Hailed by the Windwheel Corporation as “a true showcase for climate architecture,” the Dutch Windwheel is a unique building focused on being as sustainable as possible while still providing a complete mixed-use development for the city of Rotterdam.
The Windwheel will be outfitted with myriad advanced technological solutions focused on sustainability. An innovation consortium that includes Arup, the Royal BAM Group, Deltares, Dura Vermeer, ECN, Eneco, Evides, Siemens, SPIE and TNO is researching these technologies, some of which are in latter developmental stages, according to Windwheel Corporation.
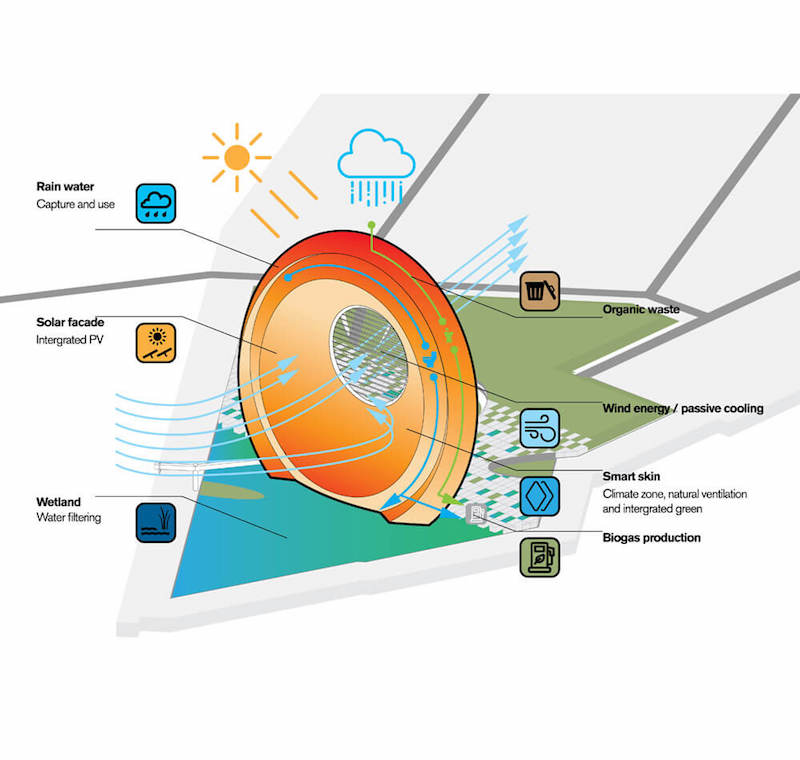 Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Some of the technologies planned for the structure include a smart skin climate zone with natural ventilation and integrated greenery, wind energy and passive cooling, biogas production, a solar façade, and rain water collection. The building will be constructed with materials from the Rotterdam region and is designed to be dynamic and upgradeable after it has been built to stay at the forefront of sustainable innovation.
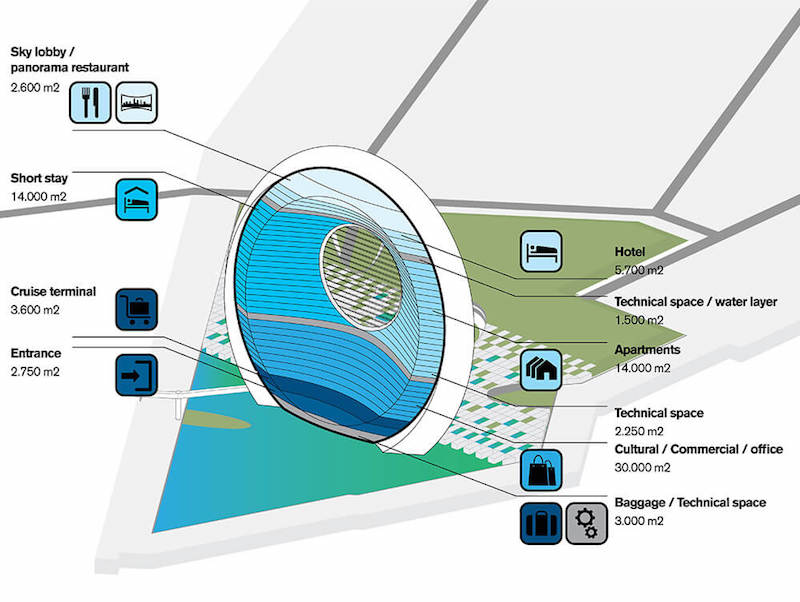 Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
The sustainability of the Windwheel is obviously the most important aspect of the building, but that doesn’t mean everything else has been pushed aside. The Windwheel wants to become a mixed-use development and economic boon for the Dutch port city.
“Coaster cabins” will be used to move visitors to the top of the 174-meter-tall building. These coaster cabins will rotate around the building like a ferris wheel and use innovative lighting concepts and digital information layers that act as a virtual tour guide for visitors, pointing out what can be seen and providing information.
 Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
30,000 sm of commercial space, 14,000 sm of apartments, 14,000 sm of short stay space, a 5,700-sm hotel, and a 2,600-sm sky lobby and panorama restaurant will all be included. Visitors will enter the building via a 2,750-sm entrance lobby.
The Windwheel was originally unveiled in 2015, but this most recent look at the structure provides a more detailed look into the buildings sustainable and mixed-use features. Current projections put a completion date for the project between 2022 and 2025.
 Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Image courtesy of DoepelStrijkers.
Related Stories
| Nov 9, 2010
Just how green is that college campus?
The College Sustainability Report Card 2011 evaluated colleges and universities in the U.S. and Canada with the 300 largest endowments—plus 22 others that asked to be included in the GreenReportCard.org study—on nine categories, including climate change, energy use, green building, and investment priorities. More than half (56%) earned a B or better, but 6% got a D. Can you guess which is the greenest of these: UC San Diego, Dickinson College, University of Calgary, and Dartmouth? Hint: The Red Devil has turned green.
| Nov 9, 2010
U.S. Army steps up requirements for greening building
Cool roofs, solar water heating, and advanced metering are among energy-efficiency elements that will have to be used in new permanent Army buildings in the U.S. and abroad starting in FY 2013. Designs for new construction and major renovations will incorporate sustainable design and development principles contained in ASHRAE 189.1.
| Nov 3, 2010
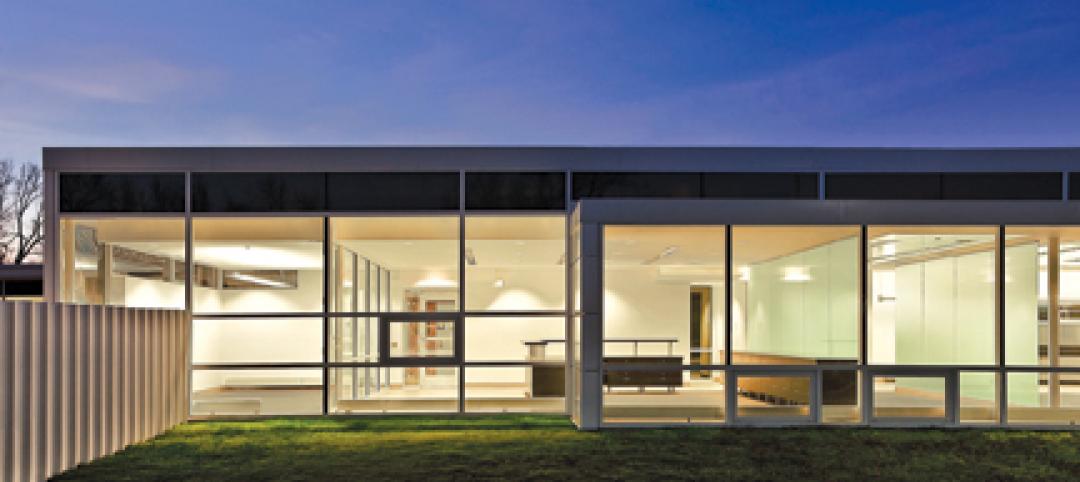
First of three green labs opens at Iowa State University
Designed by ZGF Architects, in association with OPN Architects, the Biorenewable Research Laboratory on the Ames campus of Iowa State University is the first of three projects completed as part of the school’s Biorenewables Complex. The 71,800-sf LEED Gold project is one of three wings that will make up the 210,000-sf complex.
| Nov 3, 2010
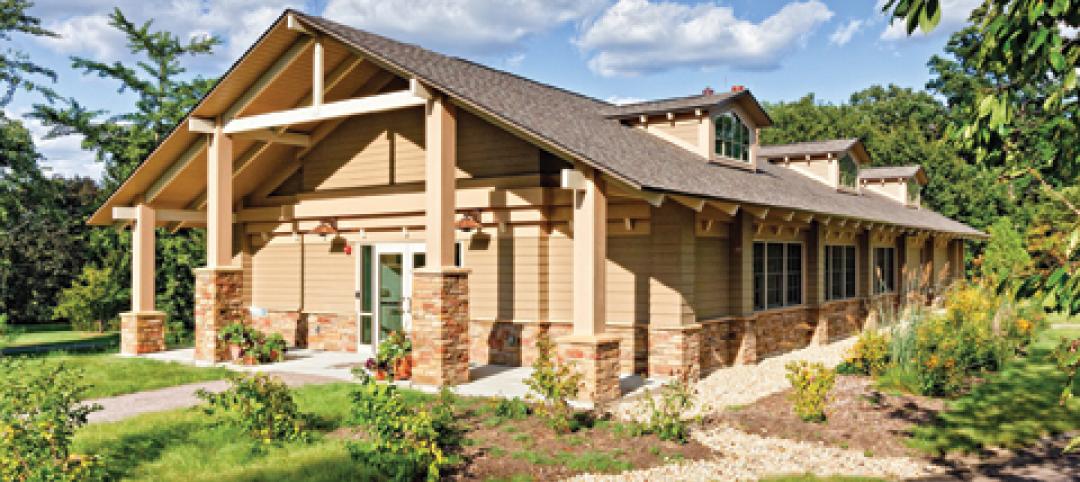
Park’s green education center a lesson in sustainability
The new Cantigny Outdoor Education Center, located within the 500-acre Cantigny Park in Wheaton, Ill., earned LEED Silver. Designed by DLA Architects, the 3,100-sf multipurpose center will serve patrons of the park’s golf courses, museums, and display garden, one of the largest such gardens in the Midwest.
| Nov 3, 2010
Public works complex gets eco-friendly addition
The renovation and expansion of the public works operations facility in Wilmette, Ill., including a 5,000-sf addition that houses administrative and engineering offices, locker rooms, and a lunch room/meeting room, is seeking LEED Gold certification.
| Nov 3, 2010
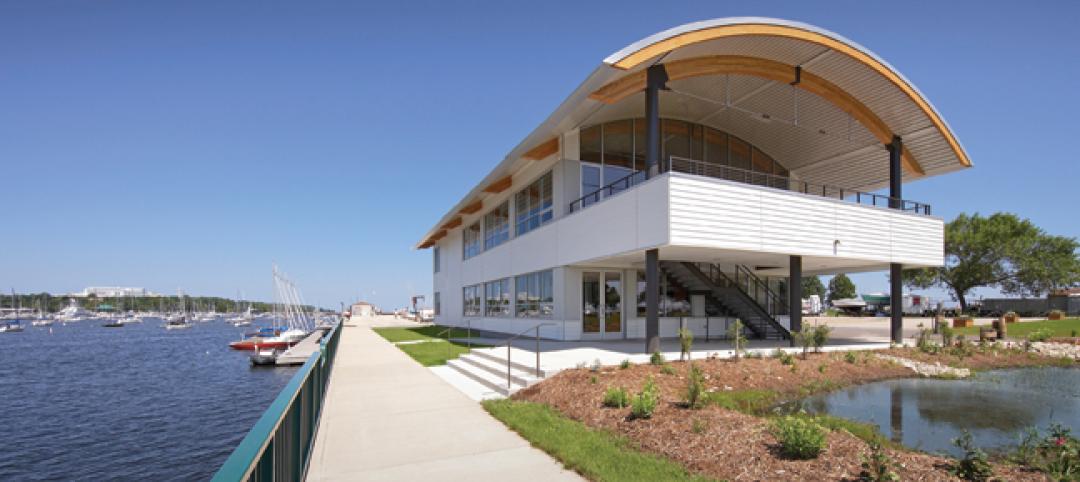
Sailing center sets course for energy efficiency, sustainability
The Milwaukee (Wis.) Community Sailing Center’s new facility on Lake Michigan counts a geothermal heating and cooling system among its sustainable features. The facility was designed for the nonprofit instructional sailing organization with energy efficiency and low operating costs in mind.
| Nov 3, 2010
Seattle University’s expanded library trying for LEED Gold
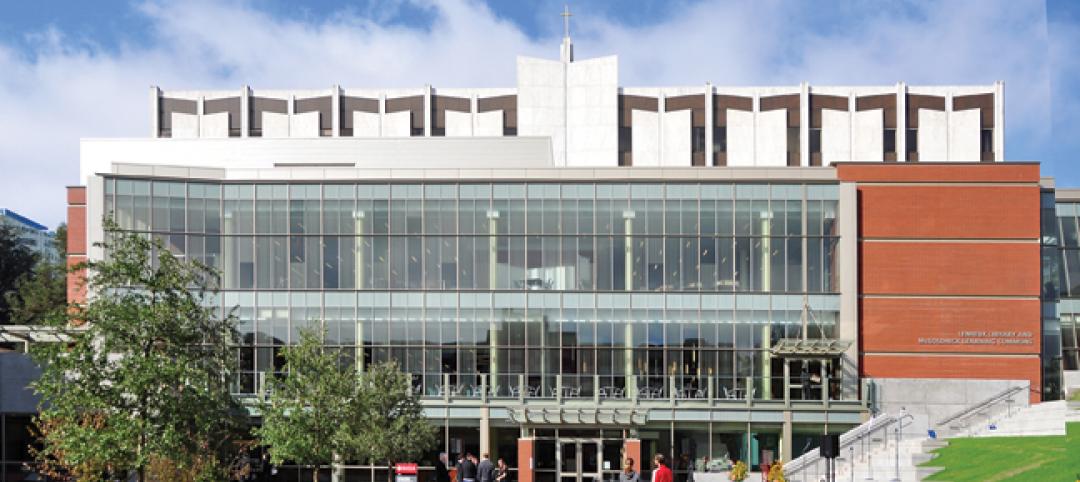
Pfeiffer Partners Architects, in collaboration with Mithun Architects, programmed, planned, and designed the $55 million renovation and expansion of Lemieux Library and McGoldrick Learning Commons at Seattle University. The LEED-Gold-designed facility’s green features include daylighting, sustainable and recycled materials, and a rain garden.
| Nov 3, 2010
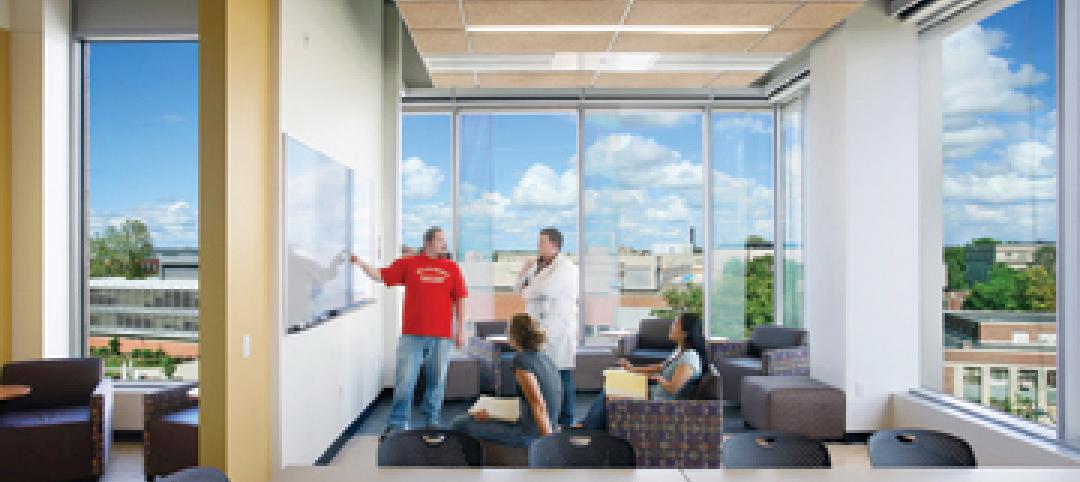
Recreation center targets student health, earns LEED Platinum
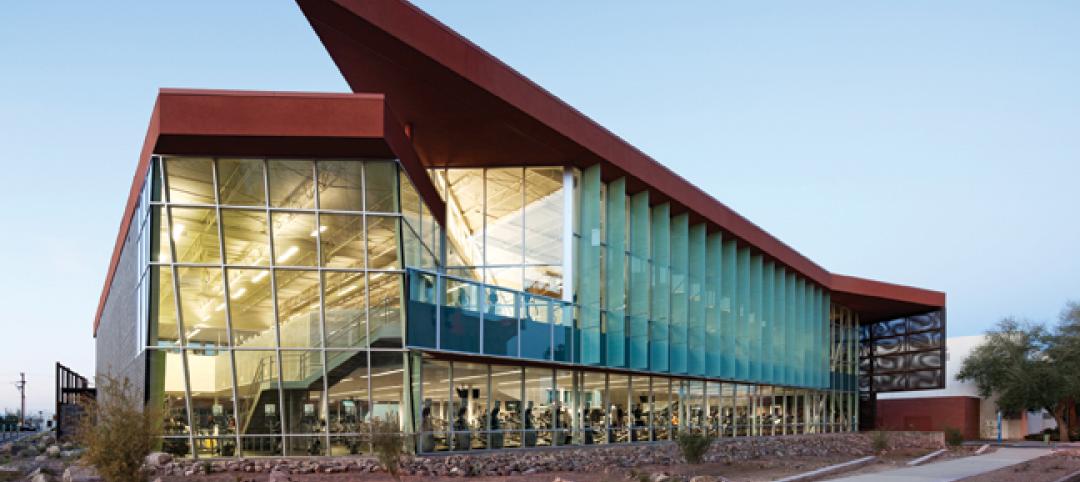
Not only is the student recreation center at the University of Arizona, Tucson, the hub of student life but its new 54,000-sf addition is also super-green, having recently attained LEED Platinum certification.
| Nov 3, 2010
Senior housing will be affordable, sustainable
Horizons at Morgan Hill, a 49-unit affordable senior housing community in Morgan Hill, Calif., was designed by KTGY Group and developed by Urban Housing Communities. The $21.2 million, three-story building will offer 36 one-bed/bath units (773 sf) and 13 two-bed/bath units (1,025 sf) on a 2.6-acre site.
| Nov 3, 2010
Virginia biofuel research center moving along
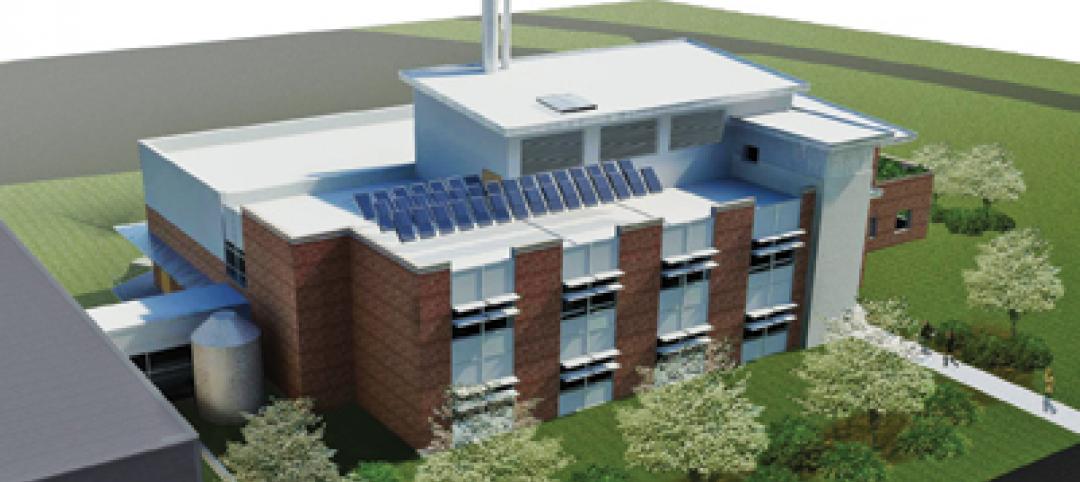
The Sustainable Energy Technology Center has broken ground in October on the Danville, Va., campus of the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research. The 25,000-sf facility will be used to develop enhanced bio-based fuels, and will house research laboratories, support labs, graduate student research space, and faculty offices. Rainwater harvesting, a vegetated roof, low-VOC and recycled materials, photovoltaic panels, high-efficiency plumbing fixtures and water-saving systems, and LED light fixtures will be deployed. Dewberry served as lead architect, with Lord Aeck & Sargent serving as laboratory designer and sustainability consultant. Perigon Engineering consulted on high-bay process labs. New Atlantic Contracting is building the facility.















