|
14. Mod Pod A Nod to Flex Biz
Designed by the British firm Tate + Hindle, the OfficePOD is a flexible office space that can be installed, well, just about anywhere, indoors or out. The self-contained modular units measure about seven feet square and are designed to serve as dedicated space for employees who work from home or other remote locations. Construction of the modular pods includes natural, recycled, and recyclable materials, as well as insulation and a high-efficiency HVAC system. The pods are plug-in powered; the fully wired units connect to an existing structure (home, garage, office building, um...Starbucks?) while IT and phone connectivity is wireless, but can also be cabled in. Delivery takes approximately 12 weeks. |
15. Transform any Work Surface into A Charging Station
 |
16. Concrete Slabs Plays up Rubber Ball Technology
17. Brown Rice for Greener Concrete
While slag from steel mills, fly ash, and silica fume are being added to concrete to reduce the material's greenhouse gas emissions and make it stronger and more resistant to corrosion, rice husks (the small cases around edible rice kernels) have so far proved an unsuitable additive because when burned, its ash is too contaminated with carbon. However, scientists were focused on finding ways to utilize rice husks because they are very rich in silicon dioxide, a core concrete ingredient. A breakthrough has come from researchers at Plano, Texas-based ChK Group, who discovered that superheating the husks to almost 1500 °F in an oxygen-free furnace produces pure, nearly carbon-free silica. ChK researchers, who are still refining their production processes, speculate a single full-size furnace could produce 15,000 tons of rice husk ash annually, which can be used to replace up to 20% of cement used in concrete production. |
18. Killer Beetles Lead to Concrete Plywood
The mountain pine beetle is devastating British Columbia's conifer forests, and while some researchers focused on controlling the destruction, others focused on salvaging the billions of dead trees. The University of Northern British Columbia's professor Ron Thring and graduate student Sorin Pasca focused on salvaging efforts and discovered that dead wood from lodgepole pine trees is an excellent ingredient for cement production. While cement typically repels organic material, the beetles "enhanced" the wood in such a way that it sticks to cement and act as a substitute for typical aggregates like stones and rocks. Researchers say the concrete plywood hybrid board (above), which they call MPB (for mountain pine beetle), is water resistant and can be used in place of drywall and gypsum board or as flooring and countertop surfacing. Boards can be cut with regular woodworking tools and nailed without pre-drilling.
Related Stories
| May 22, 2014
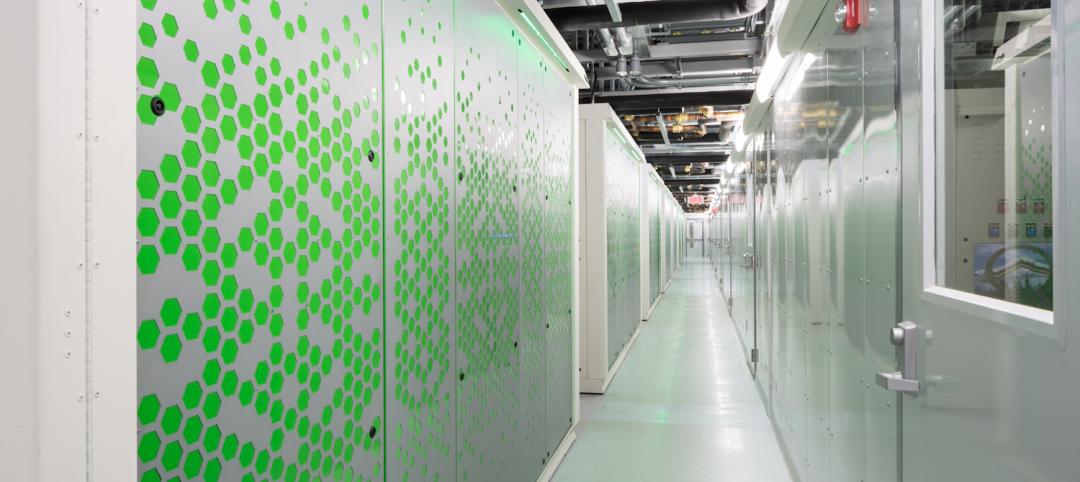
BIM-driven prototype turns data centers into a kit of parts
Data center design specialist SPARCH creates a modular scheme for solutions provider Digital Realty.
| May 22, 2014
Facebook, Telus push the limits of energy efficiency with new data centers
Building Teams are employing a range of creative solutions—from evaporative cooling to novel hot/cold-aisle configurations to heat recovery schemes—in an effort to slash energy and water demand.
| May 15, 2014
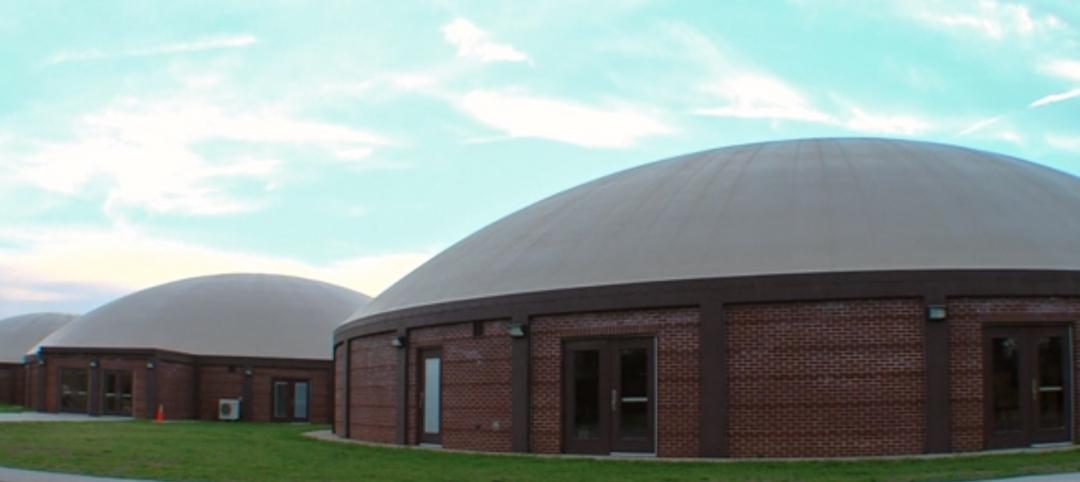
'Virtually indestructible': Utah architect applies thin-shell dome concept for safer schools
At $94 a square foot and "virtually indestructible," some school districts in Utah are opting to build concrete dome schools in lieu of traditional structures.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 12, 2014
Defining BIM – What do owners really want?
Given the complexities of the building process, it can be difficult for building owners to effectively communicate what they want and need with BIM. The response to the question usually is, “Give me everything.”
| May 2, 2014
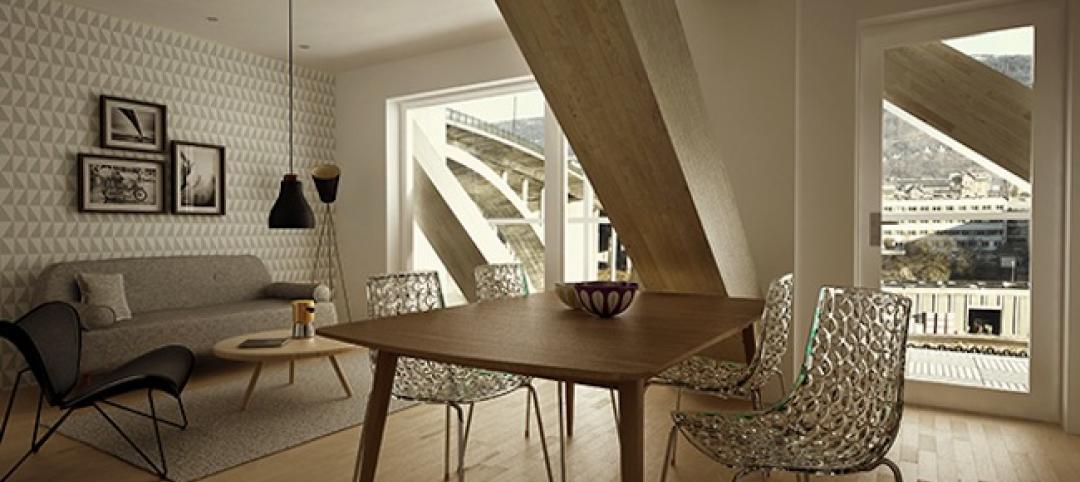
Norwegian modular project set to be world's tallest timber-frame apartment building [slideshow]
A 14-story luxury apartment block in central Bergen, Norway, will be the world's tallest timber-framed multifamily project, at 49 meters (160 feet).
| May 1, 2014
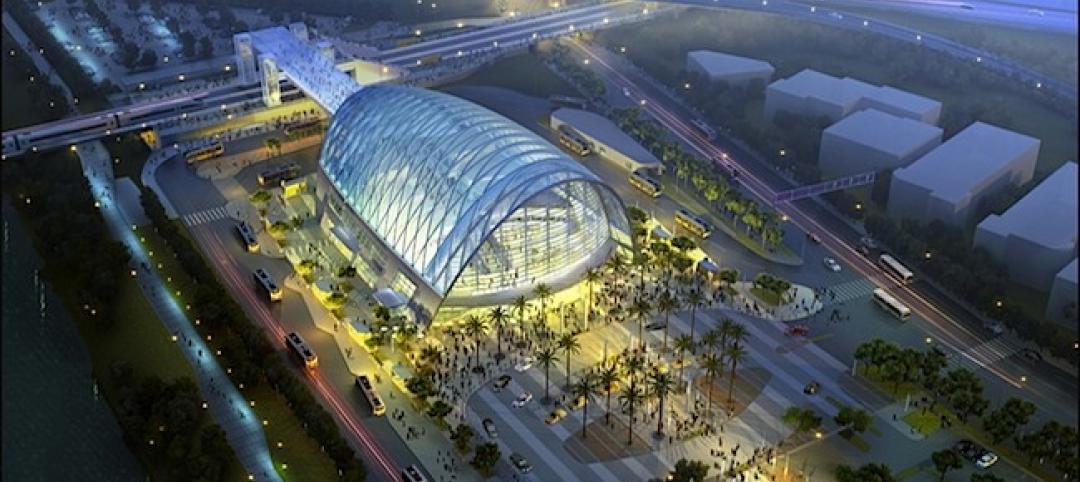
Super BIM: 7 award-winning BIM/VDC-driven projects
Thom Mayne's Perot Museum of Nature and Science and Anaheim's new intermodal center are among the 2014 AIA TAP BIM Award winners.
| May 1, 2014
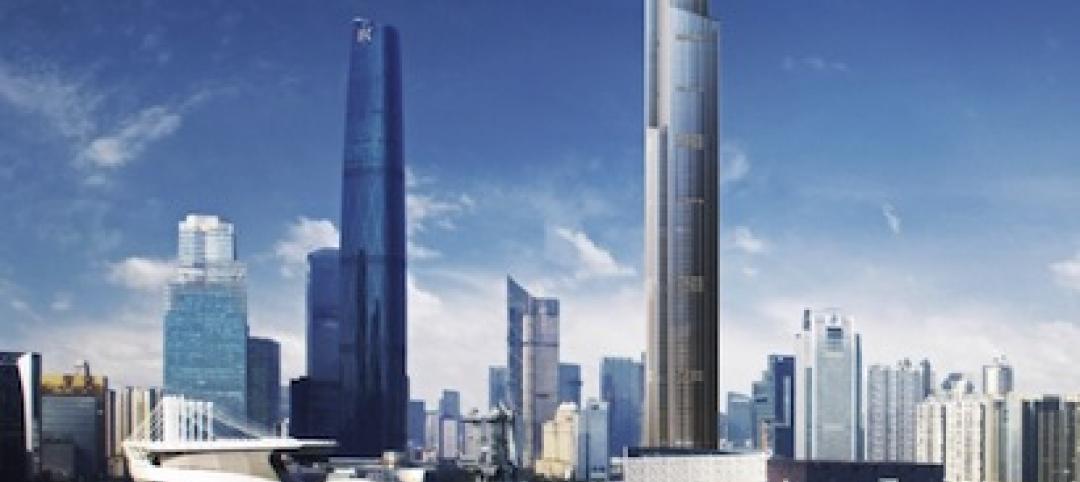
Chinese spec 'world's fastest' elevators for supertall project
Hitachi Elevator Co. will build and install 95 elevators—including two that the manufacturer labels as the "world's fastest"—for the Kohn Pedersen Fox-designed Guangzhou CTF Finance Center.
| Apr 23, 2014
Ahead of the crowd: How architects can utilize crowdsourcing for project planning
Advanced methods of data collection, applied both prior to design and after opening, are bringing a new focus to the entire planning process.