During a recent investor and analyst conference call, George Oliver, chairman and CEO of Johnson Controls, revealed that his company is looking at potential building air-system upgrade projects valued at “a couple of hundred million” dollars in just the next year. Bloomberg reported that Honeywell International has more than $600 million worth of projects in its pipelines. Carrier Global Corp. estimates that the market for indoor-air quality improvements in buildings could eventually reach $10 billion.
However, these improvements won’t necessarily make buildings more energy efficient. Carbon Lighthouse, the energy savings as a service provider, recently surveyed its clients about how they were managing their buildings’ energy use during a pandemic that forced many employees to work remotely from home, leaving many buildings largely empty.
That poll found three-fifths of the clients’ building portfolios had lowered their energy consumptions by an average of only 23% (compared to an 80% average decline in occupancy most buildings experienced). In one-quarter of the clients’ buildings, there was no change in energy use during shelter-in-place.
These findings bring into sharp relief how COVID-19 has created a massive headwind against energy conservation and continues to pose a significant environmental challenge as building operators focus on HVAC upgrades and air-quality solutions. What’s more, some operators may be under the misconception that if buildings are empty, energy efficiency no longer needs to be a priority.
OCCUPANCY AND ENERGY USE DISCONNECT
Corroborating that assessment is Johnson Controls’ latest Energy Efficiency Indicator COVID-19 Pulse study, based on its survey last September of 150 commercial, institutional, and industrial facilities executives in the U.S. This survey included questions on coronavirus-related improvements, investments, and impacts.
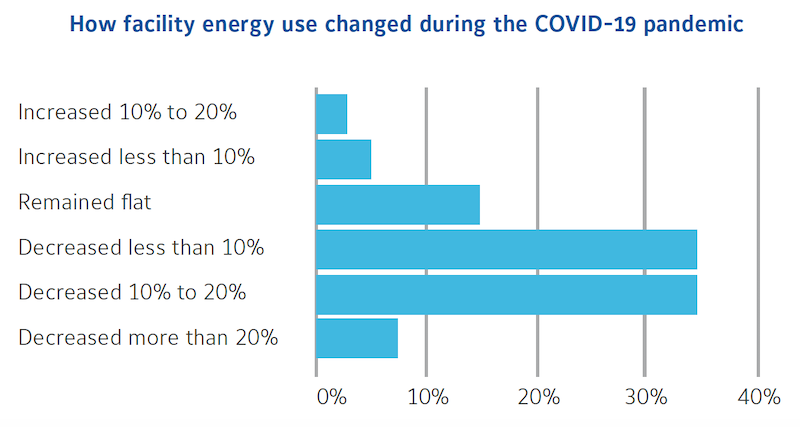
Few buildings altered their energy usage commensurate with reductions in their occupants. Image: Johnson Controls
Perhaps the most sobering finding in Johnson Controls’ study is that the virus had not substantively reduced building energy consumption, regardless of reduced occupancy rates. During the pandemic, less than 10% of the organizations surveyed reduced their energy use by more than 20%. More typical were buildings that decreased their energy consumption by between 0-20%. More than 7% of the surveyed companies increased their energy use.
There could be several reasons for this, explains Clay Nesler, Johnson Controls' Vice President of Global Sustainability. “Even buildings in New York City, where occupancy can be at around 10%, space is still being leased with service agreements that require buildings to maintain temperatures.” Nesler also points out that, typically, more than 50% of a building's energy load is under its tenants' control. “How many refrigerators, computers, and monitors are still plugged in? What's going on with the lights?” He adds that many tenants have big data closets, “and those IT loads aren't going down.”
e
Making environments safer quickly during a health event is where facilities managers say investment dollars are flowing. Image: Johnson Controls.
Most facilities managers saw a more pressing need for flexibility that can quickly respond to emergency conditions. There was a significant increase, compared to last year, of facilities managers who view occupant safety as a critical driver of investment. Another important driver, said 85% of those polled, was energy cost savings.
DID SOMEONE SAY ‘TOUCHLESS’?
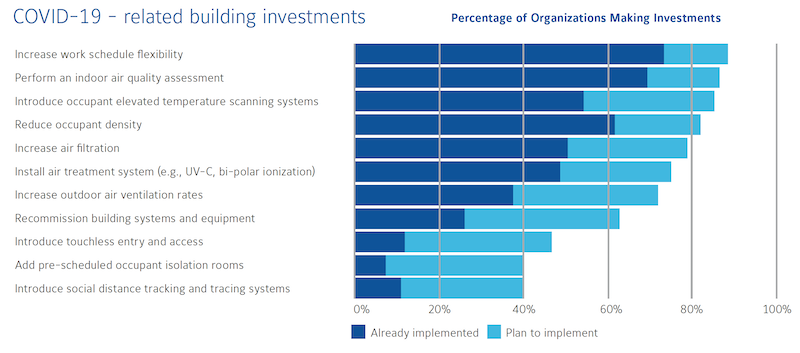
Improving indoor air quality is one of facilities managers' investment priorities. Image: Johnson Controls
When it came to actions in response to the virus’ spread, 60% of the survey’s participants said that plan to upgrade their HVAC and air filtration systems More than half had already conducted air-quality assessments, introduced elevated temperature scanning systems, and increased air filtration.
Nearly 90% of those polled by Johnson Controls said they had already implemented or planned to expand their employees’ work schedule flexibility. But there was less interest in such infection-control measures as introducing touchless entry and access, adding pre-scheduled occupant isolation rooms, or installed systems that track and trace social distancing.
Johnson Controls' Nesler acknowledges that energy efficiency can sometimes confliect with health and safe measures. But it doesn't have to be that way. He points specifically to Environmental, Social, and Governance assessments of sustainable buildings, conducted by the benchmarking firm GRESB, that found these buildings better able to regulate their energy uses, partly by giving tenants solutions to do so before an event hits.
“We believe the future is in control systems that go beyond “on” and “off” to include a pandemic mode” that would align with CDC and ASHRAE safety regulations, says Nesler. He adds that there might also be anther control for facilities managers that allow them to shut down a building's non-critical loads. “We think resilience will be a big thing going forward.”
Editor's note: Information from Clay Nesler of Johnson Controls was added to this story after its initial posting.
Related Stories
Energy Efficient Roofing | Oct 28, 2022
Rooftop mini turbines can pair with solar panels
A new type of wind turbine can pair well on roofs with solar panels, offering a double source of green energy generation for buildings.
Energy-Efficient Design | Oct 24, 2022
Roadmap shows how federal buildings can reach zero embodied carbon emissions by 2050
The Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) has released a roadmap that it says charts a path for federal buildings projects to achieve zero embodied carbon emissions by 2050.
Energy-Efficient Design | Oct 14, 2022
A DOE software suite is helping SmithGroup optimize its designs’ energy efficiency
AutoBEM can run more than 200,000 energy models in an hour.
| Sep 22, 2022
Gainesville, Fla., ordinance requires Home Energy Score during rental inspections
The city of Gainesville, Florida was recently recognized by the U.S. Dept. of Energy for an adopted ordinance that requires rental housing to receive a Home Energy Score during rental inspections.
| Sep 7, 2022
Use of GBCI building performance tools rapidly expanding
More than seven billion square feet of project space is now being tracked using Green Business Certification Inc.’s (GBCI’s) Arc performance platform.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Aug 24, 2022
Solutions for cladding performance and supply issues
This course covers design considerations and cladding assembly choices for creating high-performance building envelopes — a crucial element in healthy, energy-efficient buildings.
| Aug 23, 2022
New Mass. climate and energy law allows local bans on fossil fuel-powered appliances
A sweeping Massachusetts climate and energy bill recently signed into law by Republican governor Charlie Baker allows local bans on fossil fuel-powered appliances.
| Aug 22, 2022
Less bad is no longer good enough
As we enter the next phase of our fight against climate change, I am cautiously optimistic about our sustainable future and the design industry’s ability to affect what the American Institute of Architects (AIA) calls the biggest challenge of our generation.
| Aug 16, 2022
DOE funds 18 projects developing tech to enable buildings to store carbon
The Department of Energy announced $39 million in awards for 18 projects that are developing technologies to transform buildings into net carbon storage structures.
| Aug 15, 2022
Boston high-rise will be largest Passive House office building in the world
Winthrop Center, a new 691-foot tall, mixed-use tower in Boston was recently honored with the Passive House Trailblazer award.

















