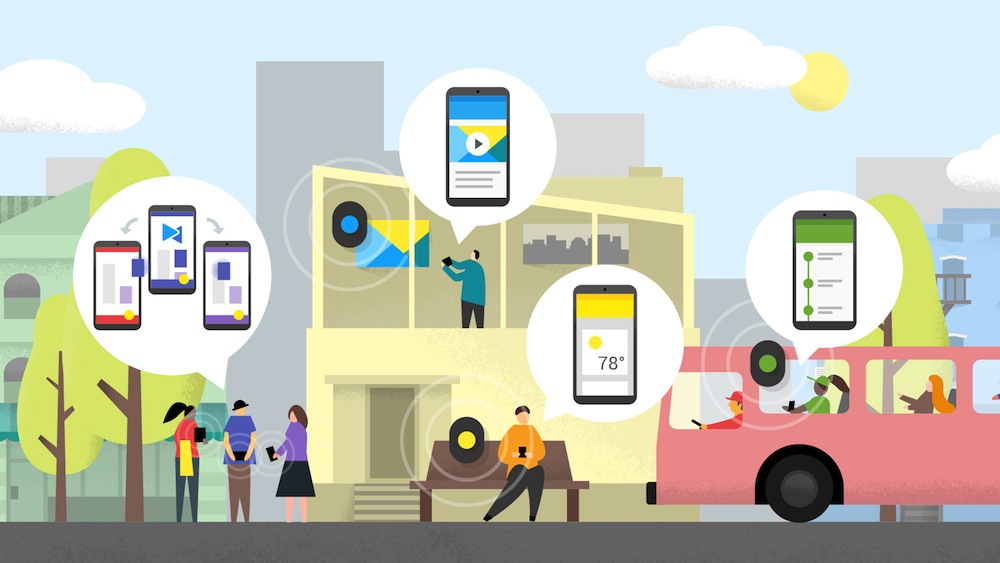
In May, BD+C's blog partner, CASE, covered the rise of indoor positioning technology, and identified architectural applications for beacon technology.
BLE (Bluetooth low energy) beacons are small battery-powered devices that connect with tablets and phones that are in the immediate vicinity. This can enable businesses and other entities to send messages to users based on where they are in a certain space. Apple released the iBeacon in 2013, and the iOS8 update last summer made the innovation even stronger.
Mashable reports that Google will challenge Apple in this realm: The company unveiled Eddystone, a new BLE beacon format, along with tools that will let developers create apps along with the service. Google named the beacon after the Eddy Lighthouse in England, and the company has drawn the parallels between new beacon technology and classic guiding lighthouses.
Unlike iBeacon, which is only compatible with iDevices, Eddystone is cross-platform and discoverable by any Bluetooth smart device. It is open-source so any beacon manufacturer can make hardware compatible with it.
Though beacons usually broadcast information publicly, Eddystone has the option to communicate privately as well. The privacy feature, called Ephemeral Identifiers (EIDs), lets users track their luggage while traveling and find their keys, for instance.
For developers, Google released two new APIs. The Nearby API connects apps with other close devices and beacons; for example, users at an art museum can receive additional facts about a piece or display over their phones. The Proximity Beacon API allows developers to associate semantic location with beacons and store it in the cloud.
Eddystone is available on GitHub under the Apache v2.0 license. Google says Eddystone can be installed with a firmware update.
Related Stories
| Nov 16, 2010
Calculating office building performance? Yep, there’s an app for that
123 Zero build is a free tool for calculating the performance of a market-ready carbon-neutral office building design. The app estimates the discounted payback for constructing a zero emissions office building in any U.S. location, including the investment needed for photovoltaics to offset annual carbon emissions, payback calculations, estimated first costs for a highly energy efficient building, photovoltaic costs, discount rates, and user-specified fuel escalation rates.
| Nov 9, 2010
12 incredible objects being made with 3D printers today
BD+C has reported on how 3D printers are attracting the attention of AEC firms. Now you can see how other creative types are utilizing this fascinating printing technology. Among the printed items: King Tut’s remains, designer shoes, and the world’s smallest Rubik’s Cube.
| Nov 5, 2010
New Millennium’s Gary Heasley on BIM, LEED, and the nonresidential market
Gary Heasley, president of New Millennium Building Systems, Fort Wayne, Ind., and EVP of its parent company, Steel Dynamics, Inc., tells BD+C’s Robert Cassidy about the Steel Joist Manufacturer’s westward expansion, its push to create BIM tools for its products, LEED, and the outlook for the nonresidential construction market.
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Oct 13, 2010
Test run on the HP Z200 SFF Good Value in a Small Package
Contributing Editor Jeff Yoders tests a new small-form factor, workstation-class desktop in Hewlett-Packard’s line that combines performance of its minitower machine with a smaller chassis and a lower price.
| Oct 13, 2010
Prefab Trailblazer
The $137 million, 12-story, 500,000-sf Miami Valley Hospital cardiac center, Dayton, Ohio, is the first major hospital project in the U.S. to have made extensive use of prefabricated components in its design and construction.