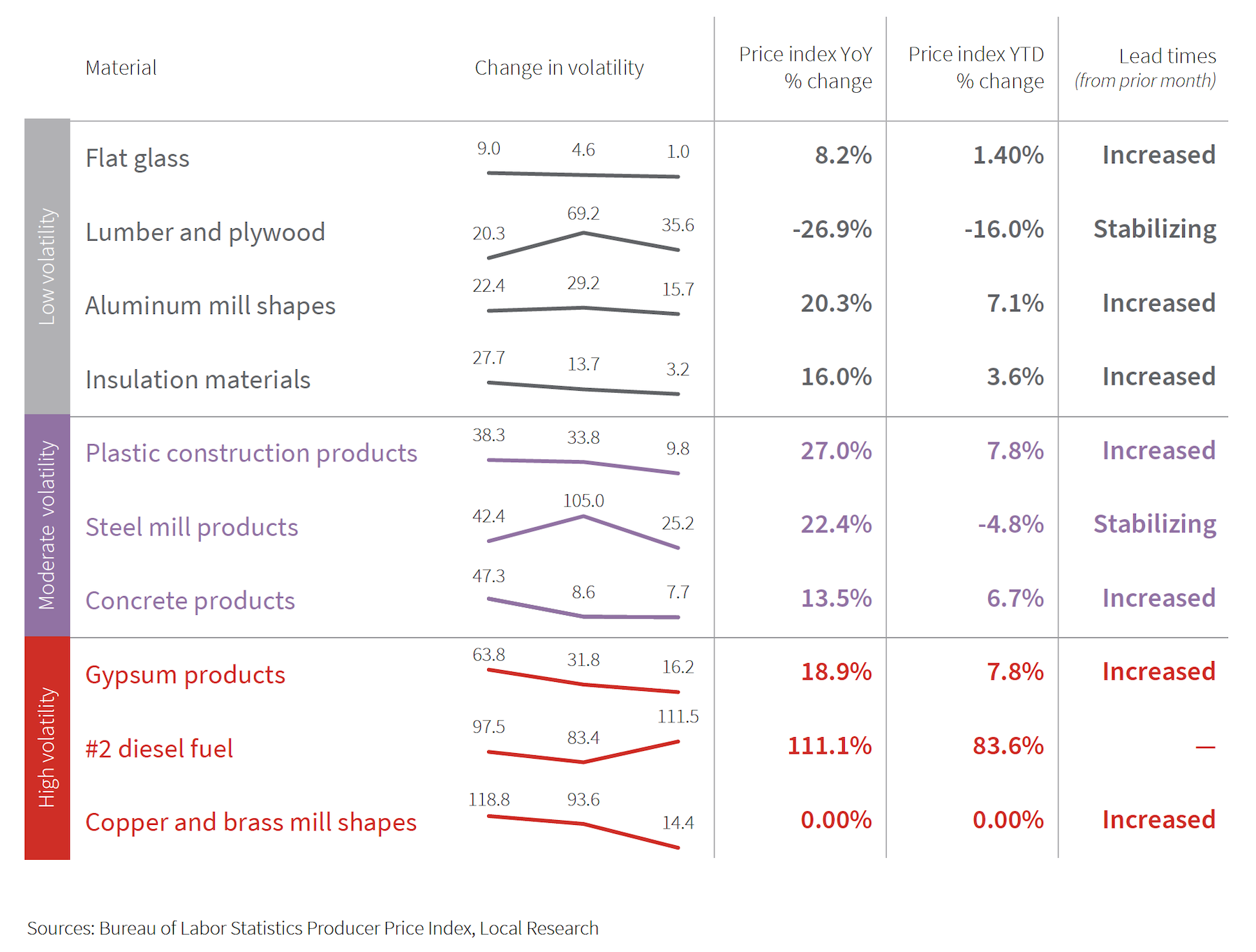
JLL’s Outlook is mixed about construction materials availability and costs. Steel and lumber, once the poster children for price inflation, have stabilized, thanks in part to domestic steel construction that’s 30 percent higher than prepandemic levels. However, “volatility has not gone down uniformly” across the spectrum of construction products.
That is particularly true of energy related materials that have been affected by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, whose damages to its built environment are estimated at $750 billion and rising. Cement, glass manufacture, and semiconductors for equipment and machinery “are among some of the larger price increases,” with concrete and glass disproportionately reliant on few producers with extremely high energy usage for production. Plus, the 10 percent increase in domestic cement and concrete production hasn’t stabilized prices yet.
Consequently, JLL has revised its previous outlook and now projects that materials prices will be up between 12 and 18 percent this year. “Uncertainty is still widespread and, as demonstrated by the current changing patterns of costs, novel issues are likely to emerge and disrupt supply chains and pricing in the near term.”
An active industry
From January to May 2022, the seasonally adjusted annual rate of total construction spending expanded at a monthly rate of 0.63 percent, above the growth rate observed in 2021. June, though, was down a percentage point, and any increases through the first half of the year were attributable to inflation.
On the bright side, JLL expects construction activity to remain healthy, global economic concerns notwithstanding. In the U.S., the Northeast has faltered with numerous months of contraction in the first half of 2022, while the West has picked up the pace of billing and backlog increases in recent months. The South and Midwest have maintained billings growth that is beginning to decelerate but will nevertheless create an appreciable pipeline of construction activity in the regions.
Related Stories
Market Data | Nov 15, 2017
Architecture Billings bounce back
Business conditions remain uneven across regions.
Market Data | Nov 14, 2017
U.S. construction starts had three consecutive quarters of positive growth in 2017
ConstructConnect’s quarterly report shows the most significant annual growth in the civil engineering and residential sectors.
Market Data | Nov 3, 2017
New construction starts in 2018 to increase 3% to $765 billion: Dodge report
Dodge Outlook Report predicts deceleration but still growth, reflecting a mixed pattern by project type.
Market Data | Nov 2, 2017
Construction spending up in September; Down on a YOY basis
Nonresidential construction spending is down 2.9% on a year-over-year basis.
Market Data | Oct 19, 2017
Architecture Billings Index backslides slightly
Business conditions easing in the West.
Industry Research | Oct 3, 2017
Nonresidential construction spending stabilizes in August
Spending on nonresidential construction services is still down on a YOY basis.
Market Data | Sep 21, 2017
Architecture Billings Index continues growth streak
Design services remain in high demand across all regions and in all major sectors.
Market Data | Sep 21, 2017
How brand research delivers competitive advantage
Brand research is a process that firms can use to measure their reputation and visibility in the marketplace.
Contractors | Sep 19, 2017
Commercial Construction Index finds high optimism in U.S. commercial construction industry
Hurricane recovery efforts expected to heighten concerns about labor scarcities in the south, where two-thirds of contractors already face worker shortages.
Multifamily Housing | Sep 15, 2017
Hurricane Harvey damaged fewer apartments in greater Houston than estimated
As of Sept. 14, 166 properties reported damage to 8,956 units, about 1.4% of the total supply of apartments, according to ApartmentData.com.