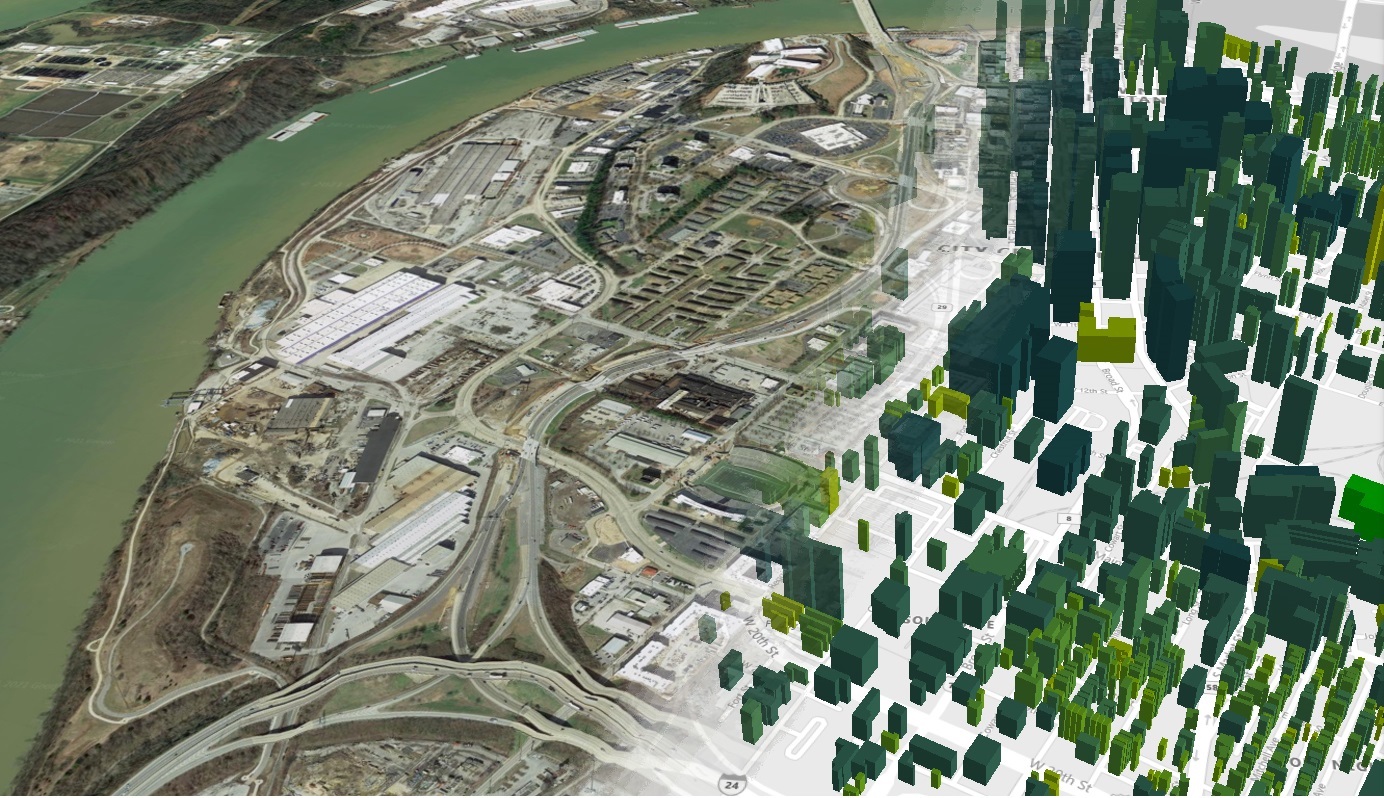
Within the next five years, the AE firm SmithGroup wants to be able to incorporate the highest level of energy efficiency into every project it designs and builds. But the challenge is selecting the right energy model from literally thousands of options.
“The number of buildings we need to touch, and the pace we need to do it, exceed what an individual could do in a lifetime,” says Stet Sanborn, engineering lead in SmithGroup’s San Francisco office.
To speed this process, SmithGroup has partnered with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), whose Automated Building Energy Modeling software suite, better known as AutoBEM, has simulated the energy use of 123 million structures, or 98 percent of U.S. Buildings.
AutoBEM was developed using high-performance computing to process layers of imaging data with information about each building, such as its size, use, construction materials, and HVAC technologies. The goal was to create a digital twin of the nation’s buildings, says Joshua New, ORNL’s project leader.
Sanborn tells BD+C that SmithGroup got involved with this technology collaboration project 18 months ago, after responding to the lab’s request for proposal. After six months of planning, SmithGroup provided information for every building type it handles, including climate zones, footprints, orientation, and envelope construction. The modeling also took into account lighting and HVAC variations.
This project generated more than 200,000 building iterations and 250,000 energy models. The computation, which took less than an hour to complete, was equal to the output of one employee working full time for 365 years.
Using AI to spot trends
AutoBEM’s information was used to train an artificial intelligence tool that will allow SmithGroup to pre-simulate the energy impact of every design possibility for any building.
Sanborn says that these data sets are still pretty rudimentary, so they should benefit from ORNL’s plans to update its information this year. “We’re looking for much better resolution, so we can eventually have real-time and predictive feedback,” he explains.
In 2023, SmithGroup plans to train the AI bots to spot trends and choose the best energy-efficient iteration for a given project. Sanborn says his team has already been surprised by how the data has highlighted “the interaction of things” like glass U-values and wall R-values. More refined data, he predicts, should make these data sets more accessible and actionable. (Sanborn says that SmithGroup already has pre-simulated climate data for every market it builds in.)
The first new designs for which this energy modeling is likely to be applied could be for a civic or higher education building, says Sanborn, where no restrictions to sharing information exist.
ORNL’s partners such as SmithGroup and Google—which is using AutoBEM to improve its free Environmental Insights Explorer tool—have committed to sharing data sets created by using AutoBEM. Some data sets have already been posted, and Sanborn thinks that open-source access is important because “SmithGroup can’t build every building, as much as we’d like to. We don’t want to hold a secret sauce or limit everyone’s ability to drive efficiency in response to what is really a climate emergency.”
SmithGroup participated in the funding of AutoBEM, whose development, expansion and collaborations are also funded by DOE’s Office of Electricity, the Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy’s Building Technologies Office and the National Nuclear Security Administration. The research team leveraged supercomputing resources from Argonne National Laboratory.
Related Stories
| Nov 3, 2010
Senior housing will be affordable, sustainable
Horizons at Morgan Hill, a 49-unit affordable senior housing community in Morgan Hill, Calif., was designed by KTGY Group and developed by Urban Housing Communities. The $21.2 million, three-story building will offer 36 one-bed/bath units (773 sf) and 13 two-bed/bath units (1,025 sf) on a 2.6-acre site.
| Nov 3, 2010
Virginia biofuel research center moving along
The Sustainable Energy Technology Center has broken ground in October on the Danville, Va., campus of the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research. The 25,000-sf facility will be used to develop enhanced bio-based fuels, and will house research laboratories, support labs, graduate student research space, and faculty offices. Rainwater harvesting, a vegetated roof, low-VOC and recycled materials, photovoltaic panels, high-efficiency plumbing fixtures and water-saving systems, and LED light fixtures will be deployed. Dewberry served as lead architect, with Lord Aeck & Sargent serving as laboratory designer and sustainability consultant. Perigon Engineering consulted on high-bay process labs. New Atlantic Contracting is building the facility.
| Nov 3, 2010
Dining center cooks up LEED Platinum rating
Students at Bowling Green State University in Ohio will be eating in a new LEED Platinum multiuse dining center next fall. The 30,000-sf McDonald Dining Center will have a 700-seat main dining room, a quick-service restaurant, retail space, and multiple areas for students to gather inside and out, including a fire pit and several patios—one of them on the rooftop.
| Nov 2, 2010
A Look Back at the Navy’s First LEED Gold
Building Design+Construction takes a retrospective tour of a pace-setting LEED project.
| Nov 2, 2010
Wind Power, Windy City-style
Building-integrated wind turbines lend a futuristic look to a parking structure in Chicago’s trendy River North neighborhood. Only time will tell how much power the wind devices will generate.
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 2, 2010
Historic changes to commercial building energy codes drive energy efficiency, emissions reductions
Revisions to the commercial section of the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) represent the largest single-step efficiency increase in the history of the national, model energy. The changes mean that new and renovated buildings constructed in jurisdictions that follow the 2012 IECC will use 30% less energy than those built to current standards.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 27, 2010
Grid-neutral education complex to serve students, community
MVE Institutional designed the Downtown Educational Complex in Oakland, Calif., to serve as an educational facility, community center, and grid-neutral green building. The 123,000-sf complex, now under construction on a 5.5-acre site in the city’s Lake Merritt neighborhood, will be built in two phases, the first expected to be completed in spring 2012 and the second in fall 2014.