The Federal Aviation Administration’s latest report to Congress projects $32.5 billion in airport construction and renovation projects from 2017 to 2021. That would be a decrease of $1 billion, or 3%, from the FAA’s 2015 report. Since that last report, construction costs have increased 1.9%, according to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.
Reconstruction is expected to be the largest spending category, accounting for 35% of funding needs over the next five years. Standards development is next, projected to account for 33% of funding needs, followed by spending to expand existing airport capacity (11%), and terminal building (8%).
The 70-page National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems (NPIAS) report, based on 3,340 public-use airports tracked, identifies projects that are eligible for federal funding under the Airport Improvement Program.
Despite multibillion-dollar renovations and expansions underway at major hubs such as Los Angeles International, LaGuardia Airport in New York and Hartsdale-Jackson Atlanta International, FAA’s latest report states that large and medium hubs would be decreasing their spending, while development at small hubs is expected to increase.
FAA anticipates that airlines will continue to concentrate their schedules at their primary hubs where large numbers of flights converge in short periods of time to maximize the opportunity for passenger transfers. No new airline hubs are expected to arise within the next five years. Conversely, FAA observes that secondary airports are becoming a focus where a major hub airport is nearing capacity and is served by low-cost carriers.
At the airports tracked by NPIAS, capacity-related development continues to decrease while development to reconstruct pavement, bring airports up to design standards, and expand or rehabilitate terminal buildings are projected to increase. The national initiative to improve nonstandard surface geometry is beginning, and is anticipated that increased development costs will be captured in the next NPIAS report.
FAA concludes that the country’s airport system “is safe, convenient, well maintained.” The majority of airport capital improvements is funded by nonfederal sources, such as rents, fees, taxes paid by users, and Passenger Facility Charges (FAA’s report does not capture the costs of airport development funded primarily PFCs). Almost 98% of NPIAS airports are owned by public entities.
There are 382 primary airports in the U.S. receiving scheduled air carrier service with 10,000 or more enplaned passengers per year. Of these, FAA designates 89 as National airports, with at least 250 aircraft (including at least 30 jets) based at these ports. Within the primary total, 530 are regional airports with at least 100 based aircraft.
Non-primary airports, of which there are 2,950, handle at least 2,500 to 9,999 passengers annually, depending on their sizes.
FAA identifies eight proposed airports (two primary and six nonprimary) that are anticipated to be developed over the next five years. One of these, in the Chicago area, is still in the planning stages, A second will replace the existing site-constrained airport at Williston, N.D., a market that has been revitalized by hydraulic fracturing from oil shale.
Total enplanements in the U.S. hit an all-time high last year, 785 million passengers, with domestic enplanements representing 87% of U.S. passenger traffic at commercial service airports. However, given the turbulence among carriers over the past 15 years, air carrier operations were actually down 9% last year, based on data from 517 airport traffic control towers. Some of this is the result of better operational efficiencies, the retirement of older and less efficient aircraft, the shifting of larger aircraft to international services, and the growing use of 70- to 90-seat regional jet aircraft in place of smaller 50-seat regional jets.
FAA quotes Department of Transportation estimates that 18.9% of all flights were delayed (i.e., departed from their gates 15 minutes or later from their scheduled time) in 2015. In its Future Airport Capacity Task series, FAA identifies those airports at risk for significant delays and congestion through 2020 and 2030. These include most of the usual suspects with extraordinary capacities, such as the New York City airports, and those serving Philadelphia, Atlanta, and San Francisco.
“It remains crucial for these airports to continue their efforts to devise long-term planning solutions to address capacity constraints,” the FAA report states. “Going forward, both new runways and NextGen improvements are needed to improve efficiency at capacity-constrained airports.
The new report touches on unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), whose professional and recreational uses are growing. “The FAA’s goal is to safely integrate the UAS into the NAS [National Airspace System],” the report states. On August 29, FAA issued new rules for non-hobbyist small UAS operations, covering a broad spectrum of commercial uses for drones weighing less than 55 pounds.
FAA sees several factors affecting airports in the future, including the new generations of larger aircraft, which more airports are gearing up to receive.
Related Stories
| Jun 2, 2014
Parking structures group launches LEED-type program for parking garages
The Green Parking Council, an affiliate of the International Parking Institute, has launched the Green Garage Certification program, the parking industry equivalent of LEED certification.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 23, 2014
Top interior design trends: Gensler, HOK, FXFOWLE, Mancini Duffy weigh in
Tech-friendly furniture, “live walls,” sit-stand desks, and circadian lighting are among the emerging trends identified by leading interior designers.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| Apr 29, 2014
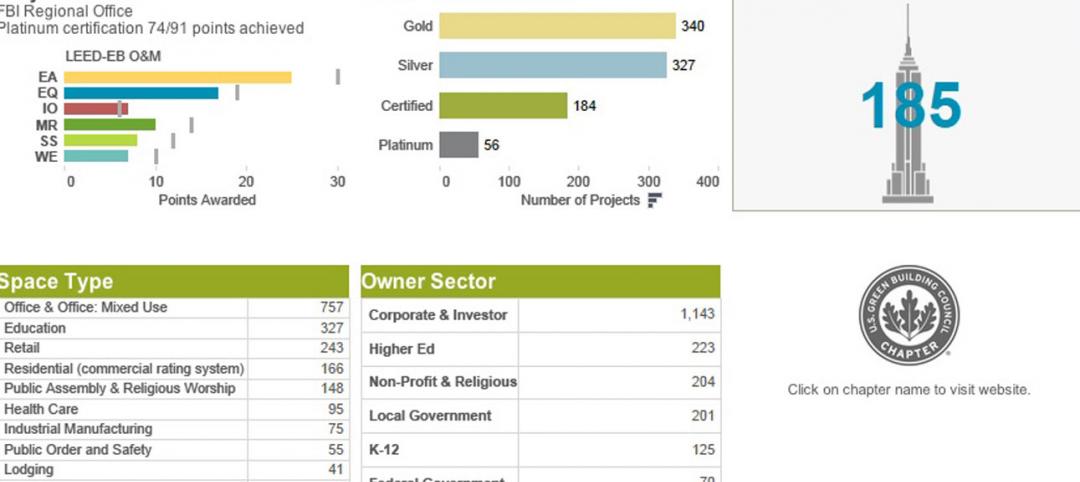
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
| Apr 22, 2014
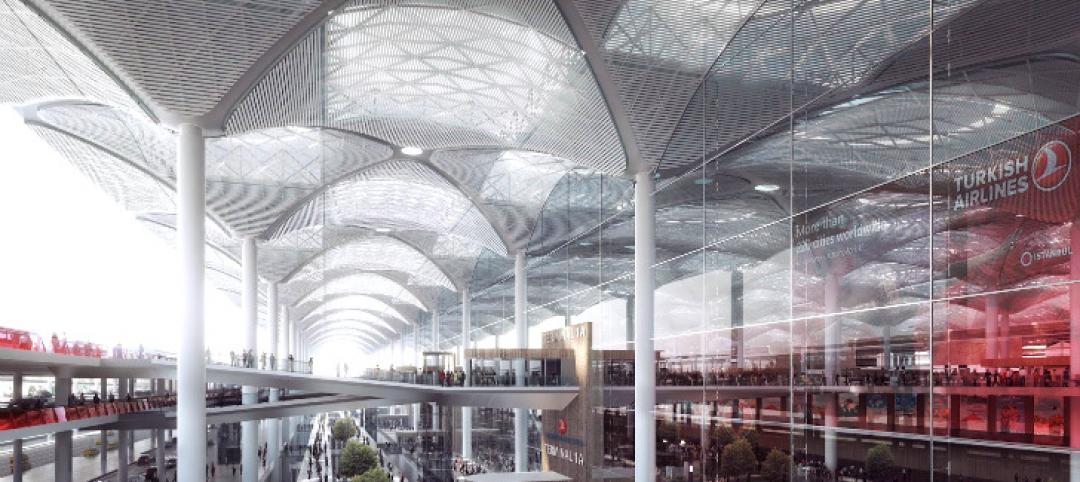
Bright and bustling: Grimshaw reveals plans for the Istanbul Grand Airport [slideshow]
In partnership with the Nordic Office of Architecture and Haptic Architects, Grimshaw Architects has revealed its plans for the terminal of what will be one of the world's busiest airports. The terminal is expected to serve 150 million passengers per year.
| Apr 9, 2014
Steel decks: 11 tips for their proper use | BD+C
Building Teams have been using steel decks with proven success for 75 years. Building Design+Construction consulted with technical experts from the Steel Deck Institute and the deck manufacturing industry for their advice on how best to use steel decking.