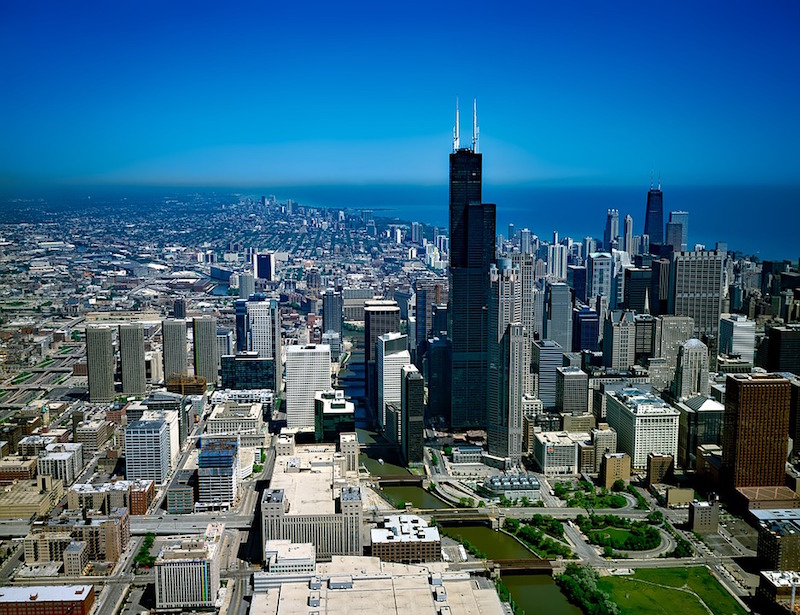
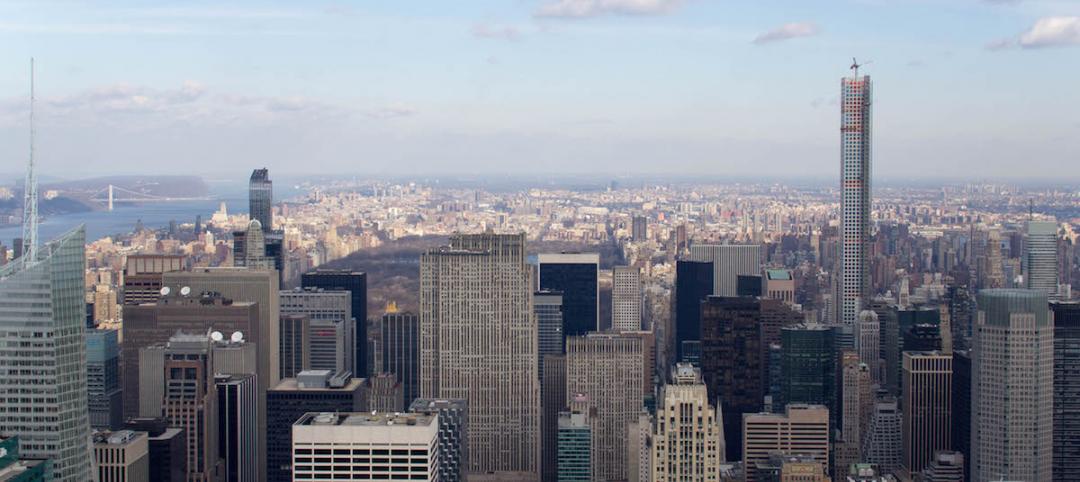
The taller the building, the more prestigious it appears. At least, that’s how the thinking goes. Recently, cities around the world are beginning to use tall buildings to show off their wealth and prosperity in the same way professional athletes use garages filled with Ferraris, Aston Martins, and Lamborghinis.
Sure, tall buildings provide a way of maximizing space in crowded cities, but a report from the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) points to the fact that many supertalls around the world have hundreds of feet of non-occupiable space. This “vanity height” as it is referred to, exists purely as a design element and to make the building taller.
In fact, if you eliminate vanity height, 44 of the world’s 72 supertalls (the number at the time of the report using July 2013 data) would measure less than 300 meters, losing their supertall status. The tallest of these building’s is Guangzhou’s 390-meter CITIC Plaza. Seeing these tall buildings only to realize so much of it is purely for aesthetics is like buying a large bag of chips only to discover a third of it is filled with air.
In terms of sheer height, the Burj Khalifa is the most egregious vanity height offender. 244 meters at the top of the world’s tallest tower is non-occupiable, that’s a whopping 800 feet. In other terms, if the Burj Khalifa’s vanity height were a building in its own right, it would be Europe’s 11th-tallest building.
In terms of percentage, another Dubai building is the worst offender. 39% of the Burj Al Arab’s height is non-occupiable space. However, at the opposite end of the spectrum, Dubai is also home to The Index, which has a vanity height of only four meters, or 1% of the buildings overall height.
New York has three of the worst offenders with the Bank of America Tower (131 meters, 36%), New York Times Tower (99 meters, 31%), and One World Trade Center (134 meters, 25%). The Empire State Building, however, plays the role of New York’s Index, as it loses just 1% of its height to non-occupiable space.
Measuring building height has been a fairly subjective practice over the years. Spires are counted toward height (which some view as counterproductive and rewarding vanity height) while antennae are not. In 1998, the then Sears Tower lost its title of tallest building in the world to Petronas Towers despite being almost 250 feet taller when its antennae were included and also having a higher occupiable top floor. The Petronas Towers’ spires, which are included in the building’s height, reach 1,483 feet in the air while the Sears Tower without its antennae, which are not included in its overall height, only reaches 1,454 feet. With the antennae the Sears Tower is 1,707 feet.
The now Willis Tower lost out again to vanity height in determining the tallest building in the United States. The Willis Tower’s roof is 442.1 meters high while One World Trade Center’s roof is 417 meters high. Again, however, One World Trade Center’s spire counts towards its height, bringing it up to 1,776 feet and giving it the distinction of being the tallest building in the U.S.
So what does all of this mean? Well, not much, except the list of the tallest buildings in the world would be shuffled around a bit if spires, masts, and antennae were counted toward a building’s overall height or, conversely, if buildings were just measured to their top floors.
But there really isn’t a simple solution: completely occupiable or not, the Burj Khalifa is still the tallest structure ever created (to this point. Jeddah Tower will take the title when it is completed, most likely with quite a bit of non-occupiable space of its own). But if you allow spires, antennae, or other non-occupiable components to count, then some architects and developers could add comically large elements to their structures just to get the accolade of tallest structure in the world.
Regardless, whichever way you measure it, architects are continuing to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of building height as more tall buildings than ever are popping up in cities around the world.
Related Stories
Game Changers | Feb 5, 2016
Asia’s modular miracle
A prefab construction company in China built a 57-story tower in 19 days. Here’s how they did it.
High-rise Construction | Feb 2, 2016
This tall tower will lower your heart rate
Matthias Olt, Associate Vice President at CallisonRTKL, discusses new ways to improve individual health and well-being through tower design.
High-rise Construction | Jan 25, 2016
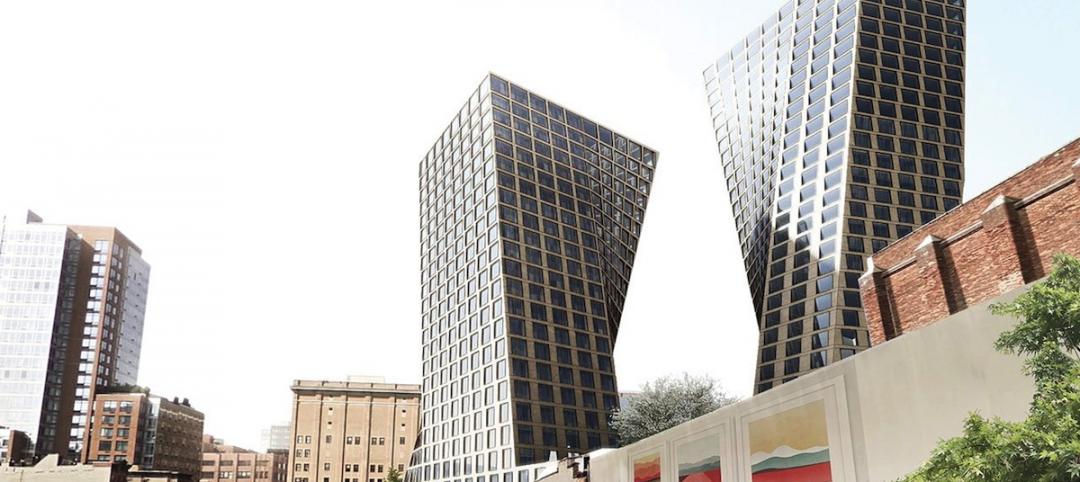
BIG unveils new renderings for NYC towers at 76 Eleventh Avenue
The twisty, asymmetrical condo complexes will have office space instead of a hotel.
Mixed-Use | Jan 25, 2016
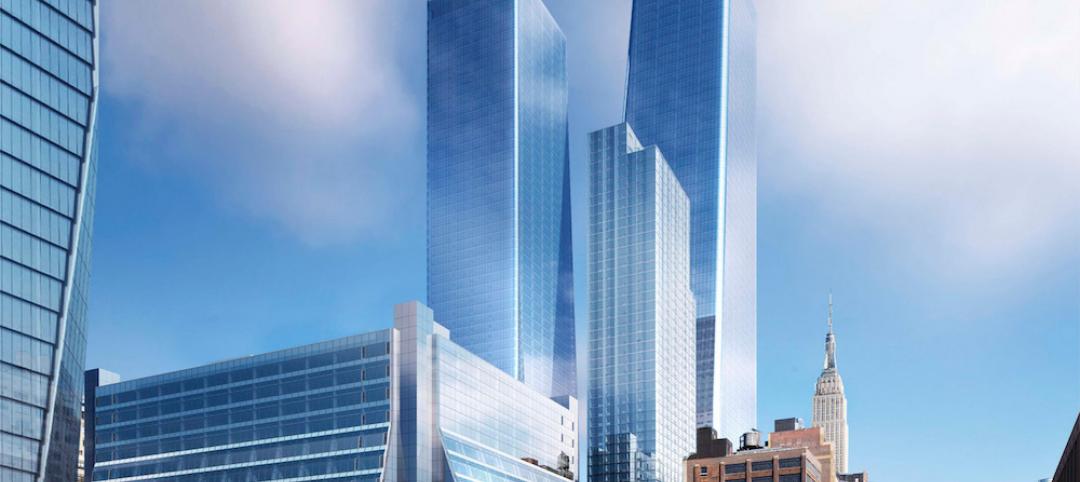
SOM unveils renderings of dual-tower Manhattan West development
The five million-sf project includes two office towers, a residential tower, retail space, and a new public square.
High-rise Construction | Jan 13, 2016
With the completion of NY’s 432 Park Avenue, there are now 100 ‘supertall’ skyscrapers in the world
That makes it an even 100. With the completion of 432 Park Avenue in New York City, the number of so-called “supertall” buildings (buildings standing at least 300 meters tall) in the world has reached the century mark, according to the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat.
High-rise Construction | Jan 12, 2016
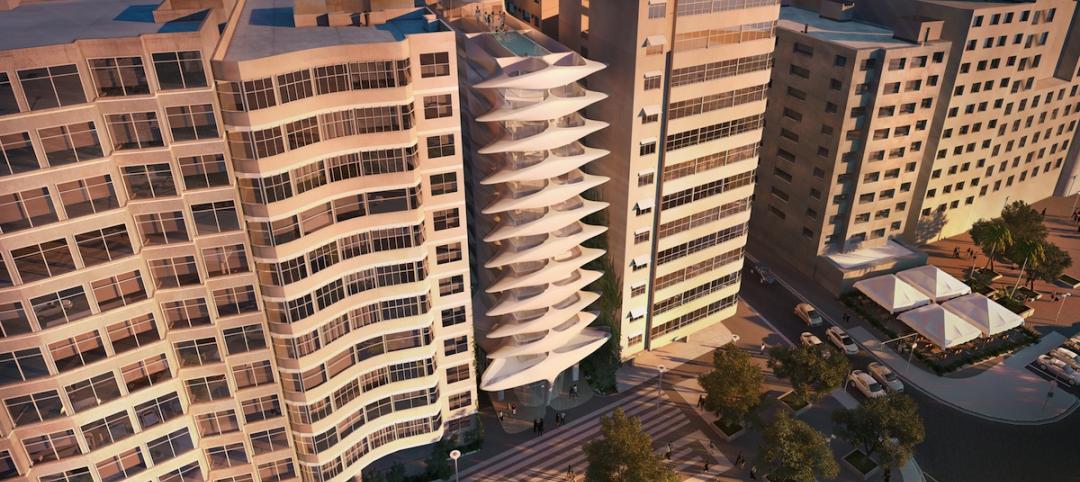
Luxury high-rise is Zaha Hadid’s first foray into South America
The Casa Atlantica is planned for Copacabana beach in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
High-rise Construction | Jan 12, 2016
Renzo Piano's curved glass tower planned for NY's Soho neighborhood
The 25-story tower is a residential building with 115 apartments and plenty of amenities.
High-rise Construction | Jan 11, 2016
World’s second-tallest building (for now) is completed in China
Shanghai Tower makes up a trio of supertall buildings in that city’s commercial district.
High-rise Construction | Jan 7, 2016
Zaha Hadid designs a tower of 'stacked vases' in Melbourne
The structure is supported by sets of curved columns that taper to four different base heights.
High-rise Construction | Jan 4, 2016
Top high-rise innovations of 2015
A crowdfunded skyscraper in Colombia and Jerusalem’s wild, pyramid-shaped tower are among the landmark projects featured in the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat’s annual yearend review.