The tuned mass damper used in Taiwan’s Taipei 101 tower represents an engineering feat that is so impressive the designers decided to make it publicly visible for all to see. Taipei 101’s 730-ton tuned mass damper may represent an extreme, but its purpose is the same as much smaller dampers that may be used in an office building or mall: to mitigate vibrations or sway that may otherwise alarm or cause discomfort to building occupants.
As building materials get lighter and designs push the limits of what is possible in architecture, structural vibrations are becoming more worrisome. A vibrating floor may not be dangerous, but it can certainly cause some unease among building occupants.
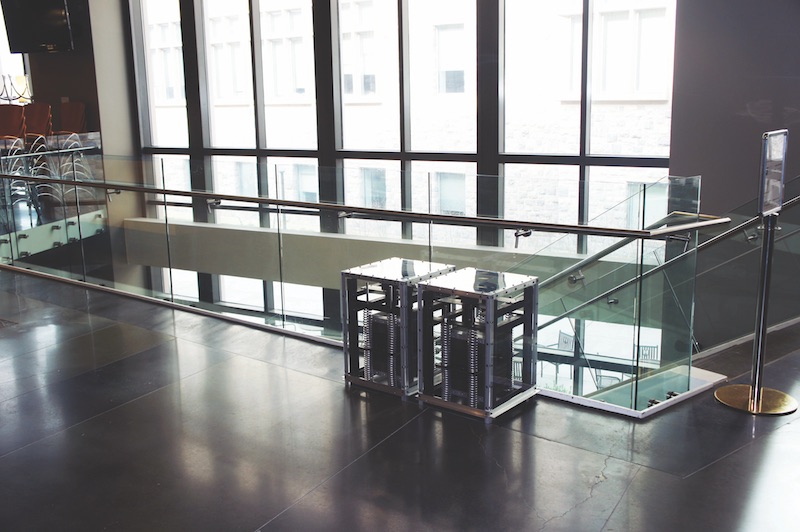
That’s where Mehdi Setareh, PhD, Professor, School of Architecture + Design at Virginia Tech’s College of Architecture and Urban Studies, comes in. With the help of a small team of students, he has created a portable tuned mass damper (PTMD) that weighs less than 275 pounds and is about the size of a shop vac. The device reduced vibrations by 40-75% in tests at Virginia Tech’s Vibration Testing Lab.
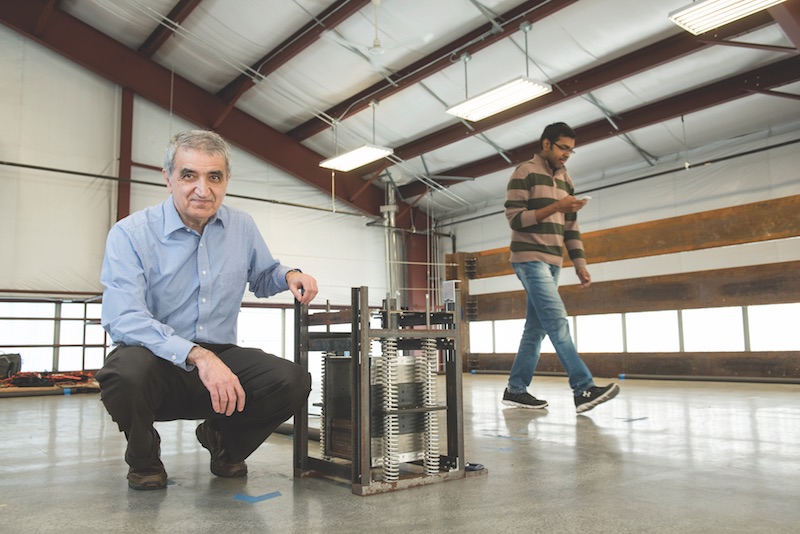 Mehdi Setareh next to an early version of the Portable Tuned Mass Damper. Courtesy Virginia Tech.
Mehdi Setareh next to an early version of the Portable Tuned Mass Damper. Courtesy Virginia Tech.
The PTMD can be incorporated in new construction or added as a corrective measure in an existing building. Even nontechnical personnel can tune the device, using a $5 iTunes application and Setareh’s instructions. Because of the device’s small size, it can be easily hidden in a cabinet or even within furniture.
Plates, springs, and dampers that are built into the two-foot-tall, 15-inch-wide box are tuned to the natural frequency of a structure and reduce vibrations by moving in the opposite direction of that structure, but at 10 to 20 times higher acceleration rates.
Currently, the unit shows the most promise for use in structures with high foot traffic, such as theaters, malls, nightclubs, and monumental staircases, or in settings that have vibration-sensitive equipment, such as hospitals and labs.
Setareh has applied for a patent on the device. He plans to place it on the market as a kit of parts with instructions on how to assemble, install, and tune the damper.
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Apr 13, 2020
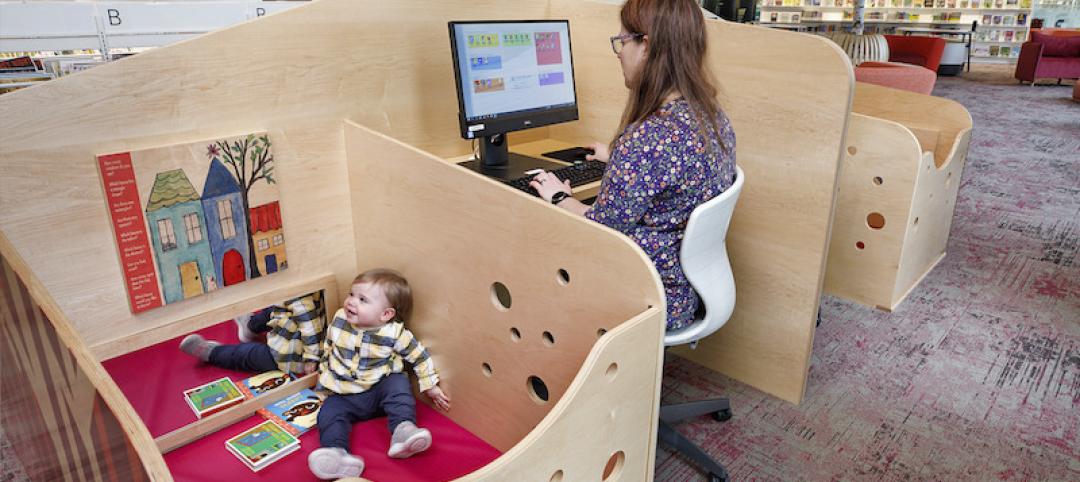
Family workstations highlight the new Fairfield Area Library
The workstations are the perfect remedy for squirming, restless children and toddlers.
Great Solutions | Feb 5, 2020
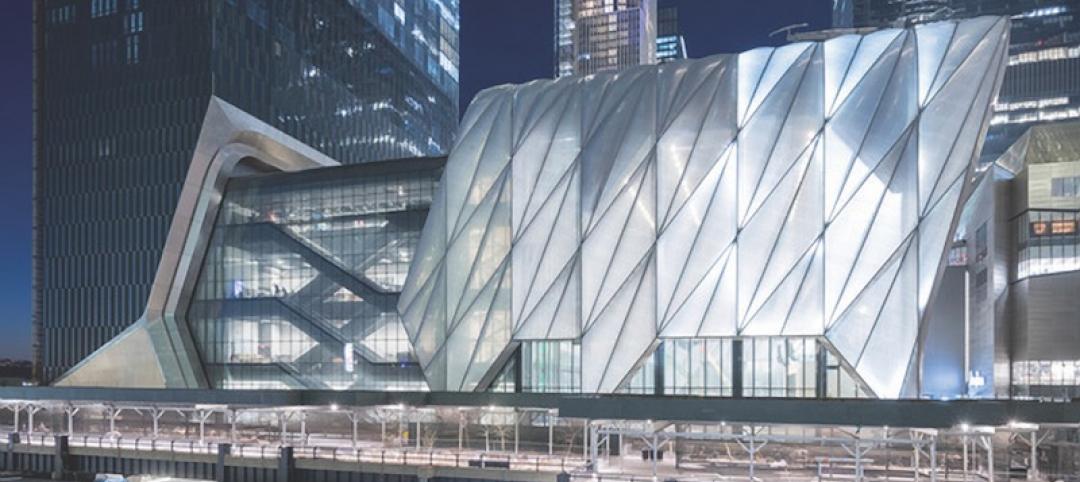
Power moves: The Shed
Precise positioning of mechanicals above its lighting keeps New York’s kinetic event space, The Shed, running.
Great Solutions | Dec 18, 2019
Robot uprising
Thyssenkrupp’s robotics interface platform helps robots use elevators like humans.
Great Solutions | Nov 12, 2019
Skanska designs personal protective equipment tailor-made for the female workforce
A safety vest is the first piece of equipment to undergo an update.
Great Solutions | Oct 3, 2019
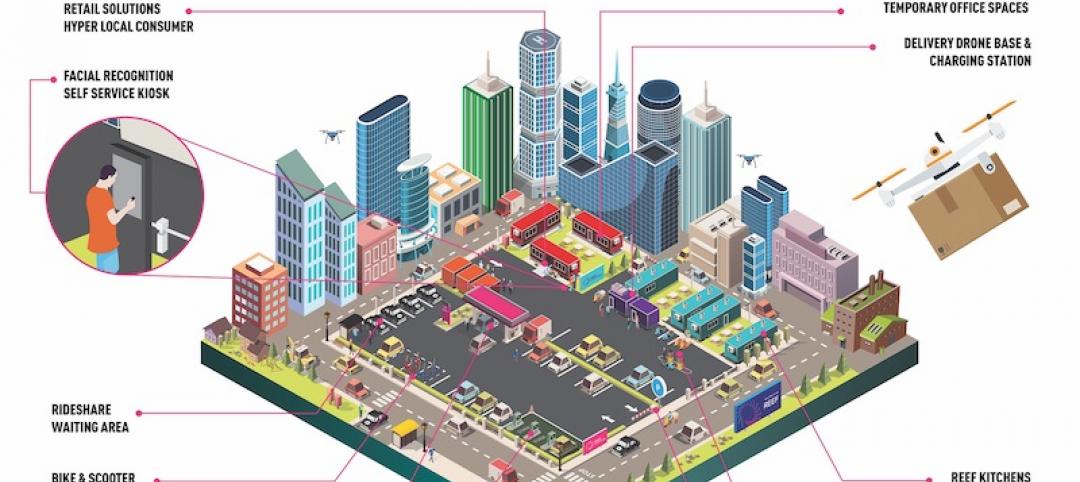
REEF Technology wants to turn parking facilities into urban mobility hubs
The company currently operates 4,500 parking lots in 25 markets across North America.
Great Solutions | Aug 30, 2019
An ‘Internet of Beings’? Kinetic flooring promises more than just energy generation
Pavegen says its technology delivers a new level of human engagement in sustainability initiatives.
Great Solutions | Aug 7, 2019
Earthquake response system takes the guesswork out of seismic safety
The platform provides real-time monitoring to help avoid unnecessary evacuations and improve emergency response.
Great Solutions | Jul 12, 2019
Smart sensor maintains privacy, enhances safety in sensitive spaces
The HALO IOT sensor is designed for use in places where cameras are not welcome.
Great Solutions | Apr 9, 2019
Raising the roof is cool again
Upbrella allows for floor-by-floor building construction that is, reportedly, safer and more productive than traditional methods.
Great Solutions | Mar 12, 2019
When is wood not really wood?
Inspired by the look and cellular nature of wood, researchers create 3D-printed “digital wood” and “metallic wood” that is as strong as titanium, with the density of water.